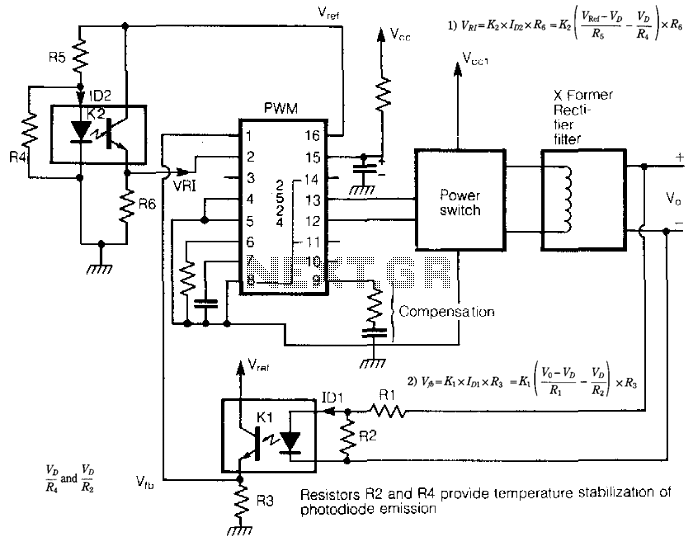
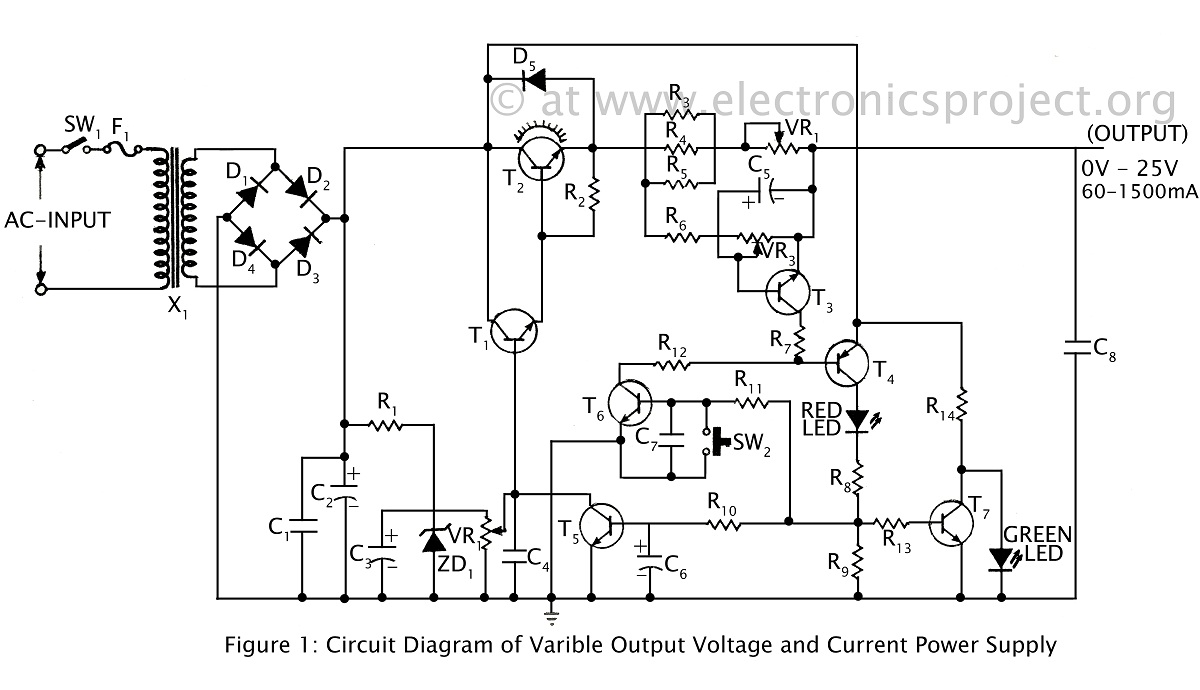
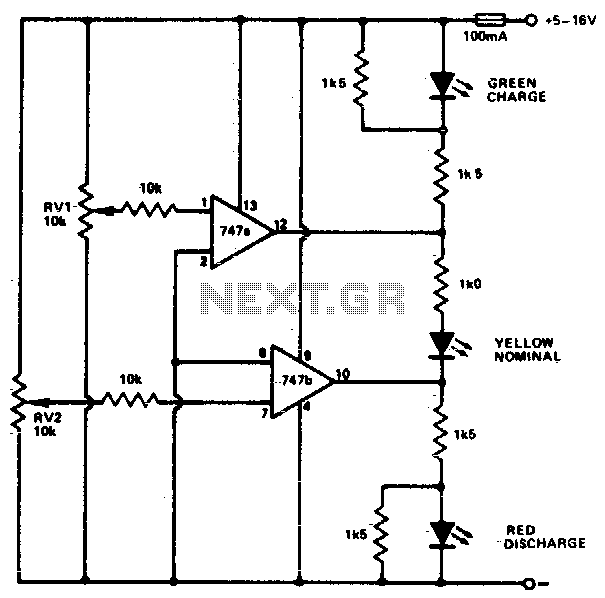
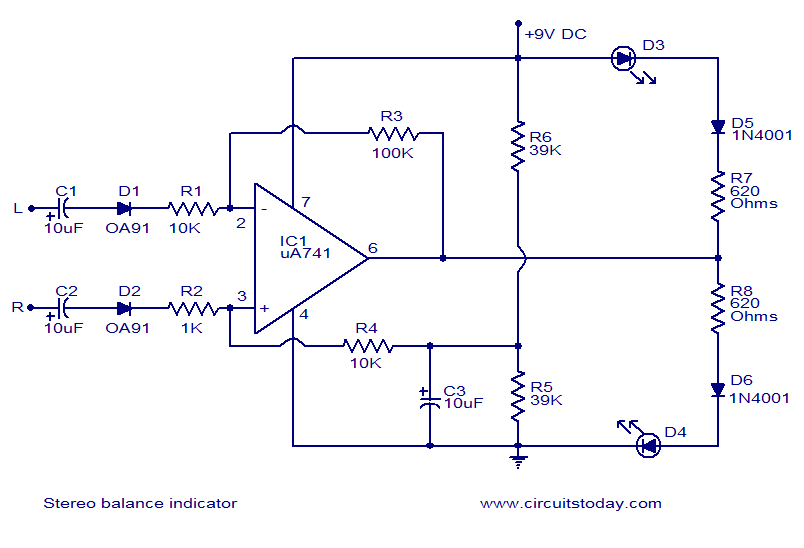
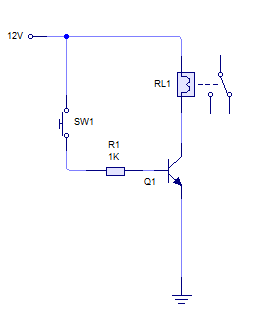
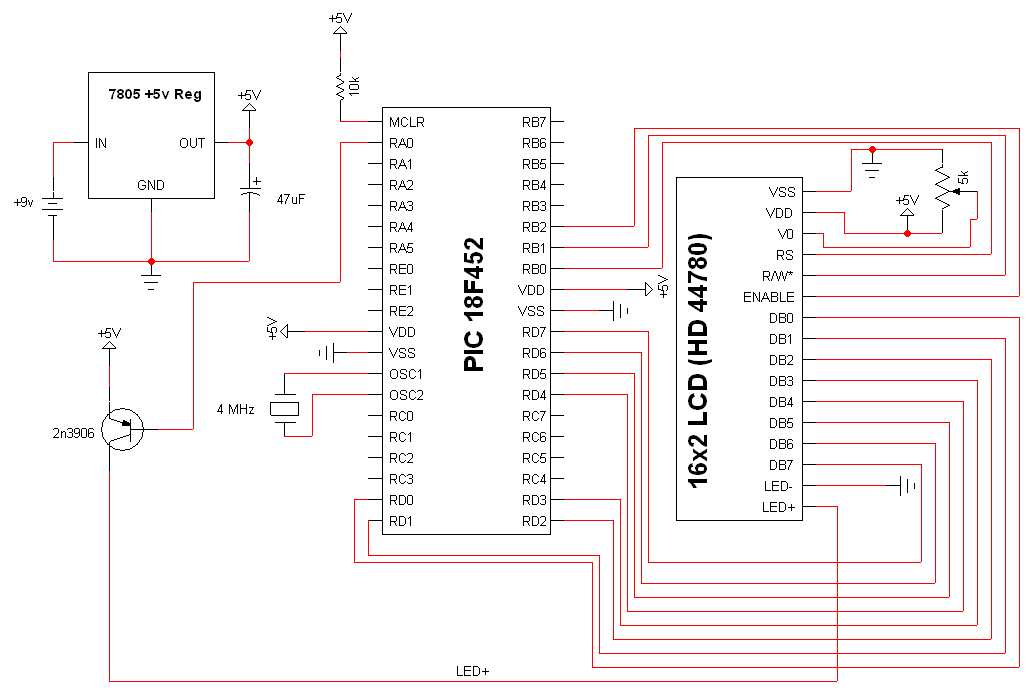
Music Bell with In / Out Indicator

A robot is an automatically guided machine capable of performing tasks independently. A notable characteristic of robots is that their appearance or movements often suggest they possess intent or agency. The term "robot" encompasses both physical robots and virtual software agents, though the latter are typically referred to as "bots." While there is no universal agreement on which machines qualify as robots, there is general consensus that they typically perform some or all of the following functions: move, operate mechanical limbs, sense and manipulate their environment, and exhibit intelligent behavior, particularly behavior that mimics humans or animals. Robots are electronic machines designed to interact with physical objects and can be programmed to execute specific tasks or a variety of actions. They may also have the capability to perceive and process data about physical objects or their environment and respond to various stimuli. This distinguishes them from simple mechanical devices, such as gears or hydraulic presses, which operate solely through mechanical processes without any