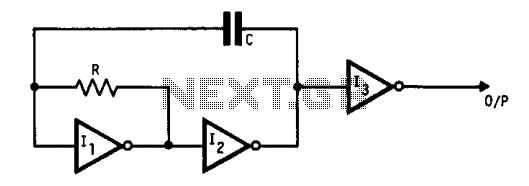
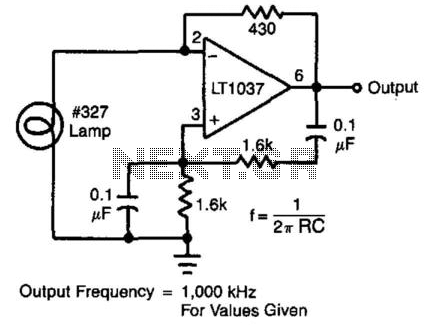
oscillator Is this a suitable sine wave osc? how would I control the frequency
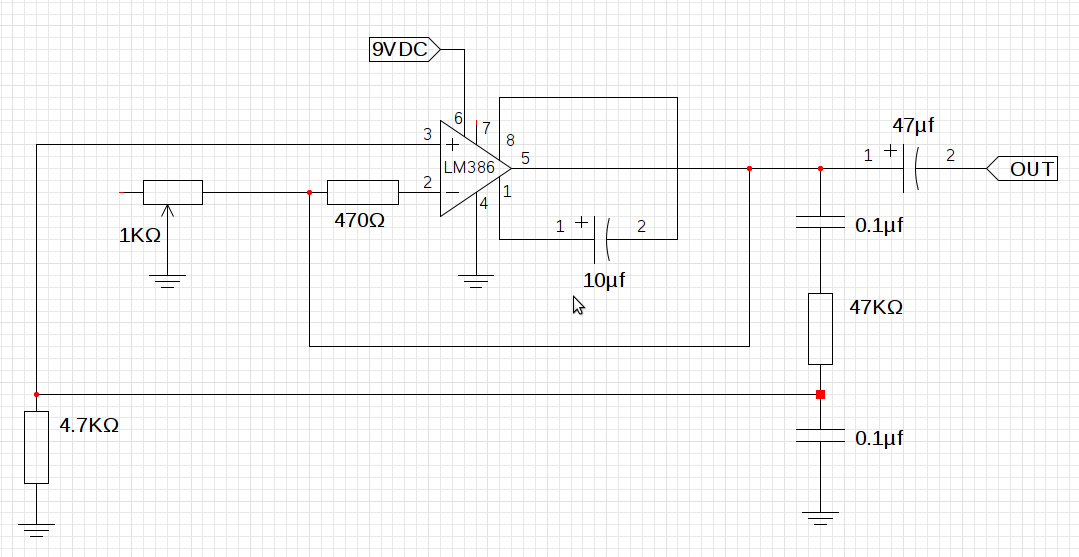
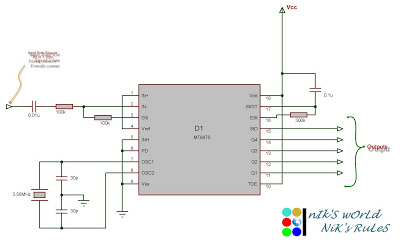
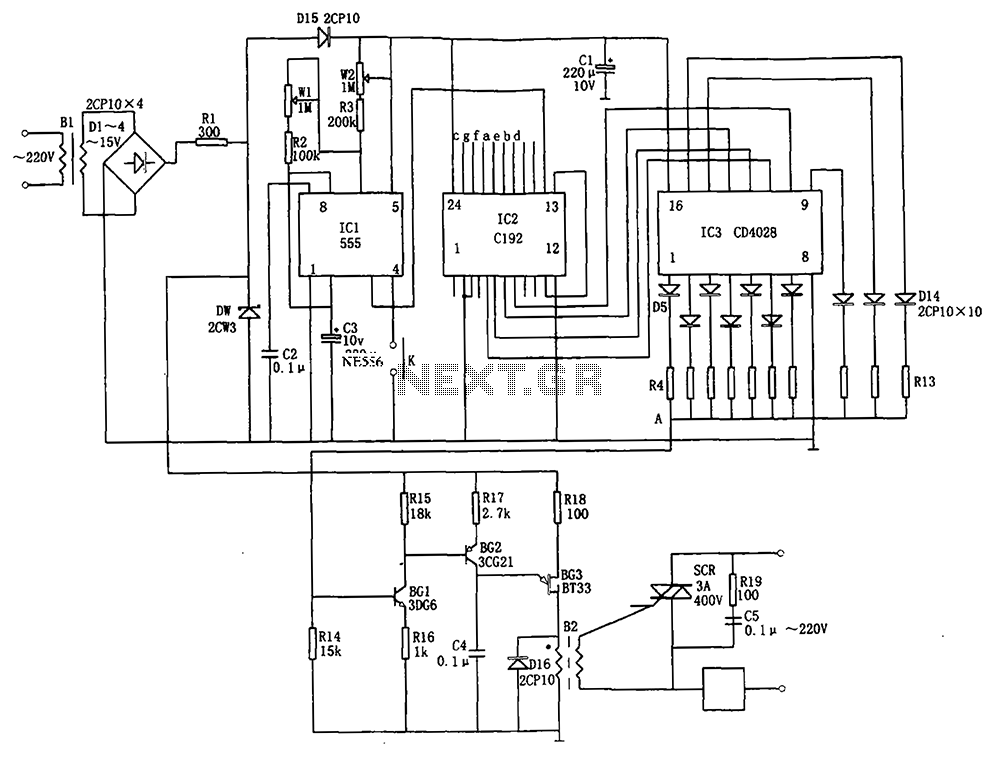
The design utilizes the LM386n-1 integrated circuit, powered by a single power supply to maintain a compact layout. There is a need to control the frequency, and the user is inquiring about which component values should be adjusted for this purpose. Attempts have been made to modify the resistors to alter the pitch, but the resistors appear to be interdependent. In the current implementation, a 1K potentiometer has replaced an incandescent bulb due to unavailability. Suggestions are also sought for the final circuit's Automatic Gain Control (AGC) component.
The LM386n-1 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier designed for use in battery-powered applications. It typically operates with a power supply range of 4 to 12 volts and is capable