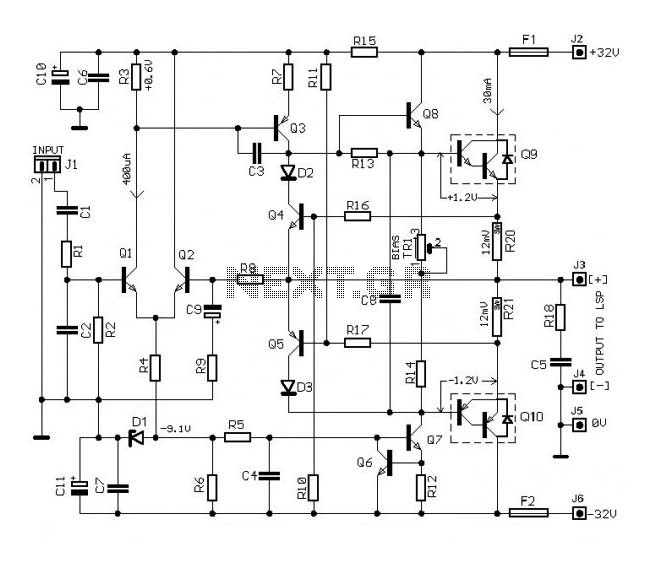
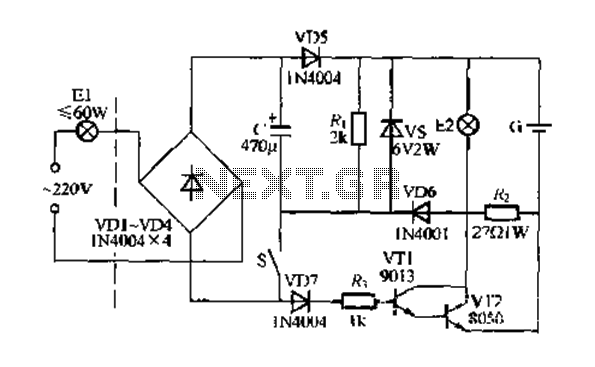
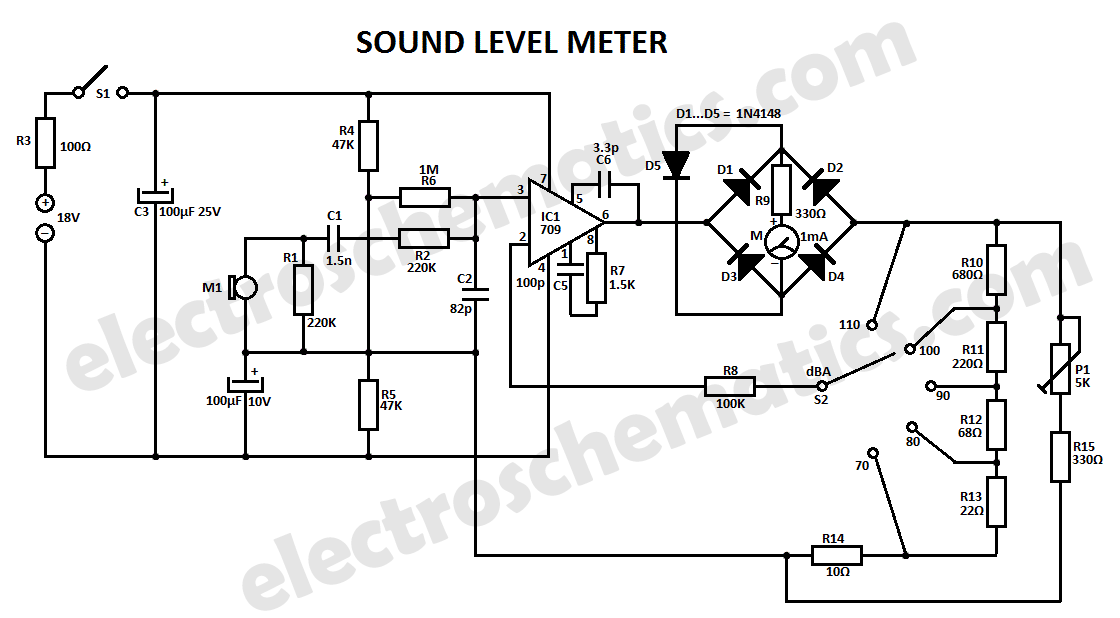
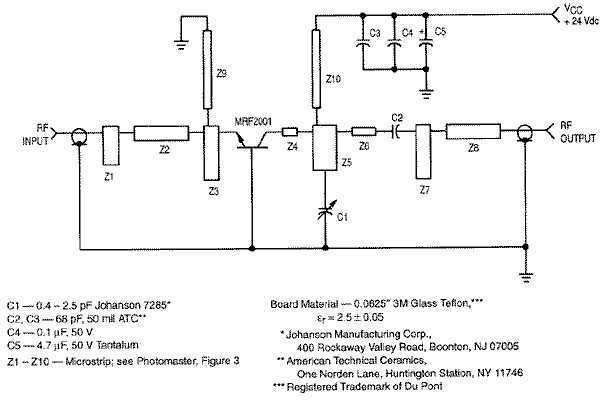
Low-noise preamplifier circuit
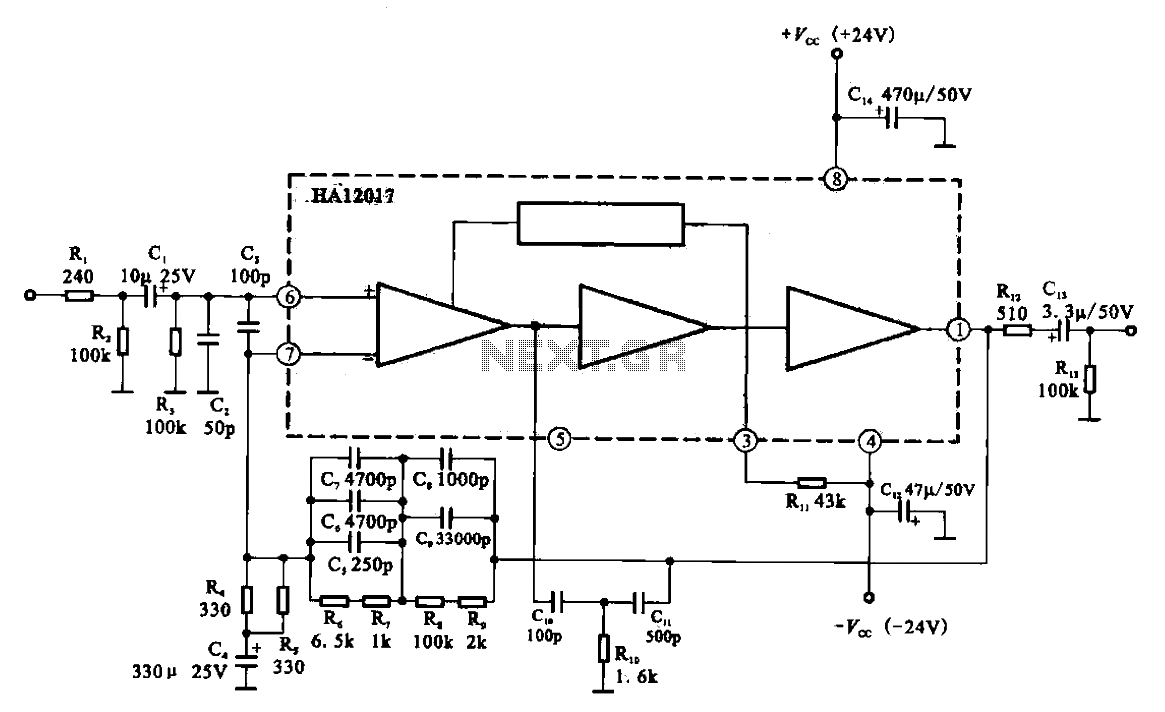
Low-noise preamplifier circuit. This circuit demonstrates a typical low-noise preamplifier design, which can be utilized to amplify signals from sources such as magnetic heads and microphones within audio applications. The input signal is coupled through a capacitor and subsequently passed through a filter circuit that prepares it for processing by the low-noise preamplifier HA12Q17. The input amplifier enhances the voltage, resulting in an amplified output signal.
The low-noise preamplifier circuit is essential for applications requiring the amplification of weak signals while minimizing noise interference. The HA12Q17 component is a specialized low-noise operational amplifier designed to deliver high gain with low distortion, making it suitable for audio signal processing.
In the circuit, the input signal is initially coupled through a capacitor, which serves to block any DC offset, allowing only the AC component of the signal to pass. This is critical in audio applications to ensure that the subsequent amplification stage only processes the intended audio signal. The filter circuit following the capacitor is designed to eliminate unwanted high-frequency noise, which could degrade the quality of the amplified output.
The HA12Q17 is configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, where the gain can be set by external resistors. This allows flexibility in adjusting the amplification level to suit different input signal strengths. The output of the HA12Q17 is a clean, amplified version of the input signal, ready for further processing or driving subsequent stages in an audio system.
The design considerations for this low-noise preamplifier include proper grounding techniques to minimize electromagnetic interference, careful selection of components to ensure low noise figures, and layout strategies that prevent crosstalk between signal paths. Overall, this low-noise preamplifier circuit is a vital component in high-fidelity audio systems, ensuring that the integrity of the original signal is preserved throughout the amplification process.Low-noise preamplifier circuit It shows a typical low-noise preamplifier circuit, an amplifier may be used to signal the magnetic head and the microphone signal as the audio circuit. After this circuit a signal from the input terminal fed by cl coupling capacitor and filter circuit filter into low-noise preamplifier HA12Q17 I; FJ @, rear foot, the input amplifier, the output voltage amplification and amplification process by O feet amplified output signal.
