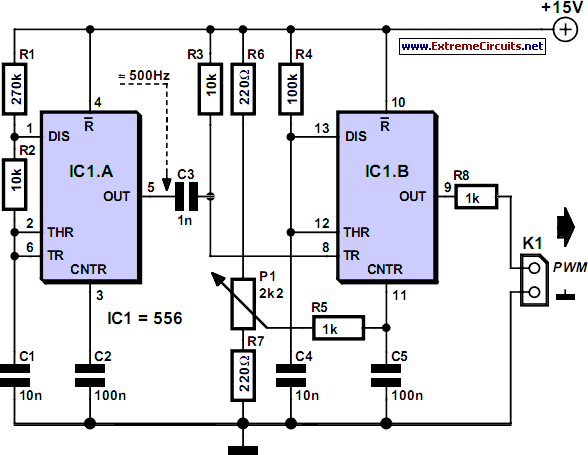
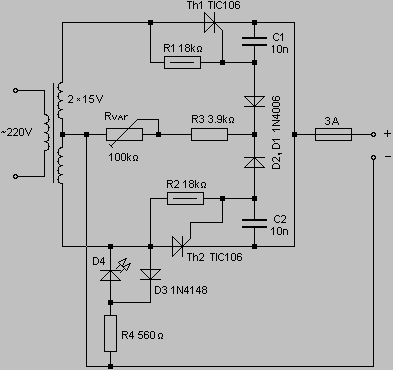
PWM tutoria
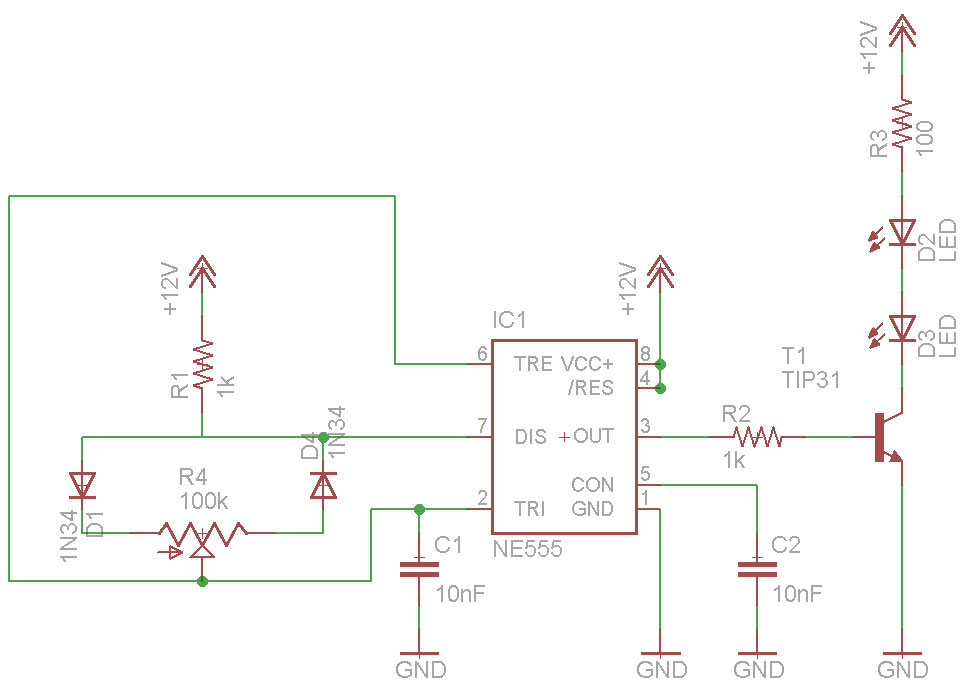
PWM circuits are versatile. They can be used to dim LEDs, regulate the speed of fans and motors, control the power supplied to thermoelectric coolers, or manage the power to nearly any device. It is essential to ensure that the maximum voltage rating of the device is not exceeded. The accompanying video provides further explanations.
