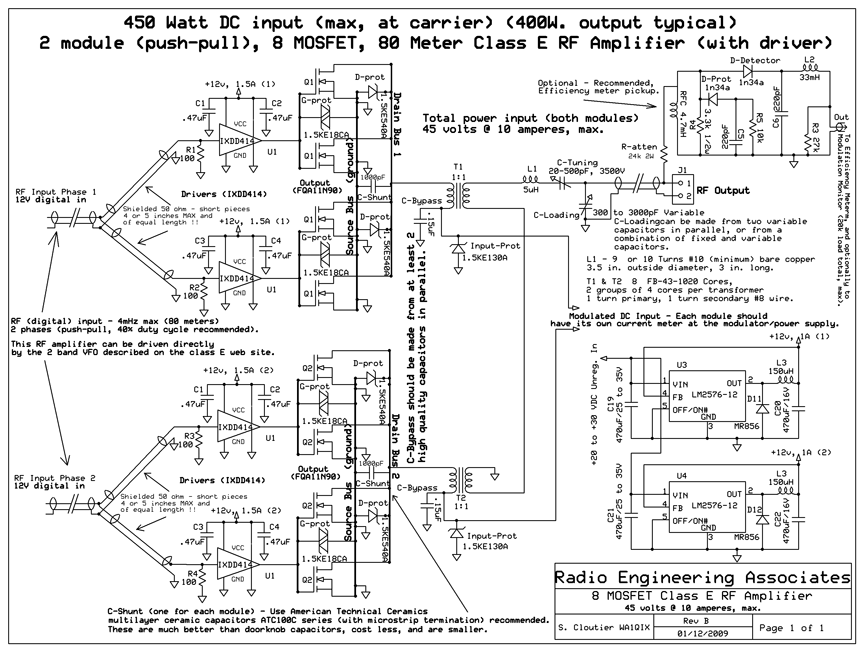
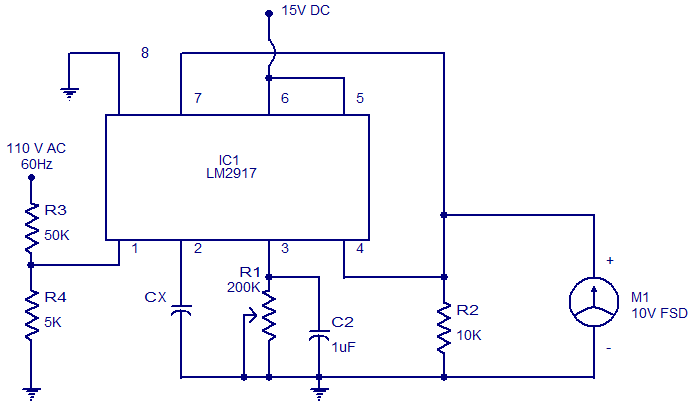
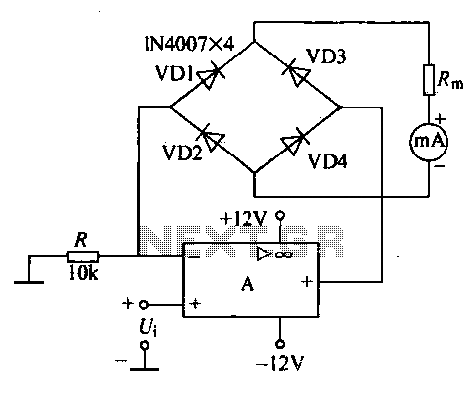
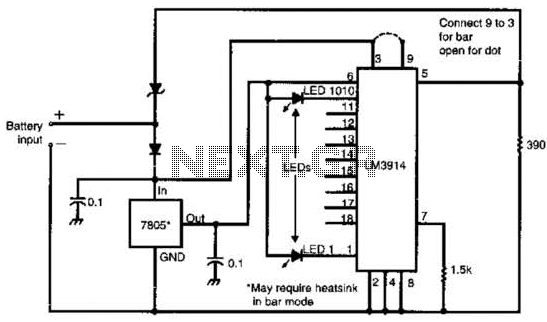
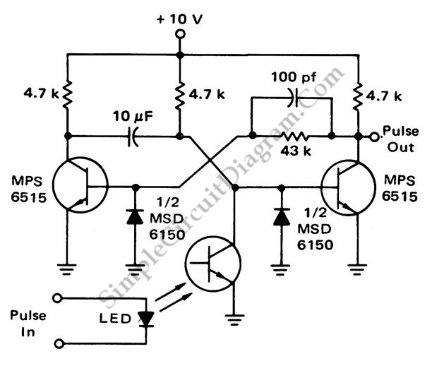
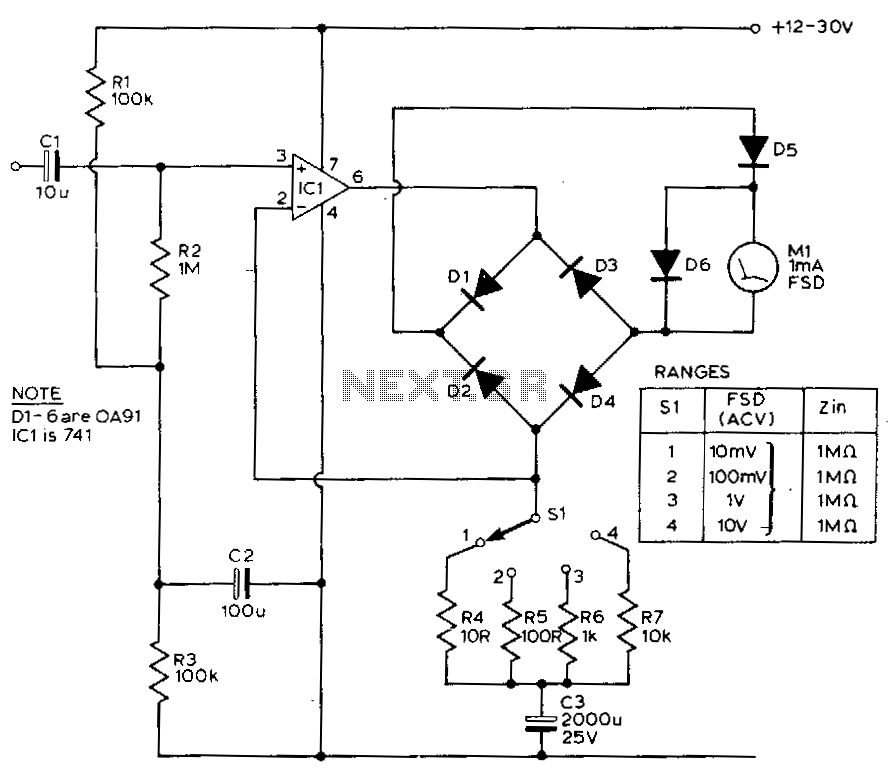
Schmitt Trigger VU Meter
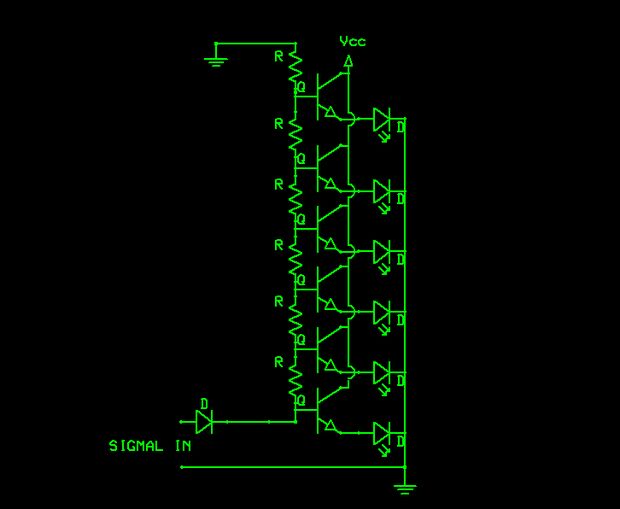
The schematic indicates that the input is routed through a voltage divider. This configuration is essential for the operation of the Schmitt triggers, which all activate under certain conditions.
The voltage divider in the schematic serves to scale down the input voltage to a level suitable for the Schmitt trigger's threshold requirements. A voltage divider typically consists of two resistors, R1 and R2, connected in series across the input voltage source. The output voltage, which is fed into the Schmitt trigger, is taken from the junction of these two resistors. The values of R1 and R2 can be selected based on the desired output voltage using the formula:
V_out = V_in * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
where V_out is the voltage at the junction of the resistors, and V_in is the input voltage. This setup allows for precise control over the input signal levels, ensuring that the Schmitt trigger operates correctly.
The Schmitt trigger itself is a type of comparator that provides hysteresis, allowing for clean transitions between high and low states in digital circuits. This is particularly useful in noisy environments where the input signal may fluctuate around the threshold levels. The output of the Schmitt trigger will change state when the input voltage crosses a defined upper or lower threshold, providing a stable output signal.
