
Portable-amplifier
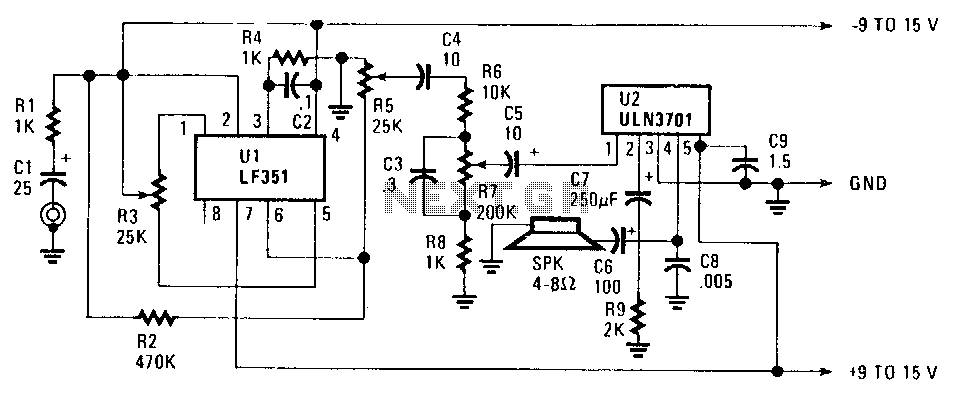
The FET operational amplifier (op amp) requires a bipolar voltage at pins 4 and 7, with a common ground to achieve optimum gain. The gain can be calculated by dividing R2 by R1. Zero-set balance can be achieved through pins 1 and 5 using resistor R3. A voltmeter should be connected between pin 6 and ground, and R3 should be adjusted until the voltage reads zero. After establishing this condition, the ohmic resistance at each side of R3's center tap can be measured, allowing for the potentiometer to be replaced with fixed resistors. Additionally, resistors R6, R7, R5, and capacitor C3 form a tone control circuit that provides an option for bass boost if desired.
The FET op amp operates effectively with a bipolar power supply, which is essential for its functionality. The voltage levels at pins 4 and 7 must be carefully regulated to maintain the desired gain characteristics. The gain of the amplifier circuit is determined by the ratio of resistors R2 and R1, where a higher value of R2 relative to R1 results in increased gain.
To achieve zero-set balance, the adjustment of R3 is critical. This potentiometer is connected to pins 1 and 5, and by monitoring the voltage at pin 6 with a voltmeter, the balance can be finely tuned. The objective is to ensure that the voltage at pin 6 is maintained at zero volts, indicating that the op amp is operating at its optimal point. Once the adjustment is complete, replacing the potentiometer with fixed resistors based on the measured resistance values ensures stability and reliability in the circuit's performance.
Furthermore, the inclusion of resistors R6, R7, R5, and capacitor C3 forms a tone control section within the circuit. This configuration allows for the modification of the audio signal, specifically targeting bass frequencies. The arrangement can be adjusted to provide a bass boost, enhancing the overall audio output as needed. The selection of resistor and capacitor values will determine the cutoff frequency and the extent of the bass enhancement, allowing for customization based on user preferences or specific application requirements. This tone control feature is particularly useful in audio applications where sound quality and frequency response are critical.Ul, an FET op amp needs a bipolar voltage atpins 4 and 7 with a common ground for optimum gain. You can calculate the gain by dividing R2 by Rl. Zero-set balance can be had through pins i and 5 through R3. Put a voltmeter between pin 6 and ground and adjust R3 for zero voltage. Once you"ve established that, you can measure the ohmic resistance at each side of R3"s center tap and replace the potentiometer with fixed resistors. R6, R7, RS,and C3 forrn a tone control that will give you added bass boost, if needed; 🔗 External reference
The FET op amp operates effectively with a bipolar power supply, which is essential for its functionality. The voltage levels at pins 4 and 7 must be carefully regulated to maintain the desired gain characteristics. The gain of the amplifier circuit is determined by the ratio of resistors R2 and R1, where a higher value of R2 relative to R1 results in increased gain.
To achieve zero-set balance, the adjustment of R3 is critical. This potentiometer is connected to pins 1 and 5, and by monitoring the voltage at pin 6 with a voltmeter, the balance can be finely tuned. The objective is to ensure that the voltage at pin 6 is maintained at zero volts, indicating that the op amp is operating at its optimal point. Once the adjustment is complete, replacing the potentiometer with fixed resistors based on the measured resistance values ensures stability and reliability in the circuit's performance.
Furthermore, the inclusion of resistors R6, R7, R5, and capacitor C3 forms a tone control section within the circuit. This configuration allows for the modification of the audio signal, specifically targeting bass frequencies. The arrangement can be adjusted to provide a bass boost, enhancing the overall audio output as needed. The selection of resistor and capacitor values will determine the cutoff frequency and the extent of the bass enhancement, allowing for customization based on user preferences or specific application requirements. This tone control feature is particularly useful in audio applications where sound quality and frequency response are critical.Ul, an FET op amp needs a bipolar voltage atpins 4 and 7 with a common ground for optimum gain. You can calculate the gain by dividing R2 by Rl. Zero-set balance can be had through pins i and 5 through R3. Put a voltmeter between pin 6 and ground and adjust R3 for zero voltage. Once you"ve established that, you can measure the ohmic resistance at each side of R3"s center tap and replace the potentiometer with fixed resistors. R6, R7, RS,and C3 forrn a tone control that will give you added bass boost, if needed; 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713