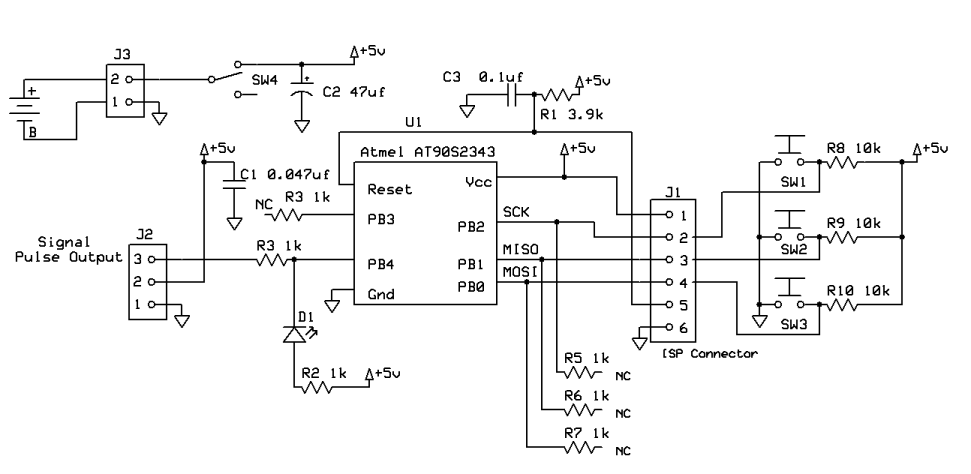
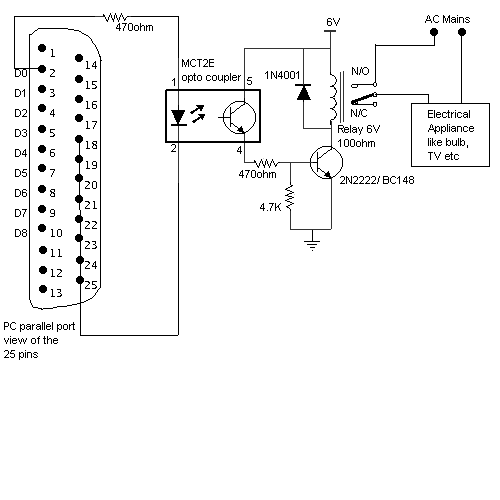
raspberry pi gpio pin electrical specifications
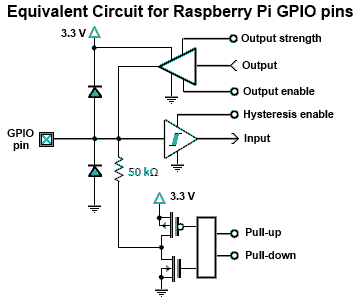
The Raspberry Pi offers general-purpose digital input/output pins, known as GPIO pins, which can be utilized for reading digital logic signals or outputting digital logic levels. Although the output current capability is limited, these pins can effectively drive devices such as LEDs.
The GPIO pins on a Raspberry Pi are versatile components essential for various electronic projects and applications. Each GPIO pin can be configured as either an input or an output, allowing for a wide range of functionalities. When configured as an input, the GPIO pins can read digital signals, which may come from sensors, switches, or other digital devices. This capability enables the Raspberry Pi to interact with the physical environment, making it suitable for automation, robotics, and IoT applications.
As output pins, the GPIO can be used to control devices such as LEDs, relays, and other small electronic components. The GPIO pins typically output a voltage of 3.3V, which is sufficient for driving low-power devices. However, due to the limited current output—usually around 16-20 mA per pin—it is crucial to ensure that the connected devices do not exceed this current limit to avoid damaging the Raspberry Pi.
For projects requiring higher current levels, it is advisable to use transistors or relays as intermediaries. This approach allows the GPIO pin to control the transistor or relay, which can then switch larger loads without putting undue stress on the Raspberry Pi's GPIO pins. Additionally, proper circuit design should include current-limiting resistors when driving LEDs to prevent excessive current flow.
In summary, the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi are a powerful feature that enables users to interface with a variety of electronic components, facilitating the development of innovative projects and solutions in the field of electronics and computing.The Raspberry Pi provides general purpose digital input/output pins (called GPIO pins) that you can use for reading digital logic signals or for outputting digital logic levels. The outputs do not have much current capability, but you can drive LEDs or..
The GPIO pins on a Raspberry Pi are versatile components essential for various electronic projects and applications. Each GPIO pin can be configured as either an input or an output, allowing for a wide range of functionalities. When configured as an input, the GPIO pins can read digital signals, which may come from sensors, switches, or other digital devices. This capability enables the Raspberry Pi to interact with the physical environment, making it suitable for automation, robotics, and IoT applications.
As output pins, the GPIO can be used to control devices such as LEDs, relays, and other small electronic components. The GPIO pins typically output a voltage of 3.3V, which is sufficient for driving low-power devices. However, due to the limited current output—usually around 16-20 mA per pin—it is crucial to ensure that the connected devices do not exceed this current limit to avoid damaging the Raspberry Pi.
For projects requiring higher current levels, it is advisable to use transistors or relays as intermediaries. This approach allows the GPIO pin to control the transistor or relay, which can then switch larger loads without putting undue stress on the Raspberry Pi's GPIO pins. Additionally, proper circuit design should include current-limiting resistors when driving LEDs to prevent excessive current flow.
In summary, the GPIO pins on the Raspberry Pi are a powerful feature that enables users to interface with a variety of electronic components, facilitating the development of innovative projects and solutions in the field of electronics and computing.The Raspberry Pi provides general purpose digital input/output pins (called GPIO pins) that you can use for reading digital logic signals or for outputting digital logic levels. The outputs do not have much current capability, but you can drive LEDs or..