Null detector
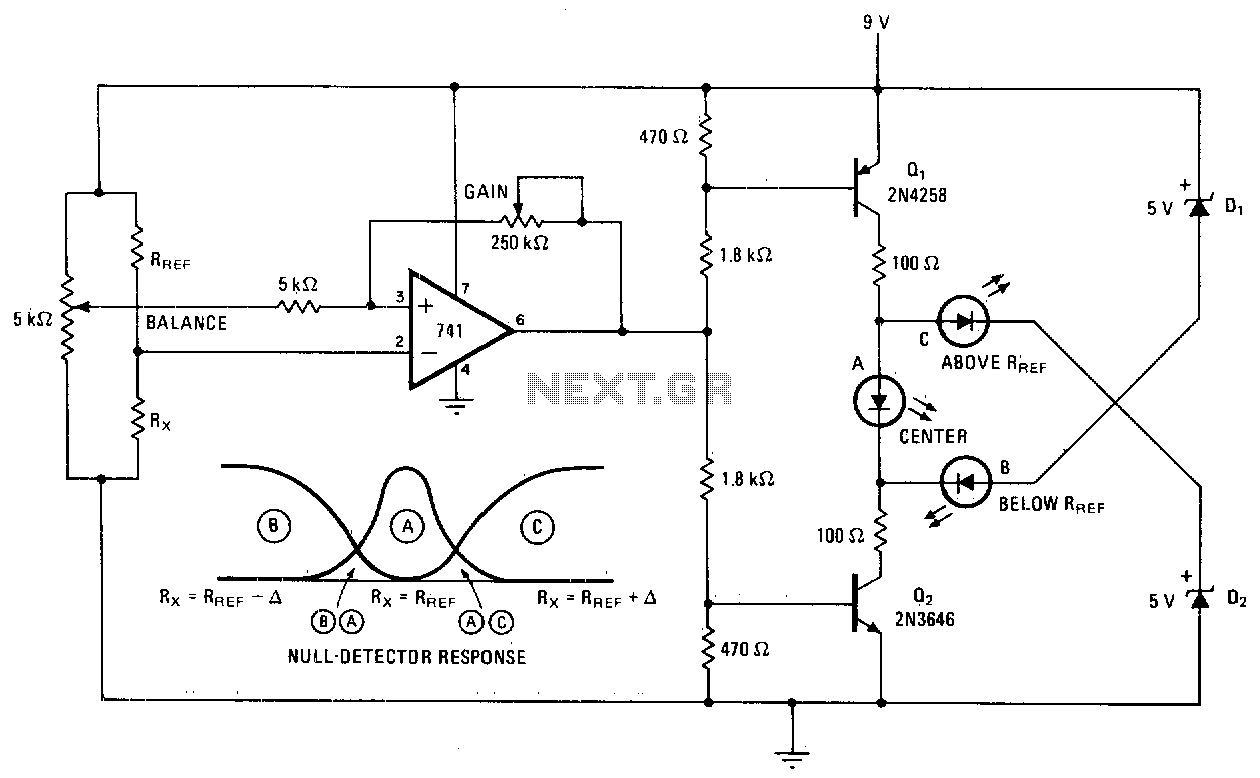
A null detector employs a basic LED readout to indicate whether the test resistor R* is below, equal to, or greater than the reference resistance Rref. When R* equals Rref, the output of the 741 operational amplifier stabilizes at a midpoint value of 4 volts, causing LED A to illuminate. In other scenarios, the 741 output disables one transistor while allowing current to flow through the other transistor, either through B or C, based on the polarity of the input voltage difference. The response of the null detector is illustrated.
The null detector circuit is designed to provide a visual indication of the relationship between a test resistor (R*) and a reference resistor (Rref) using an LED as an output indicator. The core component of this circuit is the operational amplifier (op-amp), specifically the 741 model, which is configured in a differential mode to compare the voltages across the two resistors.
When the resistance of R* matches Rref, the op-amp output stabilizes at approximately half of the supply voltage, which is typically around 4 volts in a dual-supply configuration. This mid-range voltage causes LED A to turn on, providing a clear visual signal that the two resistances are equal.
In scenarios where R* is either less than or greater than Rref, the op-amp output will either increase or decrease, leading to the activation of one of two transistors in the circuit. The transistor that is turned off will stop conducting, while the other transistor will allow current to flow through either output B or C, depending on the direction of the voltage difference. This configuration ensures that the circuit can indicate both conditions of being below or above the reference resistance.
The null detector circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional features such as hysteresis to prevent false triggering or adding a more sensitive LED output to indicate small deviations from the null point. Additionally, the circuit could be designed to include adjustable reference resistance, allowing for greater versatility in testing various resistor values. Overall, this simple yet effective design serves as a practical tool in electronic testing and measurement applications.Null detector uses simple LED readout to indicate if test resistor R* is below, equal to, or greater than test resistance Rref. IfR* = Rref, the 741 output sits at midpoint value of 4 volts and LED A lights Otherwise, the output of the 741 turns off one transistor and diverts current from the other transistor through B or C, depending on the polarity of the input voltage difference. Null-detector response is illustrated. 🔗 External reference
The null detector circuit is designed to provide a visual indication of the relationship between a test resistor (R*) and a reference resistor (Rref) using an LED as an output indicator. The core component of this circuit is the operational amplifier (op-amp), specifically the 741 model, which is configured in a differential mode to compare the voltages across the two resistors.
When the resistance of R* matches Rref, the op-amp output stabilizes at approximately half of the supply voltage, which is typically around 4 volts in a dual-supply configuration. This mid-range voltage causes LED A to turn on, providing a clear visual signal that the two resistances are equal.
In scenarios where R* is either less than or greater than Rref, the op-amp output will either increase or decrease, leading to the activation of one of two transistors in the circuit. The transistor that is turned off will stop conducting, while the other transistor will allow current to flow through either output B or C, depending on the direction of the voltage difference. This configuration ensures that the circuit can indicate both conditions of being below or above the reference resistance.
The null detector circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional features such as hysteresis to prevent false triggering or adding a more sensitive LED output to indicate small deviations from the null point. Additionally, the circuit could be designed to include adjustable reference resistance, allowing for greater versatility in testing various resistor values. Overall, this simple yet effective design serves as a practical tool in electronic testing and measurement applications.Null detector uses simple LED readout to indicate if test resistor R* is below, equal to, or greater than test resistance Rref. IfR* = Rref, the 741 output sits at midpoint value of 4 volts and LED A lights Otherwise, the output of the 741 turns off one transistor and diverts current from the other transistor through B or C, depending on the polarity of the input voltage difference. Null-detector response is illustrated. 🔗 External reference