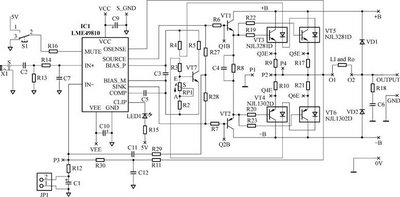
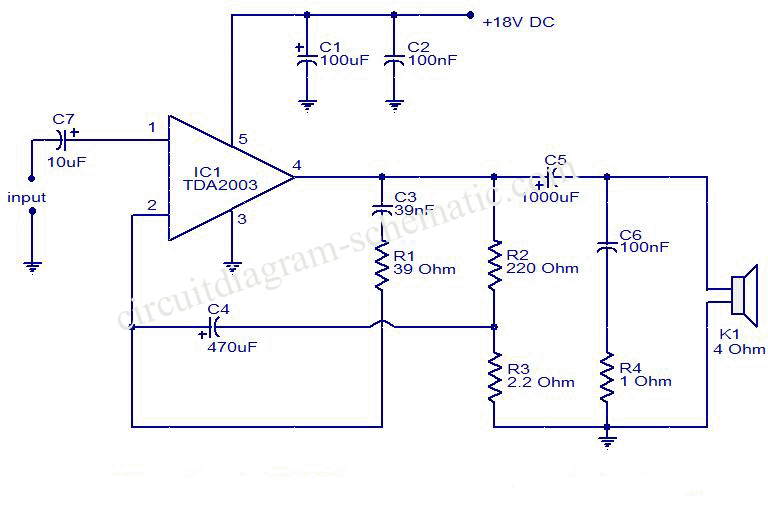
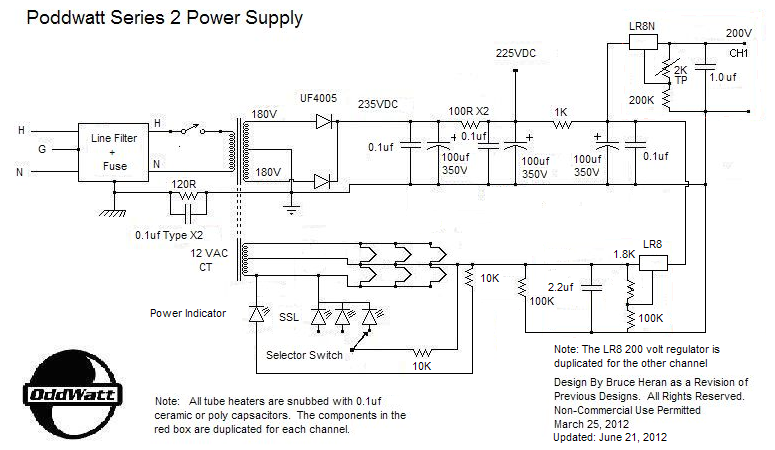
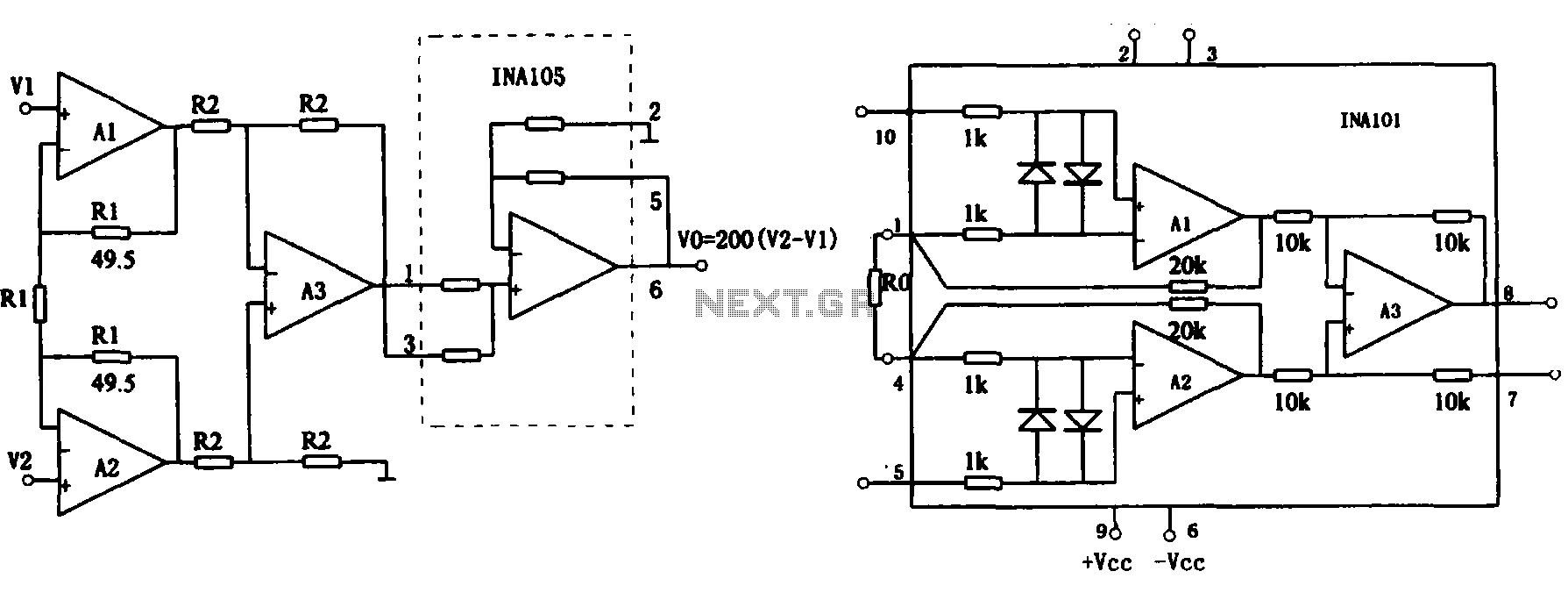
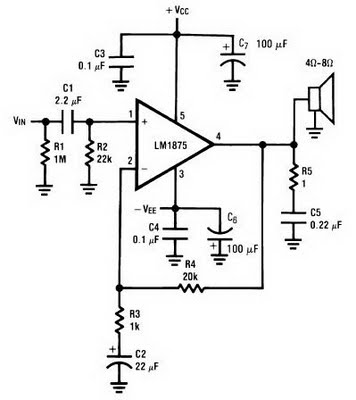
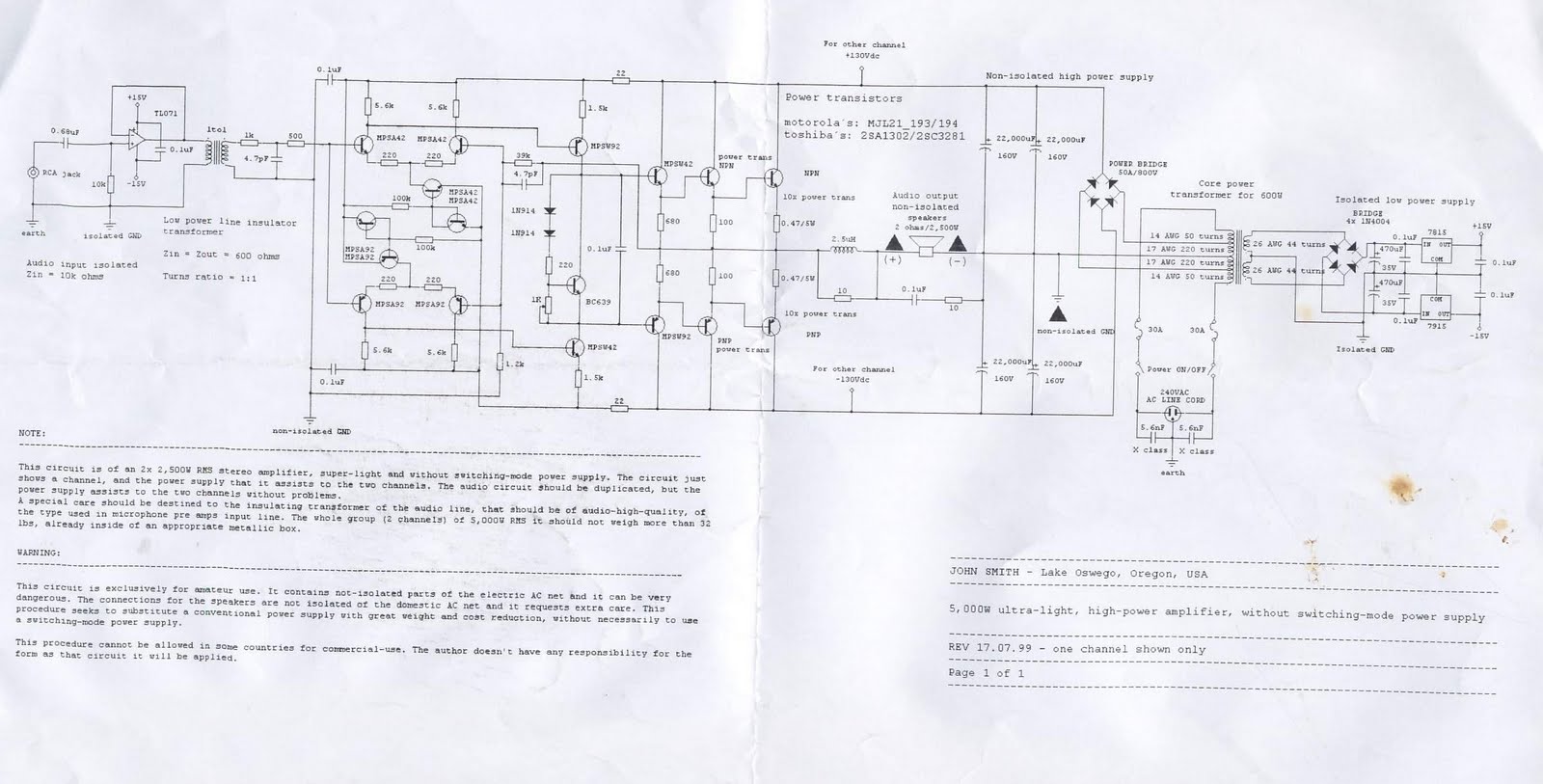
max2338 hp at the sound amplifier
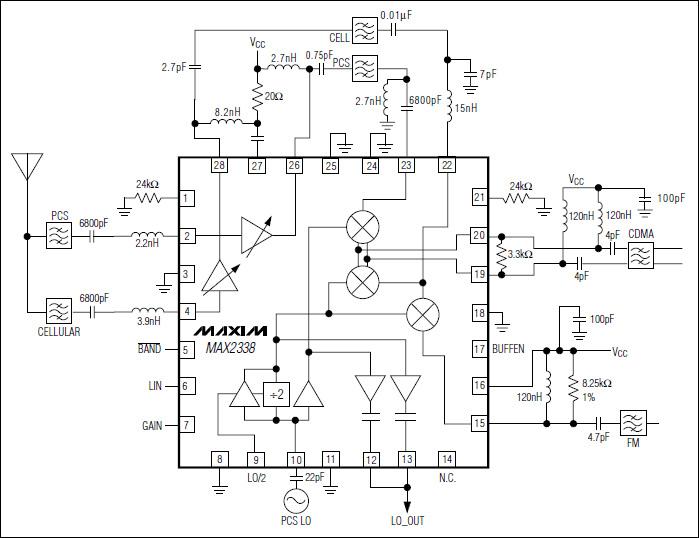
The MAX2338 receiver RF front-end integrated circuit (IC) is tailored for dual-band CDMA cellular phones and is also applicable in dual-band TDMA, GSM, or EDGE cellular phones. The integrated low-power local oscillator (LO) divider allows for the elimination of the cellular VCO module. It features a low-noise amplifier (LNA) with an adjustable high-input third-order intercept point (IIP3) to reduce intermodulation and cross-modulation effects from large interfering signals. For