
Lsolated-converter
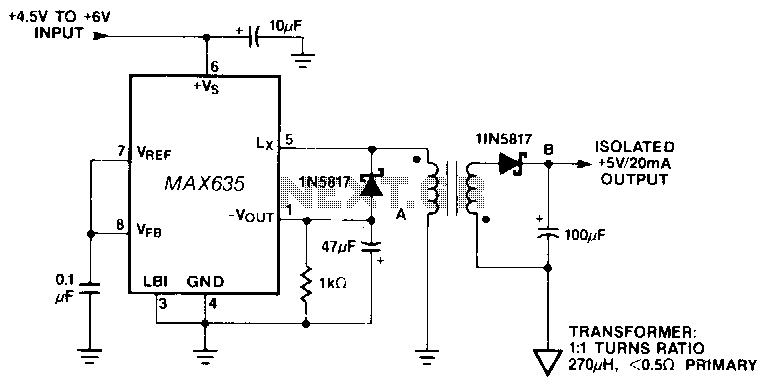
In this circuit, a negative output voltage DC-DC converter generates a -5 V output at pin A. To achieve -5 V at point A, the primary of the transformer must fly back to a diode drop that is more negative than -5 V. If the transformer has a tightly coupled 1:1 turns ratio, there will be a 5 V plus a diode drop across the secondary. The 1N5817 diode rectifies this secondary voltage to generate an isolated 5 V output. The isolated output is not fully regulated since only the -5 V at point A is sensed by the MAX635.
The described circuit employs a negative output voltage DC-DC converter that operates by utilizing a transformer with a 1:1 turns ratio. The design involves a primary winding that, during the flyback period, must reach a voltage that is more negative than the desired -5 V output. This requirement is essential for ensuring that the voltage at pin A remains stable at -5 V.
The transformer plays a crucial role in this circuit by providing isolation and voltage transformation. When the primary winding is energized, it induces a corresponding voltage in the secondary winding. Given the 1:1 turns ratio, the output voltage on the secondary side, before rectification, will be approximately +5 V. However, this voltage is subject to a diode drop, which is the forward voltage drop across the rectifying diode, the 1N5817 in this case. The 1N5817 is a Schottky diode known for its low forward voltage drop, typically around 0.3 V to 0.4 V, which is advantageous for maximizing the output voltage.
Once the secondary voltage is rectified by the 1N5817, it results in an isolated positive voltage that can be utilized for various applications. However, it is important to note that this isolated output is not fully regulated. The regulation is limited to the -5 V output at point A, which is monitored by the MAX635 voltage reference. The MAX635 is designed to provide a stable reference voltage, but since it only senses the -5 V at point A, variations in the load or input conditions may not be adequately compensated, leading to potential fluctuations in the isolated output voltage.
In summary, this circuit effectively generates a -5 V output through careful transformer design and diode rectification, while also highlighting the limitations of output regulation due to the sensing method employed. The choice of components, particularly the transformer and the 1N5817 diode, is critical in achieving the desired performance characteristics of the circuit.In this circuit. a negative output voltage de-de converter generates a -5 V output at pin A. In order to generate -5 Vat point A, the primary of the transformer must fly back to a diode drop more negative than -5 V. If the transformer has a tightly coupled 1/1 turns ratio, there will be a 5 V plus a diode drop across the secondary.
The 1N5817 rectifies this secondary voltage to generate an isolated 5-V output. The isolated output is not fully regulated since only the -5 V at point A is sensed by the MAX635. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a negative output voltage DC-DC converter that operates by utilizing a transformer with a 1:1 turns ratio. The design involves a primary winding that, during the flyback period, must reach a voltage that is more negative than the desired -5 V output. This requirement is essential for ensuring that the voltage at pin A remains stable at -5 V.
The transformer plays a crucial role in this circuit by providing isolation and voltage transformation. When the primary winding is energized, it induces a corresponding voltage in the secondary winding. Given the 1:1 turns ratio, the output voltage on the secondary side, before rectification, will be approximately +5 V. However, this voltage is subject to a diode drop, which is the forward voltage drop across the rectifying diode, the 1N5817 in this case. The 1N5817 is a Schottky diode known for its low forward voltage drop, typically around 0.3 V to 0.4 V, which is advantageous for maximizing the output voltage.
Once the secondary voltage is rectified by the 1N5817, it results in an isolated positive voltage that can be utilized for various applications. However, it is important to note that this isolated output is not fully regulated. The regulation is limited to the -5 V output at point A, which is monitored by the MAX635 voltage reference. The MAX635 is designed to provide a stable reference voltage, but since it only senses the -5 V at point A, variations in the load or input conditions may not be adequately compensated, leading to potential fluctuations in the isolated output voltage.
In summary, this circuit effectively generates a -5 V output through careful transformer design and diode rectification, while also highlighting the limitations of output regulation due to the sensing method employed. The choice of components, particularly the transformer and the 1N5817 diode, is critical in achieving the desired performance characteristics of the circuit.In this circuit. a negative output voltage de-de converter generates a -5 V output at pin A. In order to generate -5 Vat point A, the primary of the transformer must fly back to a diode drop more negative than -5 V. If the transformer has a tightly coupled 1/1 turns ratio, there will be a 5 V plus a diode drop across the secondary.
The 1N5817 rectifies this secondary voltage to generate an isolated 5-V output. The isolated output is not fully regulated since only the -5 V at point A is sensed by the MAX635. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713