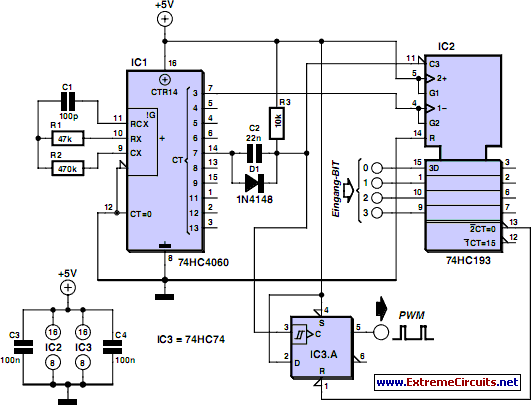
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) circuits are widely utilized in various applications due to their efficiency and simplicity in controlling power delivery. The fundamental principle behind PWM involves switching a digital signal on and off at a high frequency, thereby varying the duty cycle, which is the ratio of the on-time to the total time of the signal cycle. By adjusting the duty cycle, the average power delivered to a load can be controlled effectively.
In LED dimming applications, PWM allows for smooth brightness control without the color distortion that can occur with resistive dimming methods. For instance, a microcontroller can generate a PWM signal that modulates the brightness of an LED by turning it on and off rapidly. The perceived brightness will vary depending on the duty cycle; a higher duty cycle results in brighter illumination.
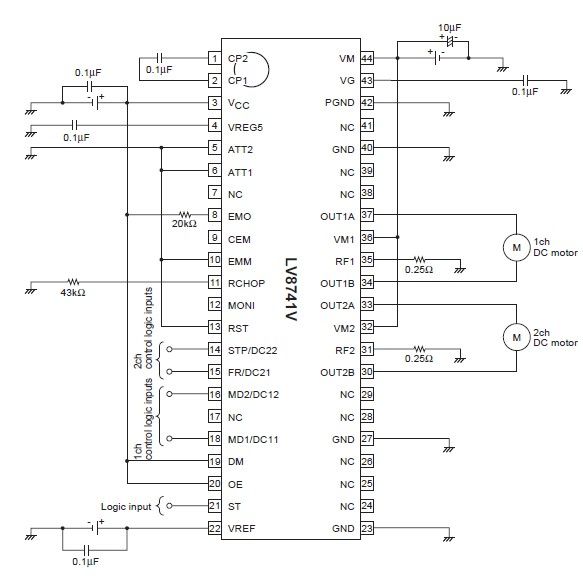
In motor control, PWM can be employed to adjust the speed of DC motors. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal sent to the motor driver, the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor can be controlled, thus regulating its speed. This method is particularly advantageous as it minimizes energy loss compared to using resistors or variable resistors.
For thermoelectric coolers (TECs), PWM control enables precise temperature regulation by modulating the power supplied to the device. This is crucial in applications requiring temperature stability, such as in cooling electronic components or maintaining specific temperatures in laboratory settings.
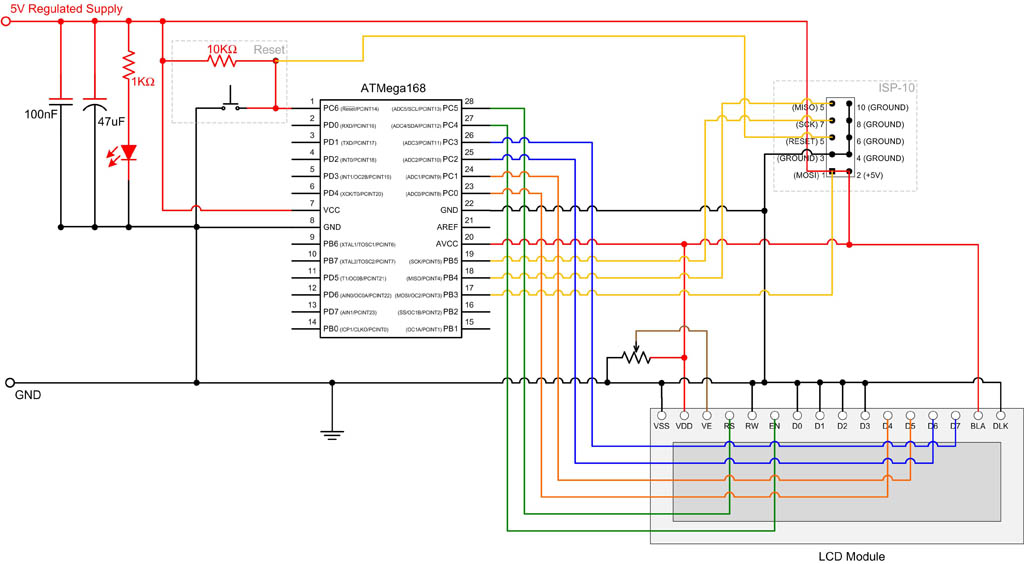
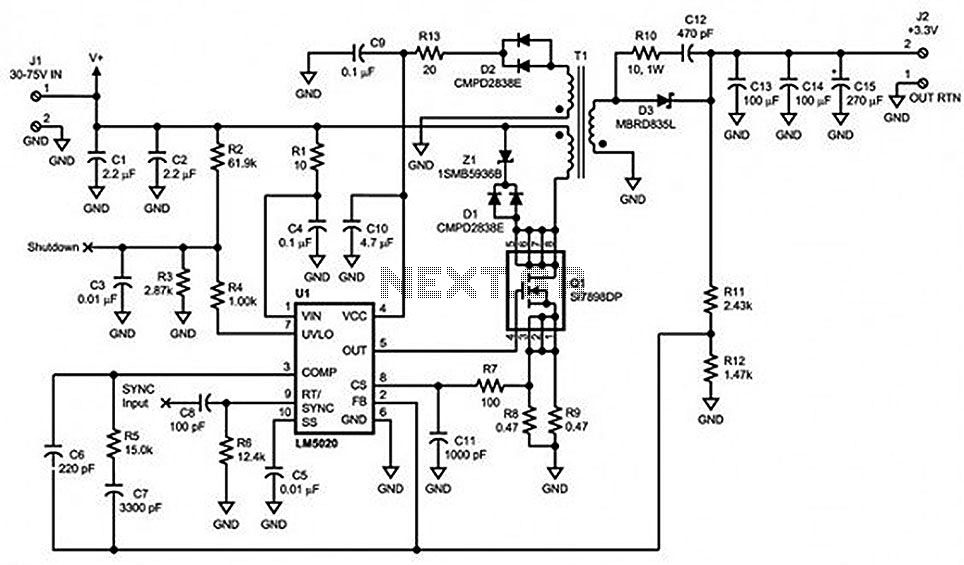
When designing PWM circuits, it is important to consider the maximum voltage and current ratings of the components involved to prevent damage. Additionally, filtering may be required to smooth out the PWM signal when driving certain loads, especially inductive loads like motors. This can be achieved using capacitors or inductors to create low-pass filters that reduce voltage ripple and provide a more stable output.
Overall, PWM circuits offer a robust solution for power management in various electronic applications, making them a fundamental topic in electronics engineering.PWM circuits are fun. You can use them to dim LEDs, control the speed of fans and motors, control the power going to a thermoelectric cooler, or control the power going to pretty much anything you want. Just make sure that you don`t exceed the maximum voltage rating of your device. The video explains it all. 🔗 External reference
