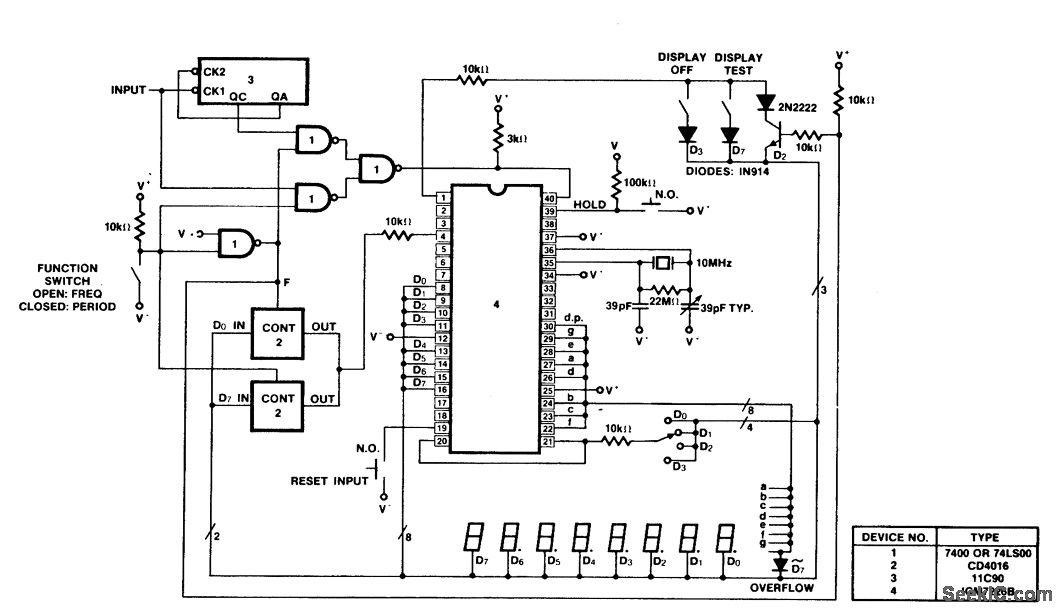
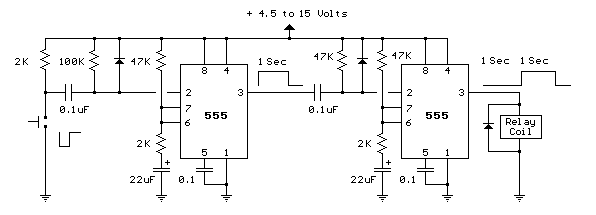
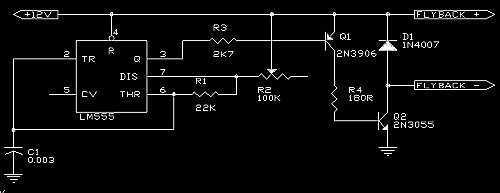
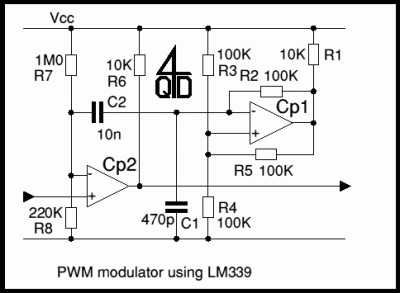
PULSE PERIOD TO VOLTAGE CONVERTER
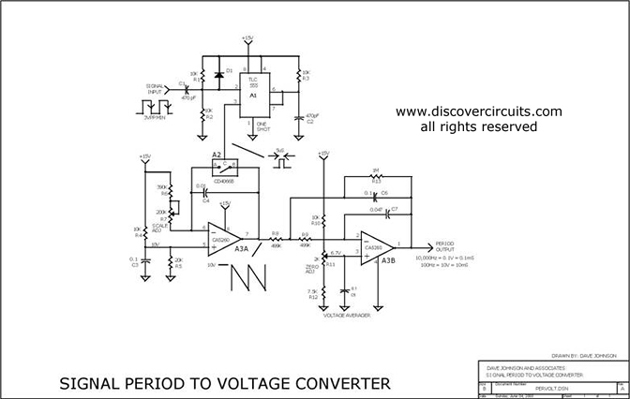
This circuit is designed to convert a square wave input signal into a voltage output. The voltage produced is proportional to the time interval between the edges (period) of the signal, rather than its frequency. The operational range of the circuit is from 100 microseconds to 10 milliseconds, resulting in an output voltage that varies from 100 millivolts to 10 volts. Additional scale factors can also be implemented. The circuit operates from a single 15V power supply and utilizes cost-effective components. It is particularly useful for applications where monitoring the signal's period is more critical than monitoring its frequency.
The circuit operates by using a timing mechanism that captures the duration of the square wave's high and low states. A monostable multivibrator can be employed to generate a pulse width that corresponds to the input signal's period. This pulse width is then fed into a voltage scaling circuit, which could be a resistor divider or an operational amplifier configured to amplify the voltage to the desired range.
The input square wave signal is connected to the trigger of the monostable multivibrator. When the signal transitions from low to high, the multivibrator generates a pulse whose width is determined by the time the input signal remains high. This pulse width is then converted into a proportional voltage using a resistive network or an op-amp circuit, which can be calibrated to output between 100mV and 10V based on the specified period range.
To ensure stability and accuracy, the circuit may include filtering components, such as capacitors, to smooth out any noise from the input signal. Proper selection of the multivibrator and voltage scaling components is crucial to achieve the desired performance characteristics. The use of a single 15V power supply simplifies the design and reduces the overall cost, making this circuit an efficient solution for applications requiring period measurement in various electronic systems.This is a test circuit converts a square wave input signal into a voltage. But, the voltage produced is proportional to the time between edges (period) of the signal, not the frequency. The range is from 100uS to to 10mS, which produces a voltage from 100mV to 10 volts. Other scale factors are also possible. The circuit is powered from single 15v supply and uses inexpensive parts. It is great when a signal`s period instead of its frequency needs to be monitored. Source: discovercircuits 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by using a timing mechanism that captures the duration of the square wave's high and low states. A monostable multivibrator can be employed to generate a pulse width that corresponds to the input signal's period. This pulse width is then fed into a voltage scaling circuit, which could be a resistor divider or an operational amplifier configured to amplify the voltage to the desired range.
The input square wave signal is connected to the trigger of the monostable multivibrator. When the signal transitions from low to high, the multivibrator generates a pulse whose width is determined by the time the input signal remains high. This pulse width is then converted into a proportional voltage using a resistive network or an op-amp circuit, which can be calibrated to output between 100mV and 10V based on the specified period range.
To ensure stability and accuracy, the circuit may include filtering components, such as capacitors, to smooth out any noise from the input signal. Proper selection of the multivibrator and voltage scaling components is crucial to achieve the desired performance characteristics. The use of a single 15V power supply simplifies the design and reduces the overall cost, making this circuit an efficient solution for applications requiring period measurement in various electronic systems.This is a test circuit converts a square wave input signal into a voltage. But, the voltage produced is proportional to the time between edges (period) of the signal, not the frequency. The range is from 100uS to to 10mS, which produces a voltage from 100mV to 10 volts. Other scale factors are also possible. The circuit is powered from single 15v supply and uses inexpensive parts. It is great when a signal`s period instead of its frequency needs to be monitored. Source: discovercircuits 🔗 External reference