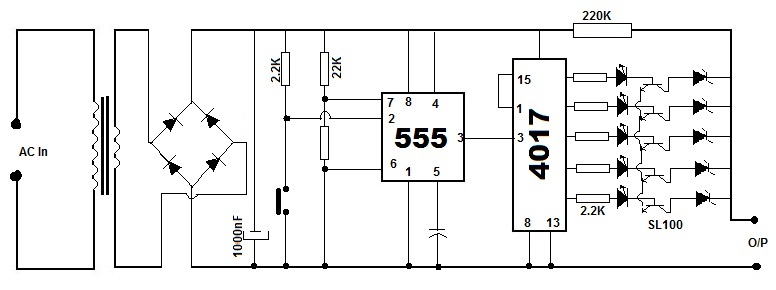
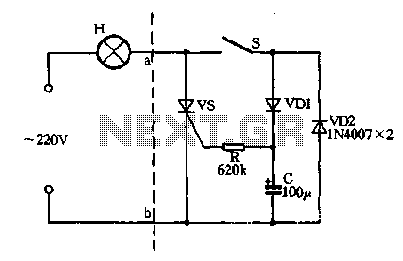
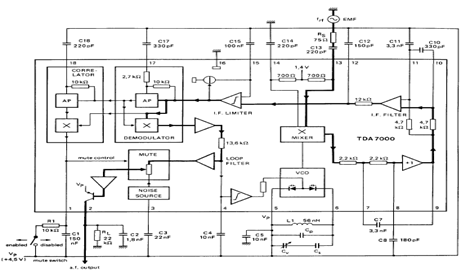
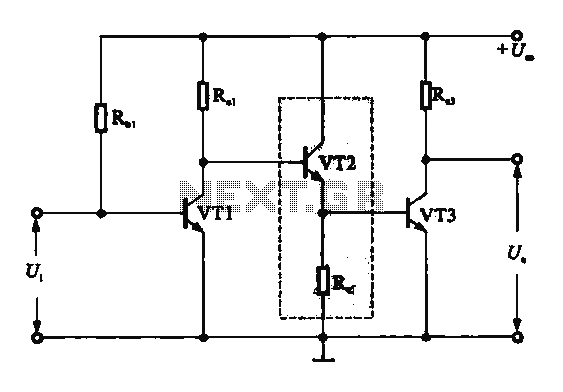
Missing pulse detector circuit using NE555

An NE555 timer integrated circuit (IC) configured in a specific manner can identify the absence of a pulse or an unusually long duration between two successive pulses in a pulse train. Such circuits are applicable for detecting the intermittent operation of an automobile spark plug or monitoring the heartbeat of a patient with health concerns. The signal from the pickup transducer is modified to create a negative-going pulse, which is then applied to pin 2 of the IC, configured in a monostable mode. As long as the interval between pulses remains shorter than the predetermined timing interval, the timing cycle is consistently reset by the incoming pulses, and the capacitor is discharged through transistor T1. A reduction in pulse frequency or the absence of a pulse allows the timing interval to complete, resulting in a change in the output level.
The NE555 timer IC operates in monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to an input trigger. In this application, the timer is set up to monitor the frequency of incoming pulse signals. The pickup transducer captures the relevant signal, which is then processed to produce a clean negative-going pulse. This pulse is fed into pin 2 of the NE555, which serves as the trigger input. The timing interval is determined by external resistors and capacitors connected to the IC, which define how long the output remains high after being triggered.
When the pulse frequency is above a certain threshold, the IC continuously resets the timing cycle, keeping the output low. However, if the pulse frequency decreases or if a pulse is missing, the timing capacitor begins to charge, and once it reaches a specific voltage level, the output of the NE555 transitions to a high state. This change in output can be used to signal an alarm or activate additional circuitry, thereby indicating a fault condition, such as a malfunctioning spark plug or an abnormal heartbeat.
Transistor T1 plays a crucial role in discharging the timing capacitor, allowing for rapid reset of the timing interval. The choice of components, including the timing capacitor and resistors, is critical in setting the sensitivity and response time of the circuit. This design can be further refined by adjusting the component values to suit specific applications, ensuring reliable detection of missing pulses or irregular intervals in various monitoring scenarios.An NE555 timer IC connected as shown here can detect a missing pulse or abnormally long period between two consecutive pulses in a train of pulses. Such circuits can be used to detect the intermittent firing of the spark plug of an automobile or to monitor the heart beat of a sick patient.
The signal from the pick up transducer is shaped to form a negative going pulse and is applied to pin 2 of the IC which is connected as a mono stable. As long as the spacing between the pulse is less than the timing interval, the timing cycle is continuously reset by the input pulses and the capacitor is discharged via T1. A decrease in pulse frequency or a missing pulse permits completion of time interval which causes a change in the output level.
🔗 External reference
The NE555 timer IC operates in monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to an input trigger. In this application, the timer is set up to monitor the frequency of incoming pulse signals. The pickup transducer captures the relevant signal, which is then processed to produce a clean negative-going pulse. This pulse is fed into pin 2 of the NE555, which serves as the trigger input. The timing interval is determined by external resistors and capacitors connected to the IC, which define how long the output remains high after being triggered.
When the pulse frequency is above a certain threshold, the IC continuously resets the timing cycle, keeping the output low. However, if the pulse frequency decreases or if a pulse is missing, the timing capacitor begins to charge, and once it reaches a specific voltage level, the output of the NE555 transitions to a high state. This change in output can be used to signal an alarm or activate additional circuitry, thereby indicating a fault condition, such as a malfunctioning spark plug or an abnormal heartbeat.
Transistor T1 plays a crucial role in discharging the timing capacitor, allowing for rapid reset of the timing interval. The choice of components, including the timing capacitor and resistors, is critical in setting the sensitivity and response time of the circuit. This design can be further refined by adjusting the component values to suit specific applications, ensuring reliable detection of missing pulses or irregular intervals in various monitoring scenarios.An NE555 timer IC connected as shown here can detect a missing pulse or abnormally long period between two consecutive pulses in a train of pulses. Such circuits can be used to detect the intermittent firing of the spark plug of an automobile or to monitor the heart beat of a sick patient.
The signal from the pick up transducer is shaped to form a negative going pulse and is applied to pin 2 of the IC which is connected as a mono stable. As long as the spacing between the pulse is less than the timing interval, the timing cycle is continuously reset by the input pulses and the capacitor is discharged via T1. A decrease in pulse frequency or a missing pulse permits completion of time interval which causes a change in the output level.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713