
Photoelectric-ac-power-switch
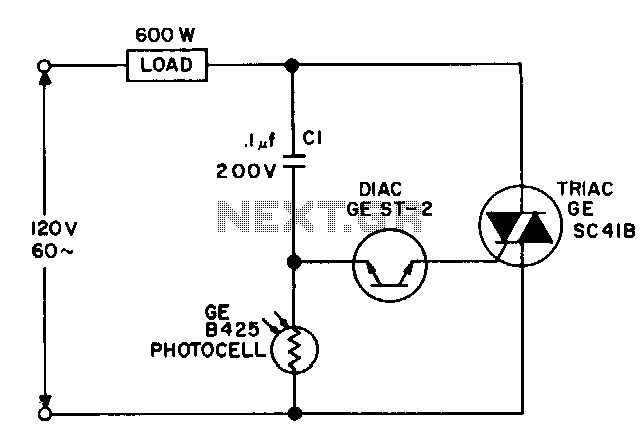
For a dark photocell with high resistance, the voltage across the diac rises rapidly in response to the line voltage due to the current flowing through capacitor C1, which triggers the diac early in the cycle. When the resistance of the photocell falls below approximately 2000 ohms, the voltage drop across it is restricted to below the diac's triggering voltage, resulting in the load power being turned off.
The circuit utilizes a dark photocell, which is a light-sensitive resistor that changes its resistance based on the ambient light level. In dark conditions, the resistance of the photocell is high, allowing the voltage across the diac to increase quickly due to the line voltage. This behavior is facilitated by capacitor C1, which charges and contributes to the rapid rise in voltage, leading to the early triggering of the diac.
The diac is a semiconductor device that remains off until the voltage across it exceeds a certain threshold, known as the triggering voltage. In this circuit, when the photocell is in dark conditions and maintains a high resistance, the voltage across the diac eventually reaches this threshold, causing it to conduct and allowing current to flow through the load.
Conversely, when the ambient light increases and the resistance of the photocell drops below approximately 2000 ohms, the voltage drop across the photocell becomes insufficient to trigger the diac. As a result, the load power is shut off, preventing unnecessary power consumption when sufficient light is present. This operation ensures that the circuit effectively controls the load based on the light conditions, providing an automatic response to changes in ambient lighting.
Overall, this circuit design is a practical application of a dark photocell in conjunction with a diac and capacitor to create an automatic load control system that reacts to light levels, enhancing energy efficiency and providing convenience in various electronic applications.For a dark photocell, high resistance, the vohage across the diac rises rapidly with the line voltage due to the current through C 1, triggering the diac early in the cycle. When the photocell resistance is less than about 2000 n, the drop across it is limited to less than the diac triggering voltage, and the load power is shut off. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a dark photocell, which is a light-sensitive resistor that changes its resistance based on the ambient light level. In dark conditions, the resistance of the photocell is high, allowing the voltage across the diac to increase quickly due to the line voltage. This behavior is facilitated by capacitor C1, which charges and contributes to the rapid rise in voltage, leading to the early triggering of the diac.
The diac is a semiconductor device that remains off until the voltage across it exceeds a certain threshold, known as the triggering voltage. In this circuit, when the photocell is in dark conditions and maintains a high resistance, the voltage across the diac eventually reaches this threshold, causing it to conduct and allowing current to flow through the load.
Conversely, when the ambient light increases and the resistance of the photocell drops below approximately 2000 ohms, the voltage drop across the photocell becomes insufficient to trigger the diac. As a result, the load power is shut off, preventing unnecessary power consumption when sufficient light is present. This operation ensures that the circuit effectively controls the load based on the light conditions, providing an automatic response to changes in ambient lighting.
Overall, this circuit design is a practical application of a dark photocell in conjunction with a diac and capacitor to create an automatic load control system that reacts to light levels, enhancing energy efficiency and providing convenience in various electronic applications.For a dark photocell, high resistance, the vohage across the diac rises rapidly with the line voltage due to the current through C 1, triggering the diac early in the cycle. When the photocell resistance is less than about 2000 n, the drop across it is limited to less than the diac triggering voltage, and the load power is shut off. 🔗 External reference