In summary, the careful design of the voltage divider and Schmitt trigger configuration is crucial for ensuring reliable operation in electronic circuits, particularly in applications requiring noise immunity and precise signal processing.If you look carefully at the schematic you will notice the input is feed into the voltage divider. This is because the Schmitt Triggers all turn on a.. 🔗 External reference
The voltage divider in the schematic serves to scale down the input voltage to a level suitable for the Schmitt trigger's threshold requirements. A voltage divider typically consists of two resistors, R1 and R2, connected in series across the input voltage source. The output voltage, which is fed into the Schmitt trigger, is taken from the junction of these two resistors. The values of R1 and R2 can be selected based on the desired output voltage using the formula:
V_out = V_in * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
where V_out is the voltage at the junction of the resistors, and V_in is the input voltage. This setup allows for precise control over the input signal levels, ensuring that the Schmitt trigger operates correctly.
The Schmitt trigger itself is a type of comparator that provides hysteresis, allowing for clean transitions between high and low states in digital circuits. This is particularly useful in noisy environments where the input signal may fluctuate around the threshold levels. The output of the Schmitt trigger will change state when the input voltage crosses a defined upper or lower threshold, providing a stable output signal.
In summary, the careful design of the voltage divider and Schmitt trigger configuration is crucial for ensuring reliable operation in electronic circuits, particularly in applications requiring noise immunity and precise signal processing.If you look carefully at the schematic you will notice the input is feed into the voltage divider. This is because the Schmitt Triggers all turn on a.. 🔗 External reference