processing ability. By the end of 2008, there were over 1 million industrial robots and an estimated 7 million service robots in operation. According to ISO 8373, an industrial robot is an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator that is programmable in three or more axes and can be either stationary or mobile for use in industrial automation. Industrial robots are primarily fixed robotic arms and manipulators used for the production and distribution of goods. The definition of a service robot is less precise; the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) has proposed that a service robot operates semi or fully autonomously to perform tasks beneficial to human well-being and equipment, excluding manufacturing operations. Throughout history, many mythologies have included artificial beings, such as the mechanical servants of the Greek god Hephaestus, the clay golems of Jewish legend, and Galatea, the statue that came to life. In Greek theater, the term "Deus Ex Machina" referred to the dramatic device of lowering a deity by wires to resolve complex problems. In the 4th century BC, the Greek mathematician Archytas of Tarentum theorized a steam-operated bird he named "The Pigeon." Hero of Alexandria (10-70 AD) developed various automated devices powered by air pressure, steam, and water. Su Song built a clock tower in China in 1088 that featured mechanical figurines that chimed the hours. Al-Jazari (1136-1206) was a Muslim inventor who designed numerous automated machines, including kitchen appliances and musical automata, and is credited with creating the first programmable humanoid robots in 1206. These robots performed as musicians on a boat, entertaining guests at royal gatherings, and their mechanism included a programmable drum machine with pegs (cams) that activated percussion instruments. Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) sketched plans for a humanoid robot around 1495, known as Leonardo's robot, which could sit up, wave its arm, and move its head and jaw, likely based on anatomical studies. It remains unclear if he ever constructed it. In 1738 and 1739, Jacques de Vaucanson showcased several life-sized automatons, including a flute player, a pipe player, and a duck.
Robotic systems encompass a wide range of technologies and applications, from industrial automation to personal assistance. The design of a robot typically integrates various components, including sensors, actuators, controllers, and software algorithms. Sensors enable robots to perceive their surroundings, facilitating tasks such as obstacle avoidance and environmental mapping. Common sensor types include ultrasonic sensors for distance measurement, infrared sensors for proximity detection, and cameras for visual input.