of delivering up to 1 watt of output power into an 8-ohm load. This IC is suitable for applications that require a compact design due to its small footprint and minimal external components.
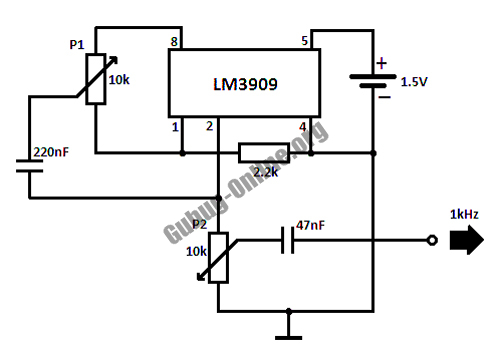
To control the frequency of the output signal, it is essential to focus on the timing components used in the circuit. The frequency can typically be adjusted by changing the values of capacitors and resistors in the feedback network of the amplifier. In many configurations, the frequency is determined by the RC time constant, which is influenced by both resistance and capacitance values.
If the goal is to modify the pitch, it may be necessary to experiment with the capacitors in the feedback loop. For instance, increasing the capacitance will lower the frequency, while decreasing it will raise the frequency. Additionally, the resistors in the feedback path can also be adjusted; however, their interdependence suggests that a systematic approach to changing one component at a time will yield the best results.
