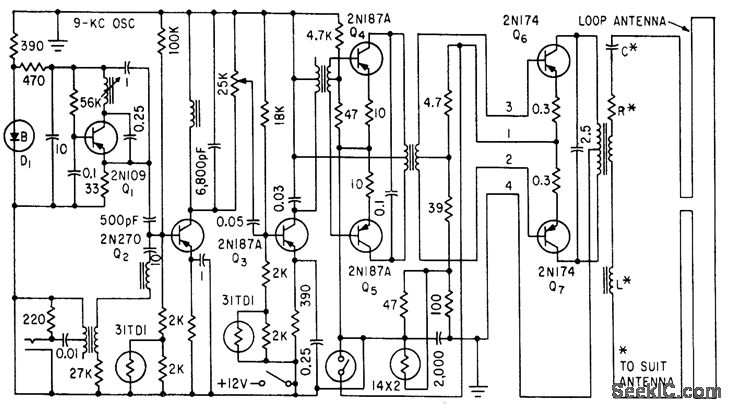
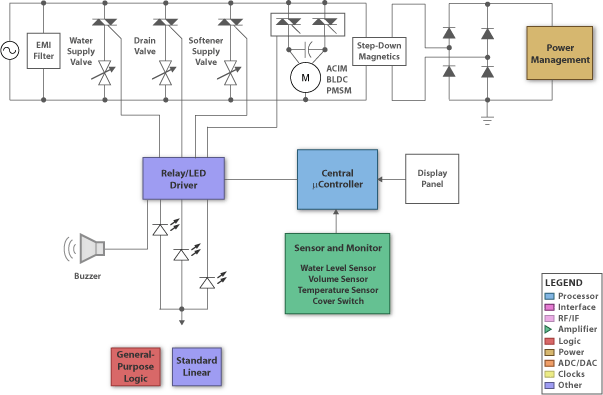
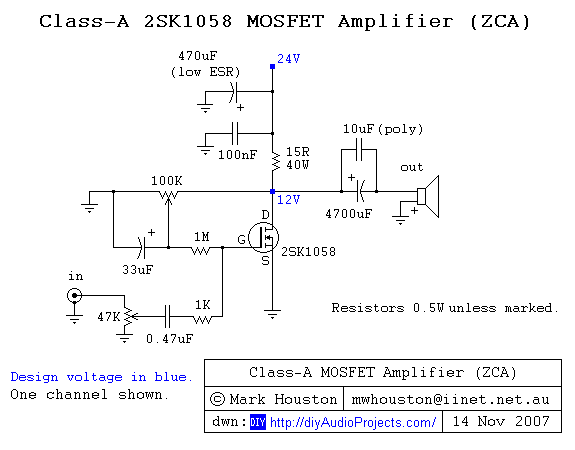
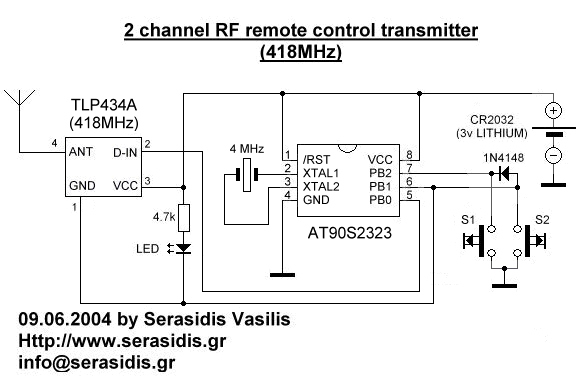
portable mic pre amp 2 transistor
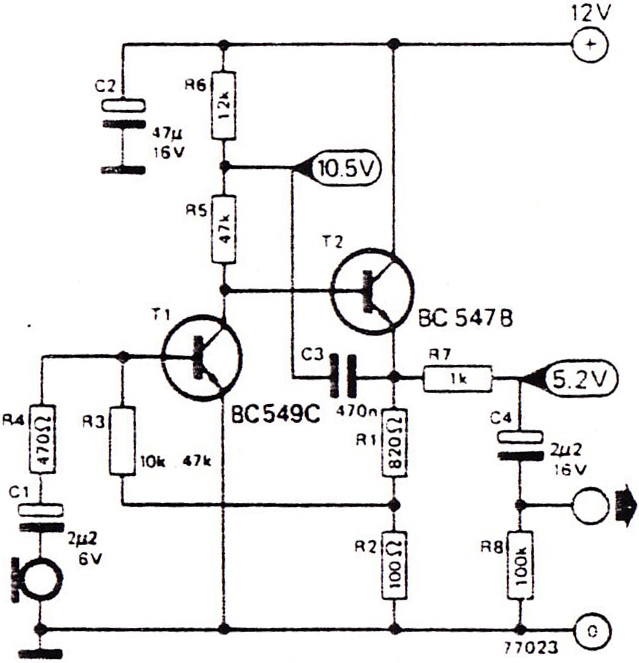
Portable microphone preamplifier using two transistors, BC549C and BC547B. The electret condenser microphone or microphone's dynamic range is very sensitive.