Actuators are crucial for robot movement and manipulation, converting electrical signals from the controller into mechanical motion. Types of actuators include electric motors, hydraulic systems, and pneumatic systems, each offering different advantages in terms of power, speed, and precision.
The controller serves as the brain of the robot, processing input from sensors and executing control algorithms to determine the robot's actions. Microcontrollers, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and embedded systems are commonly used for this purpose.
Software algorithms play a vital role in enabling robots to perform complex tasks autonomously. This includes path planning algorithms that allow robots to navigate environments, machine learning techniques for adaptive behavior, and control algorithms that ensure smooth and coordinated movements.
Robots can be classified into various categories based on their application, such as industrial robots used for manufacturing and assembly, service robots designed for tasks like cleaning and maintenance, and exploratory robots developed for research in hazardous environments. The ongoing advancements in robotics technology continue to expand the capabilities and applications of robots, making them integral to modern society.A robot is an automatically guided machine, able to do task on its own. Another common characteristic is that by its appearance or movements, a robot often conveys a sense that it has intent or agency of its own. The word robot can refer to both physical robots and virtual software agents, but the latter are usually referred to as bots.
There is n o consensus on which machines qualify as robots, but there is general agreement among experts and the public that robots tend to do some or all of the following: move around, operate a mechanical limb, sense and manipulate their environment, and exhibit intelligent behavior, especially behavior which mimics humans or other animals. It is an electric machine which has some ability to interact with physical objects and to be given electronic programming to do a specific task or to do a whole range of tasks or actions.
It may also have some ability to perceive and absorb data on physical objects, or on its local physical environment, or to process data, or to respond to various stimuli. This is an contrast to a simple mechanical device such as a gear or a hydraulic press or any other item which has no processing ability and which does tasks through purely mechanical processes and motion.
At the end of 2008, there were over 1 million industrial robots and an estimated 7 million service robots in use. Industrial robot, as defined by ISO 8373, is an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator programmable in three or more axes, which may be either fixed in place or mobile for use in industrial automation applications .
Most commonly, industrial robots are fixed robotic arms and manipulators used primarily for production and distribution of goods. The term service robot is less well defined. IFR has proposed a tentative definition, A service robot is a robot which operates semi or fully autonomously to perform services useful to the well-being of humans and equipment, excluding manufacturing operations.
Many ancient mythologies include artificial people such as the mechanical servants built by the Greek God Hephaestus (Vulcan to the Romans), the clay golems of the Jewish legend and clay giants of Norse legend and Galatea, the mythical statue that came to life. In Greek drama, Deus Ex Machina was contrived as a dramatic device that usually involved lowering a deity by wires into the play to solve a seemingly impossible problem.
In the 4th century BC, the Greek mathematician Archytas of Tarentum postulated a mechanical steam-operated bird he called The Pigeon . Hero of Alexandria ( 10-70) created numerous user friendly automated devices, and described machines by air pressure, steam and water.
Su Song built a clock tower in China in 1088 featuring mechanical figurines that chimed the hours. Al-Jazari (1136-1206), a Muslim inventor during the Artuqid dynasty, designed and constructed a number of automated machines, including kitchen appliances, musical automata powered by water, and the first programmable humanoid robots in 1206. The robots appeared as four musician on a boat in a lake, entertaining guests at royal drinking parties.
His mechanism had a programmable drum machine with pegs (cams) that bumped into little levers that operated percussion instruments. The drummer could be made to play different rhythms and different drum patterns by moving the pegs to different locations.
Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), sketched plans for a humanoid robot around 1495. Da Vinci`s notebooks, rediscovered in the 1950s, contain detailed drawings of a mechanical knight now known as Leonardo`s robot, able to sit up, wave its arm and move its head and jaw. The design was probably based on anatomical research recorded in his viridian man. It is not known whether he attempted to build it. In 1738 and 1739, Jacques de vaucanson exhibited several life sized automatons: a flute player, a pipe player and duck.
The mechanic 🔗 External reference
Robotic systems encompass a wide range of technologies and applications, from industrial automation to personal assistance. The design of a robot typically integrates various components, including sensors, actuators, controllers, and software algorithms. Sensors enable robots to perceive their surroundings, facilitating tasks such as obstacle avoidance and environmental mapping. Common sensor types include ultrasonic sensors for distance measurement, infrared sensors for proximity detection, and cameras for visual input.
