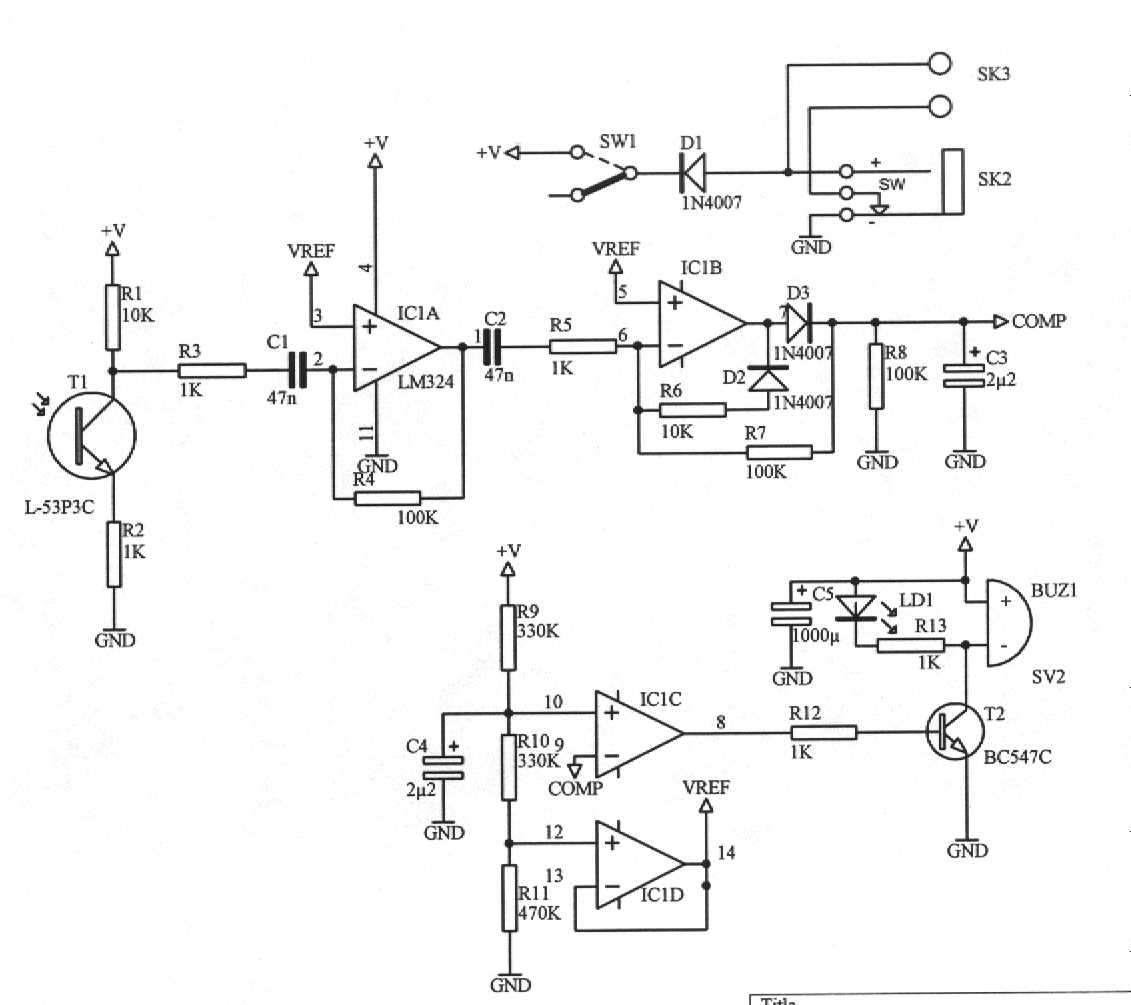
Low power monostable circuit diagram
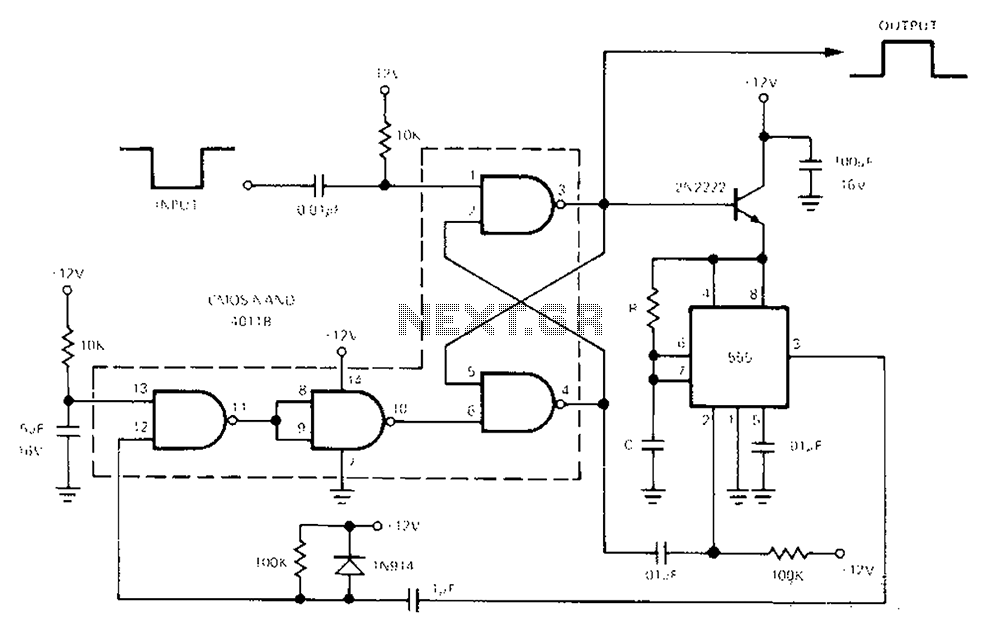
The 555 Timer facilitates a low-loss single-shot circuit and interfaces with the CMOS4011B NAND gate circuit. The standby power consumption is less than 50 µA. When the one-shot circuit is activated, the current consumption is 4.5 mA, and the pulse duration is equal to 1.1 times the product of resistance (R) and capacitance (C).
The 555 Timer is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In a single-shot configuration, it operates as a monostable multivibrator, generating a precise output pulse in response to a triggering event. The CMOS4011B NAND gate can be utilized in conjunction with the 555 Timer to create complex logic functions or signal processing tasks, enhancing the circuit's functionality.
In this configuration, the standby power consumption of less than 50 µA ensures that the circuit remains energy-efficient, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. When the one-shot circuit is activated, the current consumption rises to 4.5 mA, which is necessary for driving the output load during the pulse duration. The pulse width, determined by the equation T = 1.1RC, allows for precise control over the timing characteristics of the output signal, where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads.
This arrangement provides a reliable solution for applications requiring timed events or controlled signal generation, such as in timers, alarms, and various automation systems. The integration of the 555 Timer with the CMOS4011B NAND gate allows for additional logic processing, making it a valuable component in designing efficient electronic circuits.555 Timer enables low-loss single-shot circuit and CMOS4011B NAND gate circuit interface. Standby power consumption of less than 50 A. When the one-shot circuit is turned on, t he current consumption is 4.5mA, T pulse duration equal 1.1RC.
The 555 Timer is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In a single-shot configuration, it operates as a monostable multivibrator, generating a precise output pulse in response to a triggering event. The CMOS4011B NAND gate can be utilized in conjunction with the 555 Timer to create complex logic functions or signal processing tasks, enhancing the circuit's functionality.
In this configuration, the standby power consumption of less than 50 µA ensures that the circuit remains energy-efficient, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. When the one-shot circuit is activated, the current consumption rises to 4.5 mA, which is necessary for driving the output load during the pulse duration. The pulse width, determined by the equation T = 1.1RC, allows for precise control over the timing characteristics of the output signal, where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads.
This arrangement provides a reliable solution for applications requiring timed events or controlled signal generation, such as in timers, alarms, and various automation systems. The integration of the 555 Timer with the CMOS4011B NAND gate allows for additional logic processing, making it a valuable component in designing efficient electronic circuits.555 Timer enables low-loss single-shot circuit and CMOS4011B NAND gate circuit interface. Standby power consumption of less than 50 A. When the one-shot circuit is turned on, t he current consumption is 4.5mA, T pulse duration equal 1.1RC.