
Programmable-frequency-adjustable-rate-siren
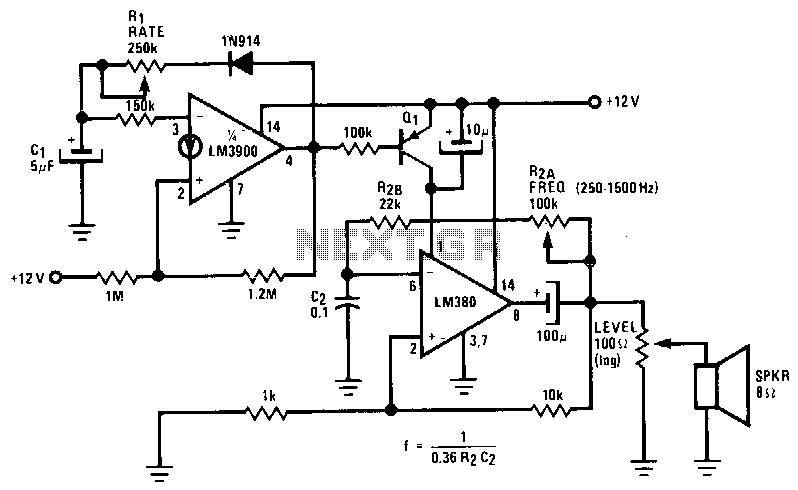
The LM380 functions as an astable oscillator, with the frequency set by R2 and C2. By adding Q1 and driving its base, the output of an LM3900 is configured as a second astable oscillator. This setup gates the output of the LM380 on and off at a rate determined by R1 and C1.
The LM380 is a power audio amplifier that can also be utilized in oscillator configurations. In this circuit, the LM380 is configured as an astable multivibrator, where the frequency of oscillation is governed by the resistor R2 and the capacitor C2. The oscillation frequency can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R2 + 2R1) \cdot C2} \]
In this configuration, the output of the LM380 toggles between high and low states, creating a square wave signal.
The addition of transistor Q1 serves a critical role in controlling the output of the LM380. When the base of Q1 is driven by the output from the LM3900, it effectively acts as a switch that gates the output of the LM380. The LM3900 is also configured as an astable oscillator, which generates a square wave signal that influences the base of Q1. The frequency of the LM3900 is determined by the components R1 and C1, which set the timing characteristics of this second oscillator.
The interaction between the two oscillators allows for modulation of the LM380 output, effectively turning it on and off at a frequency defined by R1 and C1. This can be useful in applications where pulsed signals are required, such as in tone generation or signal modulation.
Overall, this circuit demonstrates the versatility of the LM380 and LM3900 in generating oscillatory signals with adjustable frequency characteristics, providing a robust solution for various electronic applications.The LM380 operates as an astable oscillator with the frequency determined by R2/C2. Adding Ql and driving its base, with the output of an LM3900 wired as a second astable oscillator, acts to gate the output of the LM380 on and off, at a rate fixed by Rl/Cl. 🔗 External reference
The LM380 is a power audio amplifier that can also be utilized in oscillator configurations. In this circuit, the LM380 is configured as an astable multivibrator, where the frequency of oscillation is governed by the resistor R2 and the capacitor C2. The oscillation frequency can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R2 + 2R1) \cdot C2} \]
In this configuration, the output of the LM380 toggles between high and low states, creating a square wave signal.
The addition of transistor Q1 serves a critical role in controlling the output of the LM380. When the base of Q1 is driven by the output from the LM3900, it effectively acts as a switch that gates the output of the LM380. The LM3900 is also configured as an astable oscillator, which generates a square wave signal that influences the base of Q1. The frequency of the LM3900 is determined by the components R1 and C1, which set the timing characteristics of this second oscillator.
The interaction between the two oscillators allows for modulation of the LM380 output, effectively turning it on and off at a frequency defined by R1 and C1. This can be useful in applications where pulsed signals are required, such as in tone generation or signal modulation.
Overall, this circuit demonstrates the versatility of the LM380 and LM3900 in generating oscillatory signals with adjustable frequency characteristics, providing a robust solution for various electronic applications.The LM380 operates as an astable oscillator with the frequency determined by R2/C2. Adding Ql and driving its base, with the output of an LM3900 wired as a second astable oscillator, acts to gate the output of the LM380 on and off, at a rate fixed by Rl/Cl. 🔗 External reference