On-Off Temperature Control circuit
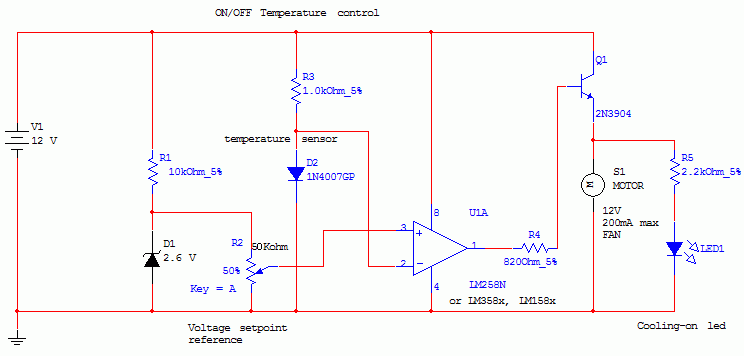
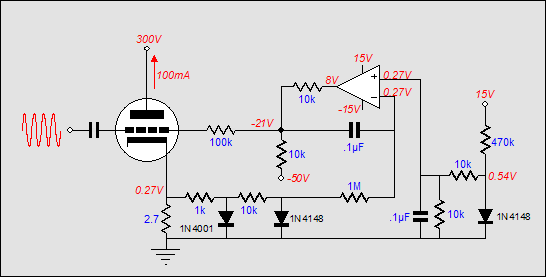
This circuit controls a load, specifically a DC brushless fan, based on a temperature comparison with a setpoint. The transducer utilized is a diode in the forward bias configuration. When forward biased, the forward voltage drop across the diode exhibits temperature dependence, characterized by a negative linear slope. This behavior is attributed to the Boltzmann distribution, which facilitates the thermal excitation of electrons into the conduction band, thereby reducing the voltage drop across the diode.
The circuit operates by using a temperature sensor, which may be a thermistor or a diode, to monitor the ambient temperature. The output from this sensor is compared to a predetermined setpoint. When the temperature exceeds the setpoint, the circuit activates the DC brushless fan to dissipate heat and maintain the desired temperature range. The diode's forward voltage drop serves as a reliable means to gauge temperature changes, as it varies predictably with temperature fluctuations.
In practical implementation, the circuit may include additional components such as an operational amplifier to amplify the voltage signal from the temperature sensor, and a transistor or MOSFET to drive the fan. The operational amplifier can be configured as a comparator, providing a clear on/off signal based on the comparison between the sensor output and the reference voltage corresponding to the setpoint.
For stability and noise reduction, bypass capacitors may be employed across the power supply lines. Additionally, a feedback mechanism can be integrated to adjust the fan speed proportionally to the temperature difference, allowing for more efficient thermal management. This circuit design is suitable for various applications where temperature regulation is critical, such as in computer cooling systems, HVAC units, and other electronic devices requiring thermal control.This circuit controls a load (in this case a dc brushless fan) based on a temperature compared with a setpoint. THe transduced is a diode in the forward polarization regime. In fact when forward biased, the forward voltage drop accross a diode has a temperature dependance, in particular has a negative linear(ish) slope.
This because of the boltzmann distribuition, causing electrons to pass to the conduction band thermically, lowering the voltage drop accross the diode.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by using a temperature sensor, which may be a thermistor or a diode, to monitor the ambient temperature. The output from this sensor is compared to a predetermined setpoint. When the temperature exceeds the setpoint, the circuit activates the DC brushless fan to dissipate heat and maintain the desired temperature range. The diode's forward voltage drop serves as a reliable means to gauge temperature changes, as it varies predictably with temperature fluctuations.
In practical implementation, the circuit may include additional components such as an operational amplifier to amplify the voltage signal from the temperature sensor, and a transistor or MOSFET to drive the fan. The operational amplifier can be configured as a comparator, providing a clear on/off signal based on the comparison between the sensor output and the reference voltage corresponding to the setpoint.
For stability and noise reduction, bypass capacitors may be employed across the power supply lines. Additionally, a feedback mechanism can be integrated to adjust the fan speed proportionally to the temperature difference, allowing for more efficient thermal management. This circuit design is suitable for various applications where temperature regulation is critical, such as in computer cooling systems, HVAC units, and other electronic devices requiring thermal control.This circuit controls a load (in this case a dc brushless fan) based on a temperature compared with a setpoint. THe transduced is a diode in the forward polarization regime. In fact when forward biased, the forward voltage drop accross a diode has a temperature dependance, in particular has a negative linear(ish) slope.
This because of the boltzmann distribuition, causing electrons to pass to the conduction band thermically, lowering the voltage drop accross the diode.. 🔗 External reference