
Low-power-rs-232c-driver
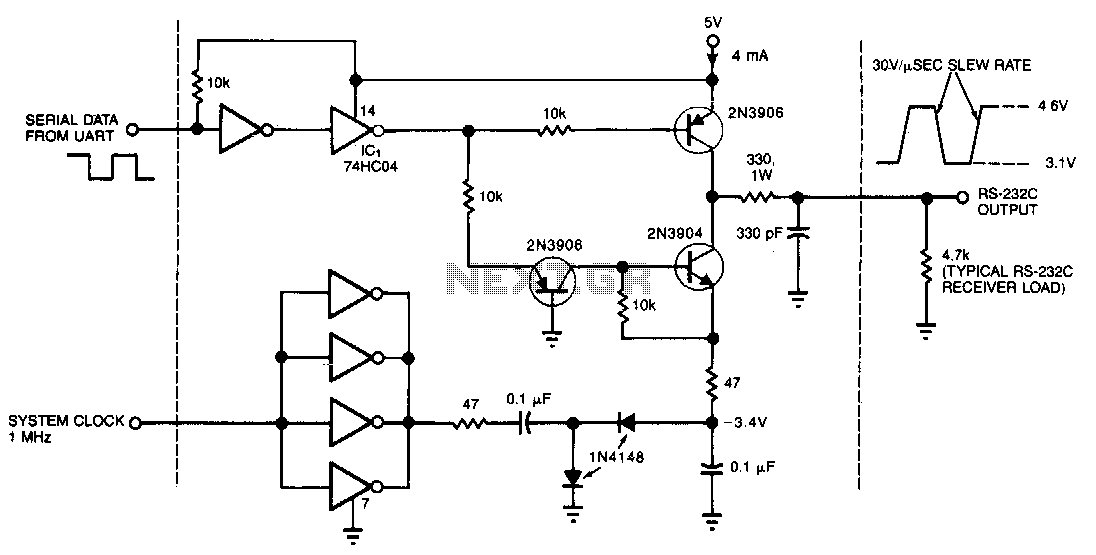
This circuit draws only 4 mA from a 5-V supply while driving a standard RS-232C receiver. The system clock drives a de-de converter that produces -3.4 V. The frequency can range from 0.5 to 8 MHz, but a range of 0.5 to 1 MHz will minimize power dissipation. The circuit output withstands direct shorts to ground or to either of the supplies (±12 V max). In place of the 74HC04 high-speed CMOS driver shown, one may want to substitute miscellaneous spare gates; one non-inverting buffer, for example, can replace the two inverting types that receive the UART signal.
The described circuit is designed to interface with an RS-232C receiver while maintaining low power consumption, drawing only 4 mA from a 5-V supply. The core of the circuit involves a system clock that drives a de-de converter, which generates a negative voltage of -3.4 V essential for RS-232 communication. The operational frequency of the circuit is flexible, ranging from 0.5 MHz to 8 MHz; however, operation within the 0.5 MHz to 1 MHz range is recommended to achieve optimal power efficiency and minimize heat generation.
The circuit's output is robust, capable of enduring direct shorts to ground or to either of the supply voltages, which can reach up to ±12 V. This feature enhances the reliability of the circuit in various applications, ensuring that accidental shorts do not lead to circuit failure.
For flexibility in component selection, the design allows for the substitution of the 74HC04 high-speed CMOS driver with other available logic gates. Specifically, a single non-inverting buffer can effectively replace two inverting buffers that typically process the UART signal. This adaptability not only facilitates component sourcing but also allows for design modifications based on available parts without compromising circuit functionality. The careful selection of components and operating parameters ensures that the circuit remains efficient and reliable in its intended applications.This circuit draws only 4 mA from a 5-V supply while driving a standard RS-232C receiver. The system clock drives a de-de converter that produces -3.4 V. The frequency can range from 0.5 to 8 MHz, but a range of 0.5 to 1 MHz will minimize power dissipation. The circuit output withstands direct shorts to ground or to either of the supplies ( ±12 V max). In place of the 74HC04 high-speed CMOS driver shown, you may want to substitute miscellaneous spare gates; one noninverting buffer, for example, can replace the two inverting types that receive the UART signal. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to interface with an RS-232C receiver while maintaining low power consumption, drawing only 4 mA from a 5-V supply. The core of the circuit involves a system clock that drives a de-de converter, which generates a negative voltage of -3.4 V essential for RS-232 communication. The operational frequency of the circuit is flexible, ranging from 0.5 MHz to 8 MHz; however, operation within the 0.5 MHz to 1 MHz range is recommended to achieve optimal power efficiency and minimize heat generation.
The circuit's output is robust, capable of enduring direct shorts to ground or to either of the supply voltages, which can reach up to ±12 V. This feature enhances the reliability of the circuit in various applications, ensuring that accidental shorts do not lead to circuit failure.
For flexibility in component selection, the design allows for the substitution of the 74HC04 high-speed CMOS driver with other available logic gates. Specifically, a single non-inverting buffer can effectively replace two inverting buffers that typically process the UART signal. This adaptability not only facilitates component sourcing but also allows for design modifications based on available parts without compromising circuit functionality. The careful selection of components and operating parameters ensures that the circuit remains efficient and reliable in its intended applications.This circuit draws only 4 mA from a 5-V supply while driving a standard RS-232C receiver. The system clock drives a de-de converter that produces -3.4 V. The frequency can range from 0.5 to 8 MHz, but a range of 0.5 to 1 MHz will minimize power dissipation. The circuit output withstands direct shorts to ground or to either of the supplies ( ±12 V max). In place of the 74HC04 high-speed CMOS driver shown, you may want to substitute miscellaneous spare gates; one noninverting buffer, for example, can replace the two inverting types that receive the UART signal. 🔗 External reference