PRECISION RECTIFIER
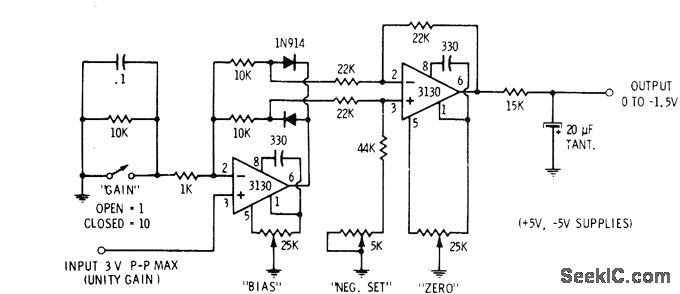
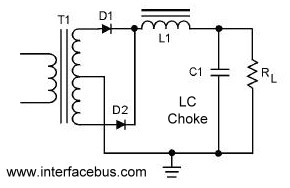
This circuit is utilized in digital voltmeters to convert an AC waveform into a full-wave rectified DC equivalent. The first operational amplifier (op-amp), designated as 3130, functions as a polarity separator. Negative-going signals appear across the upper 10K resistor, while positive-going signals are present across the lower 10K resistor. The output of the op-amp exceeds these voltage drops by a value equal to the diode's forward voltage drop. The second op-amp stage combines the positive and negative peaks. A 5K trimming potentiometer is adjusted to ensure that both peaks are of equal height. The output of the second op-amp is a negative-going full-wave replica of the input signal. After filtering, the output provides an average DC value ranging from 0 to -1.5 V for an input of 0-3 V peak-to-peak.
The described circuit operates as a full-wave rectifier using two stages of operational amplifiers to achieve precise signal processing. The first stage employs the 3130 op-amp to perform signal separation based on polarity, effectively allowing the circuit to handle both halves of the input AC waveform. The use of two 10K resistors helps ensure that the op-amp can accurately differentiate between positive and negative signal components, providing a robust method for signal conditioning.
The subsequent stage of the circuit integrates the outputs from the first stage, where the second op-amp combines the rectified peaks. The 5K trimming potentiometer is a critical component for calibrating the circuit; it allows for fine-tuning of the amplitude of the output signal, ensuring that both the positive and negative peaks are matched in height. This adjustment is essential for maintaining accuracy in applications where precise voltage measurements are required.
The output of the second op-amp stage presents a negative-going full-wave replica of the original input signal. This characteristic is particularly useful in digital voltmeter applications, where the goal is to convert the AC input into a stable DC representation. Following this stage, a filtering process is employed to smooth out the output, resulting in an average DC voltage that can be easily interpreted by subsequent measurement systems. The specified range of 0 to -1.5 V for a 0-3 V peak-to-peak input indicates the circuit's capability to handle typical voltage levels encountered in various electronic applications, making it an effective solution for accurate voltage measurement and analysis.Used in digital voltmeters to convert AC waveform to full-waverectified DC equivalent. First 3130 opamp is used as polarity separator, with negative-going signals appearing across upper 10K resistor and positive-going signals across lower 10K resistor. Output of opamp exceeds these voltage drops by exactly diode voltage drop. Second opamp stage re combines positive and negative peaks. 5K trimming pot is adjusted so both peaks are equal height. Output of second opamp is negative-going full-wave replica of input signal. After filtering, output is average DC value in range from 0 to -1. 5 V for 0-3 V P-P input. -D. Lancaster, "CMOS Cookbook, " Howard VV. Sams, Indianapolis, IN, 1977, p 345-346. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a full-wave rectifier using two stages of operational amplifiers to achieve precise signal processing. The first stage employs the 3130 op-amp to perform signal separation based on polarity, effectively allowing the circuit to handle both halves of the input AC waveform. The use of two 10K resistors helps ensure that the op-amp can accurately differentiate between positive and negative signal components, providing a robust method for signal conditioning.
The subsequent stage of the circuit integrates the outputs from the first stage, where the second op-amp combines the rectified peaks. The 5K trimming potentiometer is a critical component for calibrating the circuit; it allows for fine-tuning of the amplitude of the output signal, ensuring that both the positive and negative peaks are matched in height. This adjustment is essential for maintaining accuracy in applications where precise voltage measurements are required.
The output of the second op-amp stage presents a negative-going full-wave replica of the original input signal. This characteristic is particularly useful in digital voltmeter applications, where the goal is to convert the AC input into a stable DC representation. Following this stage, a filtering process is employed to smooth out the output, resulting in an average DC voltage that can be easily interpreted by subsequent measurement systems. The specified range of 0 to -1.5 V for a 0-3 V peak-to-peak input indicates the circuit's capability to handle typical voltage levels encountered in various electronic applications, making it an effective solution for accurate voltage measurement and analysis.Used in digital voltmeters to convert AC waveform to full-waverectified DC equivalent. First 3130 opamp is used as polarity separator, with negative-going signals appearing across upper 10K resistor and positive-going signals across lower 10K resistor. Output of opamp exceeds these voltage drops by exactly diode voltage drop. Second opamp stage re combines positive and negative peaks. 5K trimming pot is adjusted so both peaks are equal height. Output of second opamp is negative-going full-wave replica of input signal. After filtering, output is average DC value in range from 0 to -1. 5 V for 0-3 V P-P input. -D. Lancaster, "CMOS Cookbook, " Howard VV. Sams, Indianapolis, IN, 1977, p 345-346. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713