Actuators are crucial for robot movement and manipulation, converting electrical signals from the controller into mechanical motion. Types of actuators include electric motors, hydraulic systems, and pneumatic systems, each offering different advantages in terms of power, speed, and precision.
The controller serves as the brain of the robot, processing input from sensors and executing control algorithms to determine the robot's actions. Microcontrollers, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and embedded systems are commonly used for this purpose.
Software algorithms play a vital role in enabling robots to perform complex tasks autonomously. This includes path planning algorithms that allow robots to navigate environments, machine learning techniques for adaptive behavior, and control algorithms that ensure smooth and coordinated movements.
Robots can be classified into various categories based on their application, such as industrial robots used for manufacturing and assembly, service robots designed for tasks like cleaning and maintenance, and exploratory robots developed for research in hazardous environments. The ongoing advancements in robotics technology continue to expand the capabilities and applications of robots, making them integral to modern society.A robot is an automatically guided machine, able to do task on its own. Another common characteristic is that by its appearance or movements, a robot often conveys a sense that it has intent or agency of its own. The word robot can refer to both physical robots and virtual software agents, but the latter are usually referred to as bots.
There is n o consensus on which machines qualify as robots, but there is general agreement among experts and the public that robots tend to do some or all of the following: move around, operate a mechanical limb, sense and manipulate their environment, and exhibit intelligent behavior, especially behavior which mimics humans or other animals. It is an electric machine which has some ability to interact with physical objects and to be given electronic programming to do a specific task or to do a whole range of tasks or actions.
It may also have some ability to perceive and absorb data on physical objects, or on its local physical environment, or to process data, or to respond to various stimuli. This is an contrast to a simple mechanical device such as a gear or a hydraulic press or any other item which has no processing ability and which does tasks through purely mechanical processes and motion.
At the end of 2008, there were over 1 million industrial robots and an estimated 7 million service robots in use. Industrial robot, as defined by ISO 8373, is an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator programmable in three or more axes, which may be either fixed in place or mobile for use in industrial automation applications .
Most commonly, industrial robots are fixed robotic arms and manipulators used primarily for production and distribution of goods. The term service robot is less well defined. IFR has proposed a tentative definition, A service robot is a robot which operates semi or fully autonomously to perform services useful to the well-being of humans and equipment, excluding manufacturing operations.
Many ancient mythologies include artificial people such as the mechanical servants built by the Greek God Hephaestus (Vulcan to the Romans), the clay golems of the Jewish legend and clay giants of Norse legend and Galatea, the mythical statue that came to life. In Greek drama, Deus Ex Machina was contrived as a dramatic device that usually involved lowering a deity by wires into the play to solve a seemingly impossible problem.
In the 4th century BC, the Greek mathematician Archytas of Tarentum postulated a mechanical steam-operated bird he called The Pigeon . Hero of Alexandria ( 10-70) created numerous user friendly automated devices, and described machines by air pressure, steam and water.
Su Song built a clock tower in China in 1088 featuring mechanical figurines that chimed the hours. Al-Jazari (1136-1206), a Muslim inventor during the Artuqid dynasty, designed and constructed a number of automated machines, including kitchen appliances, musical automata powered by water, and the first programmable humanoid robots in 1206. The robots appeared as four musician on a boat in a lake, entertaining guests at royal drinking parties.
His mechanism had a programmable drum machine with pegs (cams) that bumped into little levers that operated percussion instruments. The drummer could be made to play different rhythms and different drum patterns by moving the pegs to different locations.
Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), sketched plans for a humanoid robot around 1495. Da Vinci`s notebooks, rediscovered in the 1950s, contain detailed drawings of a mechanical knight now known as Leonardo`s robot, able to sit up, wave its arm and move its head and jaw. The design was probably based on anatomical research recorded in his viridian man. It is not known whether he attempted to build it. In 1738 and 1739, Jacques de vaucanson exhibited several life sized automatons: a flute player, a pipe player and duck.
The mechanic 🔗 External reference