robot guts
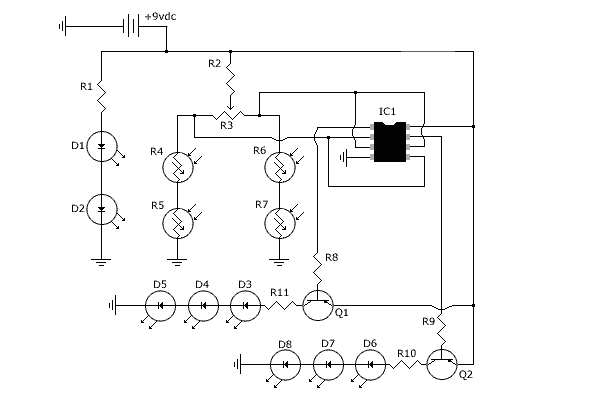
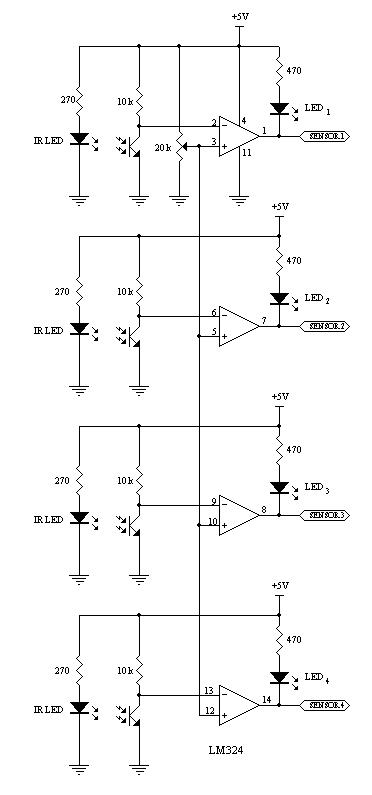
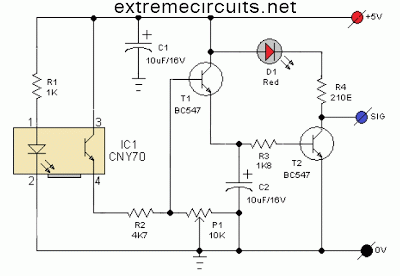
The headlights and photo cells are oriented downward, leading to the visualization of the entire circuit as being inverted. The configuration utilizes three LEDs on each side. This choice is likely due to the inability to power three LEDs in series from a single 9V battery without additional components. This design allows for the incorporation of transistors within the circuit. The robot's operational logic is straightforward, relying on a single NTE943M low power, low offset, dual voltage comparator integrated circuit (IC). This IC determines which pair of photo resistors is generating a higher voltage, indicating increased resistance due to reduced light exposure, and subsequently illuminates the corresponding set of LEDs that aligns with the photo resistors receiving more light.
The circuit described employs a straightforward yet effective design utilizing a pair of photo resistors (LDRs) and a dual voltage comparator IC. The orientation of the headlights and photo cells facing the ground suggests that the system is intended for ground detection or navigation based on light levels.
The use of three LEDs per side is strategic; it ensures that adequate brightness is achieved while managing the limitations of the 9V power supply. When connected in series, the forward voltage drop of each LED must be considered; therefore, the inclusion of transistors allows for the control of the LEDs without exceeding the supply voltage. The transistors act as switches, enabling or disabling the LEDs based on the comparator's output.
The NTE943M comparator plays a crucial role in the circuit's functionality. It compares the voltage levels from the two sets of photo resistors. When one set of LDRs detects more light, it generates a lower resistance, resulting in a higher voltage output. The comparator processes these signals and determines which set of LEDs should be activated. This feedback mechanism allows the robot to respond dynamically to changes in light conditions, effectively guiding its behavior based on environmental inputs.
In summary, this circuit exemplifies a robust design for light-sensitive applications, utilizing basic electronic components to achieve a functional and responsive system. The integration of the comparator and transistors ensures efficient operation while maintaining simplicity in the overall architecture.The headlights and photo cells will face the ground, so I find it easiest to imagine that the whole circuit is upside down Why 3 LEDs per side As far as I can tell, because you can`t power three in series from a single 9V battery without a little help, and this way Cook could include transistors in the circuit. The robot`s thinking is simple. The lone IC is an NTE943M low power, low offset, dual voltage comparator. It identifies which set of photo resistors is running at a higher voltage (a function of increased resistance, meaning which set is receiving less light), and lights the set of LEDs corresponding with the other set ” the set receiving more light. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described employs a straightforward yet effective design utilizing a pair of photo resistors (LDRs) and a dual voltage comparator IC. The orientation of the headlights and photo cells facing the ground suggests that the system is intended for ground detection or navigation based on light levels.
The use of three LEDs per side is strategic; it ensures that adequate brightness is achieved while managing the limitations of the 9V power supply. When connected in series, the forward voltage drop of each LED must be considered; therefore, the inclusion of transistors allows for the control of the LEDs without exceeding the supply voltage. The transistors act as switches, enabling or disabling the LEDs based on the comparator's output.
The NTE943M comparator plays a crucial role in the circuit's functionality. It compares the voltage levels from the two sets of photo resistors. When one set of LDRs detects more light, it generates a lower resistance, resulting in a higher voltage output. The comparator processes these signals and determines which set of LEDs should be activated. This feedback mechanism allows the robot to respond dynamically to changes in light conditions, effectively guiding its behavior based on environmental inputs.
In summary, this circuit exemplifies a robust design for light-sensitive applications, utilizing basic electronic components to achieve a functional and responsive system. The integration of the comparator and transistors ensures efficient operation while maintaining simplicity in the overall architecture.The headlights and photo cells will face the ground, so I find it easiest to imagine that the whole circuit is upside down Why 3 LEDs per side As far as I can tell, because you can`t power three in series from a single 9V battery without a little help, and this way Cook could include transistors in the circuit. The robot`s thinking is simple. The lone IC is an NTE943M low power, low offset, dual voltage comparator. It identifies which set of photo resistors is running at a higher voltage (a function of increased resistance, meaning which set is receiving less light), and lights the set of LEDs corresponding with the other set ” the set receiving more light. 🔗 External reference