operation in the cellular band, a low-gain LNA is provided to achieve higher cascaded IIP3 at lower current consumption. The CDMA mixers are engineered for high linearity, low noise, and differential intermediate frequency (IF) outputs, while the FM mixer is designed for lower current consumption and single-ended output. The MAX2338's triple-mode LNA/mixer incorporates an on-chip LO frequency divider, enabling the use of a single VCO across both bands. This device is offered in an ultra-small 28-pin leadless QFN package.
The MAX2338 RF front-end integrated circuit serves as a versatile solution for dual-band cellular applications, providing significant enhancements in performance and efficiency. The elimination of the cellular VCO module through the on-chip low-power LO divider not only simplifies the design but also contributes to the overall reduction in power consumption, which is critical for battery-operated devices such as mobile phones.
The low-noise amplifier (LNA) integrated within the MAX2338 is crucial for enhancing signal quality by amplifying weak incoming signals while minimizing noise. The adjustable high-input third-order intercept point (IIP3) feature allows for fine-tuning to optimize performance in environments with strong interfering signals, thereby improving the linearity of the system. The option for a low-gain LNA specifically tailored for cellular band operations is a strategic design choice, as it enables higher cascaded IIP3 values while maintaining lower power consumption, aligning with the current trends in mobile technology towards energy efficiency.
