pull up and pull down resistor
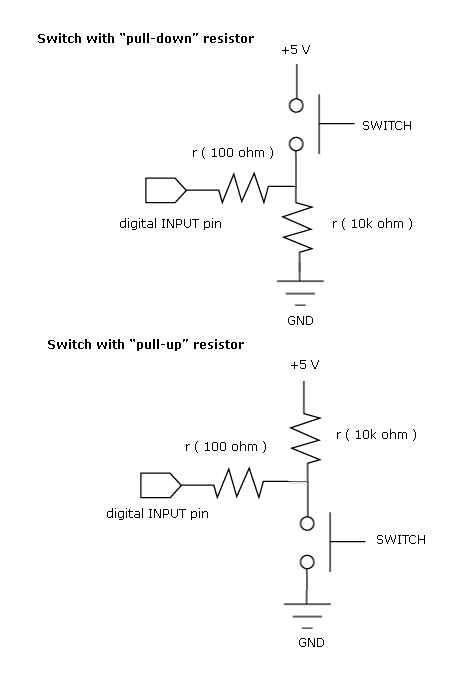
Most beginners in digital electronics assume that a floating input represents a logic 0, which is a misconception. Floating inputs are in a neutral state and can represent either a logic 0 or a logic 1. This misunderstanding can lead to erratic circuit behavior. In each case, there is a default input state: for a pull-up resistor configuration, the default input to the logic integrated circuit (IC) is logic 1, while in a pull-down configuration, the default input is logic 0. The resistor also provides a current-limiting function, which influences the power consumption of the input section. A common value for this resistor is 10 kΩ, but any value can be used depending on the specific application.
In digital electronics, understanding the behavior of floating inputs is crucial for reliable circuit operation. A floating input is one that is not connected to a definite voltage level, and it can pick up noise, leading to unpredictable states in digital logic devices. To avoid this, pull-up and pull-down resistors are employed.
In a pull-up resistor configuration, the resistor is connected between the input pin of the logic IC and the positive supply voltage (Vcc). This ensures that when the input is not actively driven low, it defaults to a high state (logic 1). Conversely, in a pull-down configuration, the resistor connects the input pin to ground, ensuring that the input defaults to a low state (logic 0) when not driven high.
The choice of resistor value is important for balancing power consumption and response speed. A 10 kΩ resistor is commonly used as it provides a good compromise between current draw and response time. Lower resistor values will result in higher current consumption, while higher values may lead to slower response times due to increased resistance to rapid voltage changes.
In summary, proper handling of floating inputs through the use of pull-up or pull-down resistors is essential in digital circuit design to ensure predictable behavior and efficient power management.Most of the beginners in digital electronics assume that the hanging input is a logic 0. Then, that`s a misconception. They are neutral state which can be a logic 0 or a logic 1. This will bring chaos on your circuit operation. As you can see, in each case there is a default input. For a pull-up, the default input to the logic IC is 1. And for the pull-down, the logic is 0. The resistor also provide a current limiting function thus affecting power consumption of the input section. 10kohms is the commonly value but any value can be use depending on your application. 🔗 External reference
In digital electronics, understanding the behavior of floating inputs is crucial for reliable circuit operation. A floating input is one that is not connected to a definite voltage level, and it can pick up noise, leading to unpredictable states in digital logic devices. To avoid this, pull-up and pull-down resistors are employed.
In a pull-up resistor configuration, the resistor is connected between the input pin of the logic IC and the positive supply voltage (Vcc). This ensures that when the input is not actively driven low, it defaults to a high state (logic 1). Conversely, in a pull-down configuration, the resistor connects the input pin to ground, ensuring that the input defaults to a low state (logic 0) when not driven high.
The choice of resistor value is important for balancing power consumption and response speed. A 10 kΩ resistor is commonly used as it provides a good compromise between current draw and response time. Lower resistor values will result in higher current consumption, while higher values may lead to slower response times due to increased resistance to rapid voltage changes.
In summary, proper handling of floating inputs through the use of pull-up or pull-down resistors is essential in digital circuit design to ensure predictable behavior and efficient power management.Most of the beginners in digital electronics assume that the hanging input is a logic 0. Then, that`s a misconception. They are neutral state which can be a logic 0 or a logic 1. This will bring chaos on your circuit operation. As you can see, in each case there is a default input. For a pull-up, the default input to the logic IC is 1. And for the pull-down, the logic is 0. The resistor also provide a current limiting function thus affecting power consumption of the input section. 10kohms is the commonly value but any value can be use depending on your application. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713