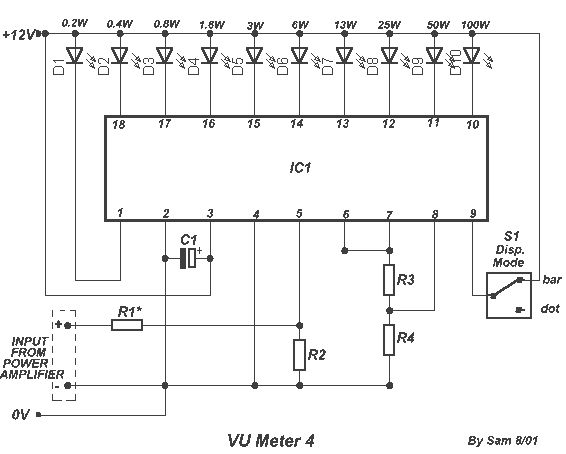
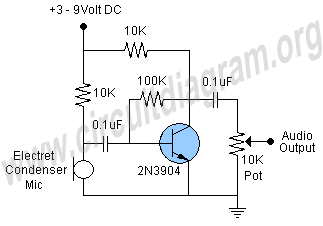
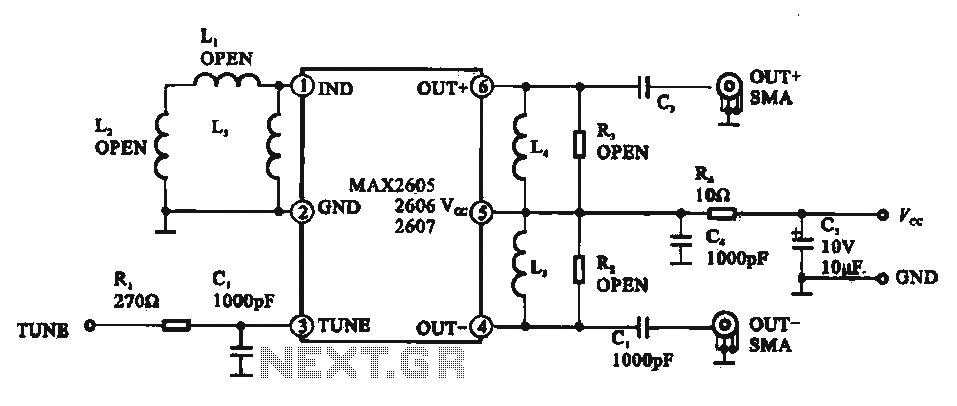
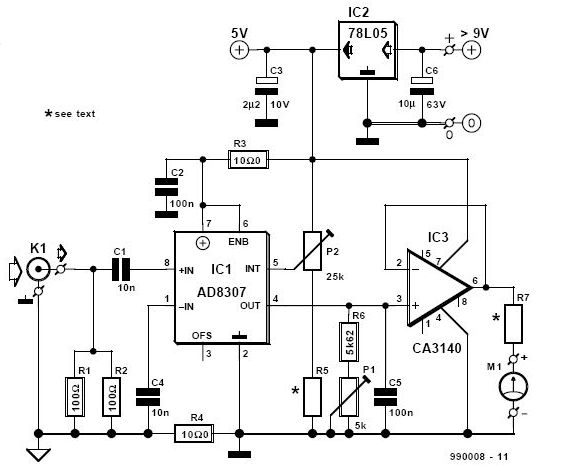
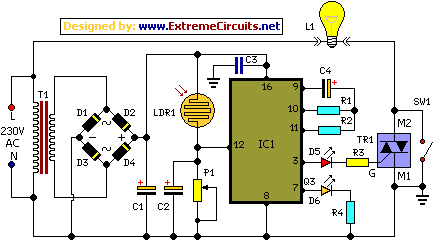
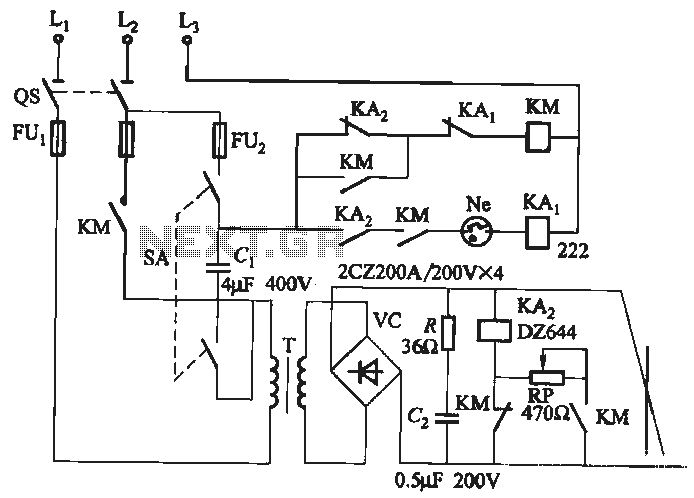
Run/Stop Relay Circuit
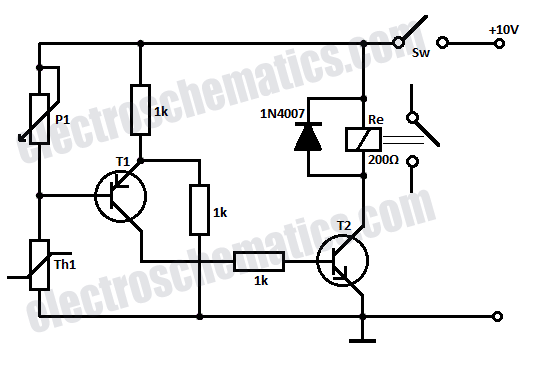
Safety is a significant concern in many motor-driven applications. This is particularly true in industrial settings where motion begins immediately upon the application of power.
In motor-driven applications, safety mechanisms are essential to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of operators and equipment. Various strategies can be employed to enhance safety in these systems.
One common approach is the implementation of emergency stop (E-stop) circuits, which allow operators to quickly halt motor operation in case of an emergency. These circuits typically involve a normally closed push-button switch that, when pressed, interrupts the power supply to the motor, effectively stopping its operation.
Another important safety feature is the use of overload protection devices, such as thermal relays or fuses. These components monitor the current flowing to the motor and can disconnect the power if the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, preventing damage to the motor and reducing the risk of fire.
Additionally, safety interlocks can be integrated into the motor control circuitry. These interlocks ensure that the motor cannot start unless certain conditions are met, such as the closure of safety guards or the presence of an operator at a safe distance.
Furthermore, the use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) can enhance safety by providing soft start and stop capabilities, reducing mechanical stress on the motor and connected equipment. VFDs can also include built-in safety features that monitor motor performance and provide feedback to the control system.
In summary, implementing effective safety measures in motor-driven applications is crucial for minimizing risks and enhancing operational reliability. The integration of E-stop circuits, overload protection, safety interlocks, and advanced motor control technologies contributes to a safer working environment in industrial settings.Safety is a major concern in a good many motor-driven applications. This is true in industrial applications where motion starts when power is applied and e.. 🔗 External reference
