Power Quality for Audio Systems
Power supplies: Linear or SMPS (Switched Mode). A distinction is made between linear and switch mode power supplies. What is the difference? A power supply fundamentally is an...
Power supplies are essential components in electronic circuits, providing the necessary voltage and current to power various devices. The two primary types of power supplies are linear power supplies and switched mode power supplies (SMPS).
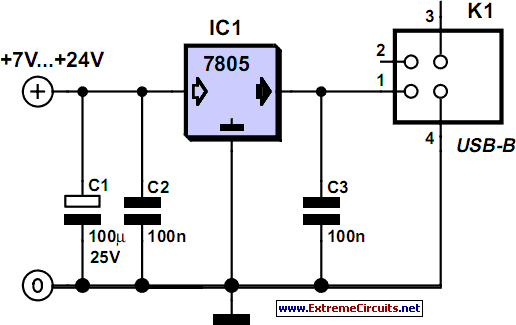
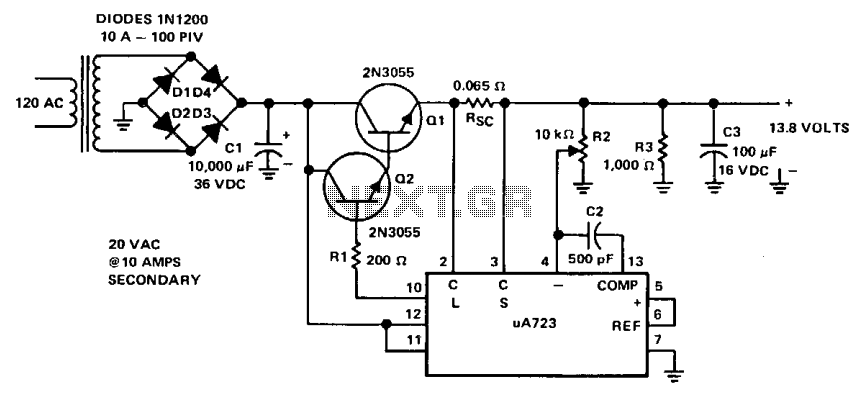
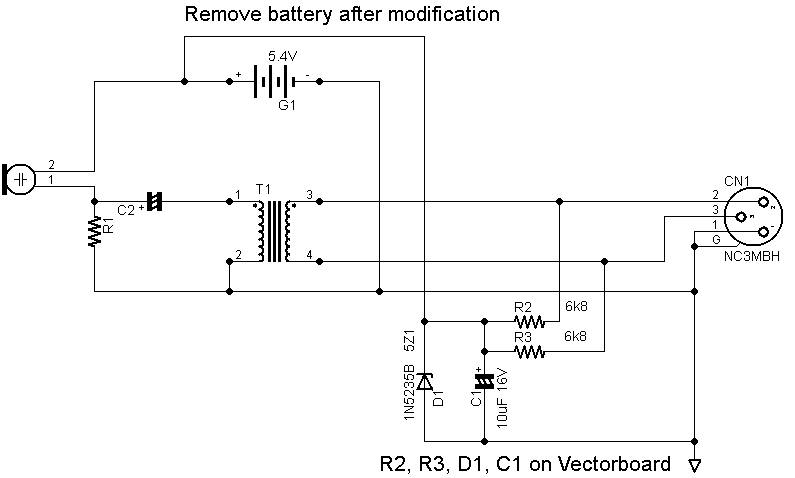
Linear power supplies operate by using a transformer to step down the voltage, followed by rectification and filtering to produce a stable output voltage. They are characterized by their simplicity, low noise, and excellent voltage regulation. However, they tend to be less efficient and bulkier due to the transformer and heat dissipation components. Linear supplies are often used in applications where noise sensitivity is critical, such as in audio equipment and precision measurement instruments.