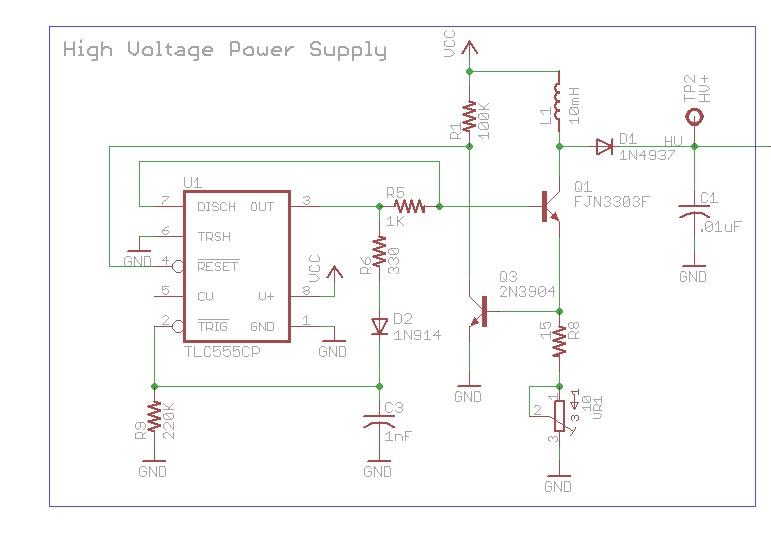
In terms of implementing an Automatic Gain Control (AGC), various options are available. One common approach is to use a diode-based AGC circuit, which can help maintain a consistent output level by adjusting the gain based on the input signal amplitude. Another option could be to integrate a dedicated AGC IC that automatically adjusts the gain based on the detected signal level.
Ultimately, the selection of components for the AGC will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired response time and the dynamic range of the input signal. Careful consideration of these factors will enhance the overall performance of the final circuit design.As I`m working from a single power supply and I`m trying to keep the design small, I`ve been using the LM386n-1 IC. Also, how would you suggest I control the frequency, which component value should be changed to achieve this - I`ve tried messing with all the resistors to change the pitch, but theyall seem to be interdependent.
And this is what my implementation looks like, I don`t have a suitable incandescent bulb so I`ve just replaced it with a 1K © pot. I`m still not sure what I`ll use in the final circuit as AGC, suggestions are welcome. 🔗 External reference
The LM386n-1 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier designed for use in battery-powered applications. It typically operates with a power supply range of 4 to 12 volts and is capable of delivering up to 1 watt of output power into an 8-ohm load. This IC is suitable for applications that require a compact design due to its small footprint and minimal external components.
To control the frequency of the output signal, it is essential to focus on the timing components used in the circuit. The frequency can typically be adjusted by changing the values of capacitors and resistors in the feedback network of the amplifier. In many configurations, the frequency is determined by the RC time constant, which is influenced by both resistance and capacitance values.
If the goal is to modify the pitch, it may be necessary to experiment with the capacitors in the feedback loop. For instance, increasing the capacitance will lower the frequency, while decreasing it will raise the frequency. Additionally, the resistors in the feedback path can also be adjusted; however, their interdependence suggests that a systematic approach to changing one component at a time will yield the best results.
In terms of implementing an Automatic Gain Control (AGC), various options are available. One common approach is to use a diode-based AGC circuit, which can help maintain a consistent output level by adjusting the gain based on the input signal amplitude. Another option could be to integrate a dedicated AGC IC that automatically adjusts the gain based on the detected signal level.
Ultimately, the selection of components for the AGC will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired response time and the dynamic range of the input signal. Careful consideration of these factors will enhance the overall performance of the final circuit design.As I`m working from a single power supply and I`m trying to keep the design small, I`ve been using the LM386n-1 IC. Also, how would you suggest I control the frequency, which component value should be changed to achieve this - I`ve tried messing with all the resistors to change the pitch, but theyall seem to be interdependent.
And this is what my implementation looks like, I don`t have a suitable incandescent bulb so I`ve just replaced it with a 1K © pot. I`m still not sure what I`ll use in the final circuit as AGC, suggestions are welcome. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713