In motor-driven applications, safety mechanisms are essential to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of operators and equipment. Various strategies can be employed to enhance safety in these systems.
One common approach is the implementation of emergency stop (E-stop) circuits, which allow operators to quickly halt motor operation in case of an emergency. These circuits typically involve a normally closed push-button switch that, when pressed, interrupts the power supply to the motor, effectively stopping its operation.
Another important safety feature is the use of overload protection devices, such as thermal relays or fuses. These components monitor the current flowing to the motor and can disconnect the power if the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, preventing damage to the motor and reducing the risk of fire.
Additionally, safety interlocks can be integrated into the motor control circuitry. These interlocks ensure that the motor cannot start unless certain conditions are met, such as the closure of safety guards or the presence of an operator at a safe distance.
Furthermore, the use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) can enhance safety by providing soft start and stop capabilities, reducing mechanical stress on the motor and connected equipment. VFDs can also include built-in safety features that monitor motor performance and provide feedback to the control system.
In summary, implementing effective safety measures in motor-driven applications is crucial for minimizing risks and enhancing operational reliability. The integration of E-stop circuits, overload protection, safety interlocks, and advanced motor control technologies contributes to a safer working environment in industrial settings.Safety is a major concern in a good many motor-driven applications. This is true in industrial applications where motion starts when power is applied and e.. 🔗 External reference