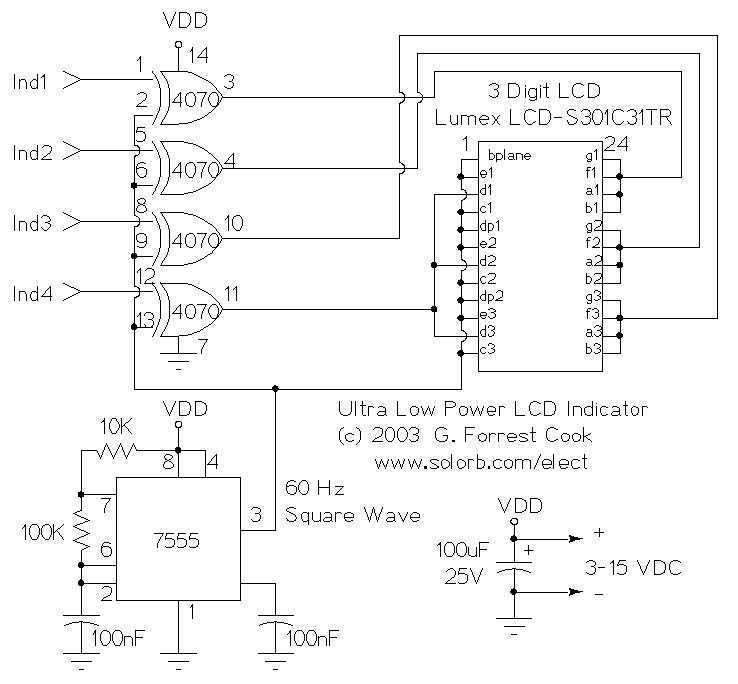
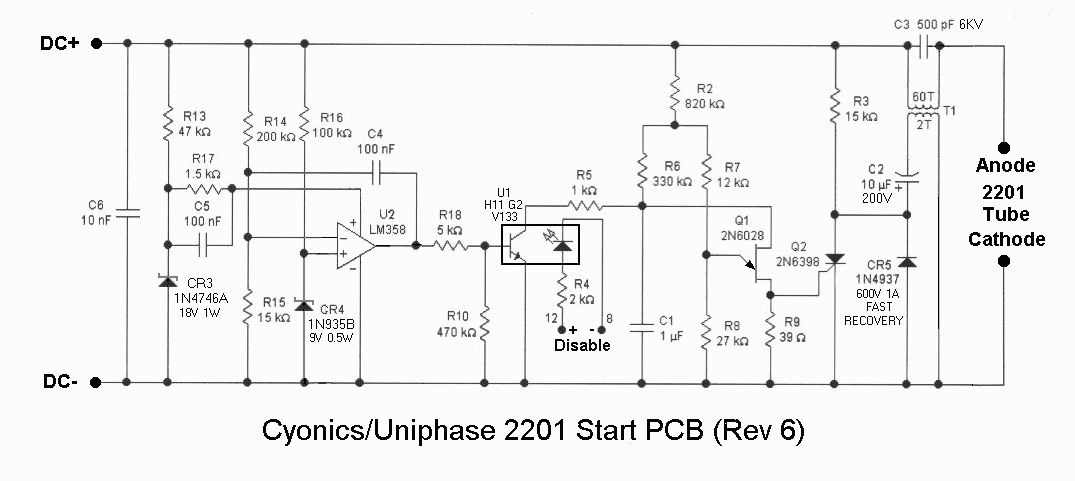
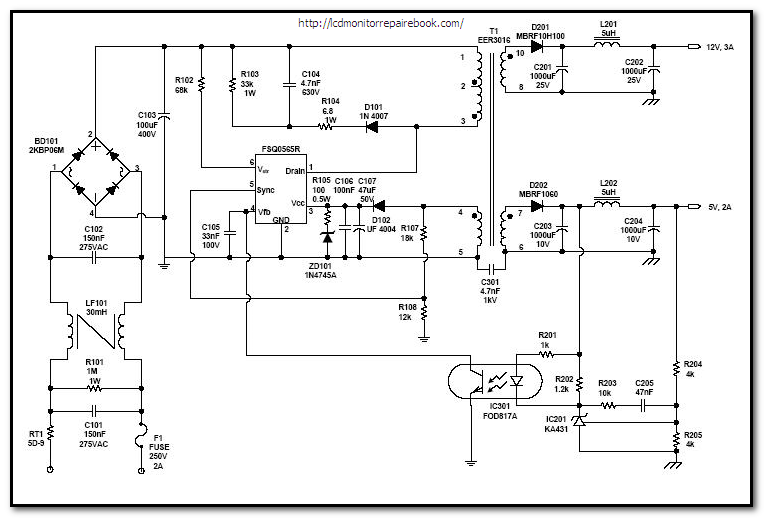
On the other hand, switched mode power supplies (SMPS) utilize high-frequency switching techniques to convert electrical power. They typically consist of a switch (usually a transistor), an inductor or transformer, a rectifier, and filtering components. SMPS are highly efficient, allowing for smaller and lighter designs compared to linear supplies. They can handle a wide input voltage range and provide adjustable output voltages, making them suitable for various applications, including computers and telecommunications equipment.
The choice between linear and switched mode power supplies depends on the specific requirements of the application, including efficiency, size, noise tolerance, and cost. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers when selecting the appropriate power supply for their electronic circuits.Power supplies ? Linear or SMPS (Switched mode) Right away there?s a distinction made between a linear and a switch mode power supply, what?s the difference? A power supply fundamentally is an.. 🔗 External reference
Power supplies are essential components in electronic circuits, providing the necessary voltage and current to power various devices. The two primary types of power supplies are linear power supplies and switched mode power supplies (SMPS).
Linear power supplies operate by using a transformer to step down the voltage, followed by rectification and filtering to produce a stable output voltage. They are characterized by their simplicity, low noise, and excellent voltage regulation. However, they tend to be less efficient and bulkier due to the transformer and heat dissipation components. Linear supplies are often used in applications where noise sensitivity is critical, such as in audio equipment and precision measurement instruments.
On the other hand, switched mode power supplies (SMPS) utilize high-frequency switching techniques to convert electrical power. They typically consist of a switch (usually a transistor), an inductor or transformer, a rectifier, and filtering components. SMPS are highly efficient, allowing for smaller and lighter designs compared to linear supplies. They can handle a wide input voltage range and provide adjustable output voltages, making them suitable for various applications, including computers and telecommunications equipment.
The choice between linear and switched mode power supplies depends on the specific requirements of the application, including efficiency, size, noise tolerance, and cost. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and designers when selecting the appropriate power supply for their electronic circuits.Power supplies ? Linear or SMPS (Switched mode) Right away there?s a distinction made between a linear and a switch mode power supply, what?s the difference? A power supply fundamentally is an.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713