The low-noise preamplifier circuit is essential for applications requiring the amplification of weak signals while minimizing noise interference. The HA12Q17 component is a specialized low-noise operational amplifier designed to deliver high gain with low distortion, making it suitable for audio signal processing.
In the circuit, the input signal is initially coupled through a capacitor, which serves to block any DC offset, allowing only the AC component of the signal to pass. This is critical in audio applications to ensure that the subsequent amplification stage only processes the intended audio signal. The filter circuit following the capacitor is designed to eliminate unwanted high-frequency noise, which could degrade the quality of the amplified output.
The HA12Q17 is configured in a non-inverting amplifier configuration, where the gain can be set by external resistors. This allows flexibility in adjusting the amplification level to suit different input signal strengths. The output of the HA12Q17 is a clean, amplified version of the input signal, ready for further processing or driving subsequent stages in an audio system.
The design considerations for this low-noise preamplifier include proper grounding techniques to minimize electromagnetic interference, careful selection of components to ensure low noise figures, and layout strategies that prevent crosstalk between signal paths. Overall, this low-noise preamplifier circuit is a vital component in high-fidelity audio systems, ensuring that the integrity of the original signal is preserved throughout the amplification process.Low-noise preamplifier circuit It shows a typical low-noise preamplifier circuit, an amplifier may be used to signal the magnetic head and the microphone signal as the audio circuit. After this circuit a signal from the input terminal fed by cl coupling capacitor and filter circuit filter into low-noise preamplifier HA12Q17 I; FJ @, rear foot, the input amplifier, the output voltage amplification and amplification process by O feet amplified output signal.