The portable microphone preamplifier circuit utilizes two transistors, BC549C and BC547B, to amplify the low-level audio signals from an electret condenser microphone. The BC549C is an NPN transistor commonly used for low-noise amplification, while the BC547B serves as a general-purpose NPN transistor capable of handling moderate current levels.
In this configuration, the electret microphone is powered by a biasing resistor connected to the positive supply voltage, allowing it to convert sound waves into an electrical signal. The output from the microphone is typically weak, necessitating amplification to make it suitable for further processing or transmission.
The first transistor (BC549C) is configured as a common-emitter amplifier. It provides initial amplification of the microphone signal, with the gain determined by the resistor values in the circuit. The output from this stage is then fed into the second transistor (BC547B), which acts as a buffer and further amplifies the signal to a level suitable for driving subsequent audio processing stages, such as an audio mixer or digital audio converter.
The circuit may also include coupling capacitors at the input and output to block any DC component and allow only the AC audio signal to pass through. Proper biasing of the transistors is crucial for ensuring linear operation and minimizing distortion. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be employed to stabilize the power supply and reduce noise.
Overall, this portable microphone preamplifier design is compact and efficient, making it suitable for various applications, including portable recording devices, public address systems, and other audio applications where high-quality sound capture is required.Portable Mic Pre-amp 2 transistor using BC549C, BC547B The electret condenser microphone or microphone`s dynamic range contains a very sensitive.. 🔗 External reference
The portable microphone preamplifier circuit utilizes two transistors, BC549C and BC547B, to amplify the low-level audio signals from an electret condenser microphone. The BC549C is an NPN transistor commonly used for low-noise amplification, while the BC547B serves as a general-purpose NPN transistor capable of handling moderate current levels.
In this configuration, the electret microphone is powered by a biasing resistor connected to the positive supply voltage, allowing it to convert sound waves into an electrical signal. The output from the microphone is typically weak, necessitating amplification to make it suitable for further processing or transmission.
The first transistor (BC549C) is configured as a common-emitter amplifier. It provides initial amplification of the microphone signal, with the gain determined by the resistor values in the circuit. The output from this stage is then fed into the second transistor (BC547B), which acts as a buffer and further amplifies the signal to a level suitable for driving subsequent audio processing stages, such as an audio mixer or digital audio converter.
The circuit may also include coupling capacitors at the input and output to block any DC component and allow only the AC audio signal to pass through. Proper biasing of the transistors is crucial for ensuring linear operation and minimizing distortion. Additionally, bypass capacitors may be employed to stabilize the power supply and reduce noise.
Overall, this portable microphone preamplifier design is compact and efficient, making it suitable for various applications, including portable recording devices, public address systems, and other audio applications where high-quality sound capture is required.Portable Mic Pre-amp 2 transistor using BC549C, BC547B The electret condenser microphone or microphone`s dynamic range contains a very sensitive.. 🔗 External reference