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) circuits are widely utilized in various applications due to their efficiency and simplicity in controlling power delivery. The fundamental principle behind PWM involves switching a digital signal on and off at a high frequency, thereby varying the duty cycle, which is the ratio of the on-time to the total time of the signal cycle. By adjusting the duty cycle, the average power delivered to a load can be controlled effectively.
In LED dimming applications, PWM allows for smooth brightness control without the color distortion that can occur with resistive dimming methods. For instance, a microcontroller can generate a PWM signal that modulates the brightness of an LED by turning it on and off rapidly. The perceived brightness will vary depending on the duty cycle; a higher duty cycle results in brighter illumination.
In motor control, PWM can be employed to adjust the speed of DC motors. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal sent to the motor driver, the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor can be controlled, thus regulating its speed. This method is particularly advantageous as it minimizes energy loss compared to using resistors or variable resistors.
For thermoelectric coolers (TECs), PWM control enables precise temperature regulation by modulating the power supplied to the device. This is crucial in applications requiring temperature stability, such as in cooling electronic components or maintaining specific temperatures in laboratory settings.
When designing PWM circuits, it is important to consider the maximum voltage and current ratings of the components involved to prevent damage. Additionally, filtering may be required to smooth out the PWM signal when driving certain loads, especially inductive loads like motors. This can be achieved using capacitors or inductors to create low-pass filters that reduce voltage ripple and provide a more stable output.
Overall, PWM circuits offer a robust solution for power management in various electronic applications, making them a fundamental topic in electronics engineering.PWM circuits are fun. You can use them to dim LEDs, control the speed of fans and motors, control the power going to a thermoelectric cooler, or control the power going to pretty much anything you want. Just make sure that you don`t exceed the maximum voltage rating of your device. The video explains it all. 🔗 External reference