pwm using 555 timer ic
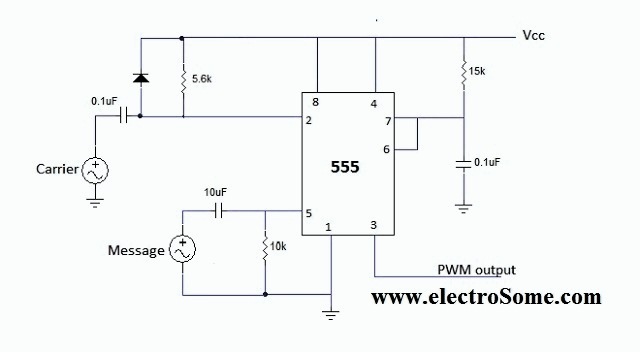
The 555 integrated circuit (IC) is configured in monostable mode of operation. In this mode, the output remains LOW (0V) when there is no trigger input. When a trigger is applied through pin 2, the output switches to HIGH (Vcc) for a predetermined duration. This duration is calculated using the formula T = 1.1 RC, where R = R2 and C = C2 as shown in the diagram. The trigger is introduced via a differentiator circuit to produce sharp pulses. The resistor in the differentiator is connected to Vcc to generate negative trigger pulses, while a diode is used to prevent positive spikes. The output is then modulated by the input voltage applied to the control pin of the IC. When the trigger pin pulses go low, the output of the IC transitions to high, which disables the internal discharge transistor connected to pin 7. Consequently, capacitor C2 charges through resistor R2. This charging continues until the voltage surpasses the input control voltage, at which point the IC switches states. The output then becomes low, activating the discharge transistor and discharging capacitor C2. Thus, the pulse width of the output is determined by the control voltage. This cycle repeats, resulting in a continuous stream of pulses that can be utilized for applications such as motor control, LED driving, and transmitting servo signals for remote control systems.
The 555 timer in monostable mode functions effectively for generating precise timing pulses. The circuit configuration typically includes a resistor (R2) and a capacitor (C2) connected to the discharge pin (pin 7) of the IC. When the trigger signal is applied, the capacitor charges through the resistor, leading to a voltage increase across C2. The time constant for this charging process is influenced by both the resistance and capacitance values, allowing for flexibility in pulse width adjustment.
The differentiator circuit, which is crucial for providing sharp trigger pulses, typically consists of a resistor and capacitor arranged to form a high-pass filter. This configuration ensures that only rapid changes in the input signal are detected as triggers, thus enhancing the responsiveness of the 555 timer. The diode in the circuit plays a vital role in protecting the timer from unintended voltage spikes that could disrupt normal operation.
The control pin (pin 5) allows for further modulation of the output pulse width by applying a varying voltage. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring dynamic pulse width adjustment, such as in motor speed control or PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for LED brightness control. The behavior of the output signal can be tailored by selecting appropriate values for R2 and C2, as well as by varying the control voltage.
In summary, the 555 timer in monostable mode is a versatile component that can be employed in various electronic applications. Its ability to generate stable timing pulses, alongside the modulation capability provided by the control pin, makes it suitable for tasks ranging from simple timing applications to more complex control systems in robotics and automation.The 555 IC is wiredin monostable mode of operation. Please read the article Monostable Multivibrator using 555 Timer for more details. In this mode the output is LOW (0V) when there is no triggering, when it istriggeredvia 2nd pin the output goes HIGH (Vcc) for some time. This time period is determinedby the expression T=1. 11 RC (R=R2 ; C=C2 in the diagram). Trigger is applied via a differentiator circuit to make sharp pulses. The resistor of differentiator is connected to Vcc to generate negative trigger pulses and the diode avoids positive spikes. And now this outputis modulated using the input voltage applied at the control pin of the IC. So whenever the trigger pin pulses become low, the output of the IC switches to high and as a result the discharge transistor (internal to the 555 IC attached to the 7th pin) is disabled.
So C2 charges through R2. This capacitor keeps on charging until the voltageis above the input control voltage, at which the IC changes its state. Now the output is low which makes the discharge transistor activated thereby discharging the capacitor C2.
Hence the output pulse width is determined by the control voltage. This process continues and we get a continuousstream of pulses which can be used for motor control, driving LED`s, transmittingservo signals for remote control applications etc. 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer in monostable mode functions effectively for generating precise timing pulses. The circuit configuration typically includes a resistor (R2) and a capacitor (C2) connected to the discharge pin (pin 7) of the IC. When the trigger signal is applied, the capacitor charges through the resistor, leading to a voltage increase across C2. The time constant for this charging process is influenced by both the resistance and capacitance values, allowing for flexibility in pulse width adjustment.
The differentiator circuit, which is crucial for providing sharp trigger pulses, typically consists of a resistor and capacitor arranged to form a high-pass filter. This configuration ensures that only rapid changes in the input signal are detected as triggers, thus enhancing the responsiveness of the 555 timer. The diode in the circuit plays a vital role in protecting the timer from unintended voltage spikes that could disrupt normal operation.
The control pin (pin 5) allows for further modulation of the output pulse width by applying a varying voltage. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring dynamic pulse width adjustment, such as in motor speed control or PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for LED brightness control. The behavior of the output signal can be tailored by selecting appropriate values for R2 and C2, as well as by varying the control voltage.
In summary, the 555 timer in monostable mode is a versatile component that can be employed in various electronic applications. Its ability to generate stable timing pulses, alongside the modulation capability provided by the control pin, makes it suitable for tasks ranging from simple timing applications to more complex control systems in robotics and automation.The 555 IC is wiredin monostable mode of operation. Please read the article Monostable Multivibrator using 555 Timer for more details. In this mode the output is LOW (0V) when there is no triggering, when it istriggeredvia 2nd pin the output goes HIGH (Vcc) for some time. This time period is determinedby the expression T=1. 11 RC (R=R2 ; C=C2 in the diagram). Trigger is applied via a differentiator circuit to make sharp pulses. The resistor of differentiator is connected to Vcc to generate negative trigger pulses and the diode avoids positive spikes. And now this outputis modulated using the input voltage applied at the control pin of the IC. So whenever the trigger pin pulses become low, the output of the IC switches to high and as a result the discharge transistor (internal to the 555 IC attached to the 7th pin) is disabled.
So C2 charges through R2. This capacitor keeps on charging until the voltageis above the input control voltage, at which the IC changes its state. Now the output is low which makes the discharge transistor activated thereby discharging the capacitor C2.
Hence the output pulse width is determined by the control voltage. This process continues and we get a continuousstream of pulses which can be used for motor control, driving LED`s, transmittingservo signals for remote control applications etc. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713