The mixers designed for CDMA applications prioritize high linearity and low noise, which are essential for maintaining signal integrity in complex communication environments. The differential IF outputs further enhance noise performance and signal fidelity. In contrast, the FM mixer is optimized for lower current consumption, making it suitable for applications where power efficiency is paramount.
The incorporation of an on-chip LO frequency divider within the MAX2338 facilitates the use of a single voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) for both frequency bands, streamlining the design and reducing component count. This integration not only saves space but also contributes to the overall reliability of the system by minimizing the number of external components.
The MAX2338 is packaged in an ultra-small 28-pin leadless QFN format, which is advantageous for modern mobile phone designs that require compact and efficient layouts. The leadless design enhances thermal performance and simplifies PCB assembly processes, making the MAX2338 an ideal choice for manufacturers aiming to optimize both performance and size in their cellular devices.The MAX2338 receiver RF front-end IC is designed for dual-band CDMA cellular phones and can also be used in dual-band TDMA, GSM, or EDGE cellular phones. Thanks to the MAX2338 ²s on-chip low-power LO divider, the cellular VCO module can be eliminated. The includes a low-noise amplifier (LNA) with an adjustable high-input third-order intercept poi nt (IIP3) to minimize inter modulation and cross-modulation in the presence of large interfering signals. For cellular band operation, a low-gain LNA is available for higher cascaded IIP3 at lower current. The CDMA mixers are designed for high linearity, low noise, and differential IF outputs. The FM mixer is designed for lower current and single-ended output. The MAX2338 triple-mode LNA/mixer includes an on-chip LO frequency divider to allow the use of a single VCO for both bands.
This device is available in an ultra-small 28-pin leadless QFN package. 🔗 External reference
The MAX2338 RF front-end integrated circuit serves as a versatile solution for dual-band cellular applications, providing significant enhancements in performance and efficiency. The elimination of the cellular VCO module through the on-chip low-power LO divider not only simplifies the design but also contributes to the overall reduction in power consumption, which is critical for battery-operated devices such as mobile phones.
The low-noise amplifier (LNA) integrated within the MAX2338 is crucial for enhancing signal quality by amplifying weak incoming signals while minimizing noise. The adjustable high-input third-order intercept point (IIP3) feature allows for fine-tuning to optimize performance in environments with strong interfering signals, thereby improving the linearity of the system. The option for a low-gain LNA specifically tailored for cellular band operations is a strategic design choice, as it enables higher cascaded IIP3 values while maintaining lower power consumption, aligning with the current trends in mobile technology towards energy efficiency.
The mixers designed for CDMA applications prioritize high linearity and low noise, which are essential for maintaining signal integrity in complex communication environments. The differential IF outputs further enhance noise performance and signal fidelity. In contrast, the FM mixer is optimized for lower current consumption, making it suitable for applications where power efficiency is paramount.
The incorporation of an on-chip LO frequency divider within the MAX2338 facilitates the use of a single voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) for both frequency bands, streamlining the design and reducing component count. This integration not only saves space but also contributes to the overall reliability of the system by minimizing the number of external components.
The MAX2338 is packaged in an ultra-small 28-pin leadless QFN format, which is advantageous for modern mobile phone designs that require compact and efficient layouts. The leadless design enhances thermal performance and simplifies PCB assembly processes, making the MAX2338 an ideal choice for manufacturers aiming to optimize both performance and size in their cellular devices.The MAX2338 receiver RF front-end IC is designed for dual-band CDMA cellular phones and can also be used in dual-band TDMA, GSM, or EDGE cellular phones. Thanks to the MAX2338 ²s on-chip low-power LO divider, the cellular VCO module can be eliminated. The includes a low-noise amplifier (LNA) with an adjustable high-input third-order intercept poi nt (IIP3) to minimize inter modulation and cross-modulation in the presence of large interfering signals. For cellular band operation, a low-gain LNA is available for higher cascaded IIP3 at lower current. The CDMA mixers are designed for high linearity, low noise, and differential IF outputs. The FM mixer is designed for lower current and single-ended output. The MAX2338 triple-mode LNA/mixer includes an on-chip LO frequency divider to allow the use of a single VCO for both bands.
This device is available in an ultra-small 28-pin leadless QFN package. 🔗 External reference