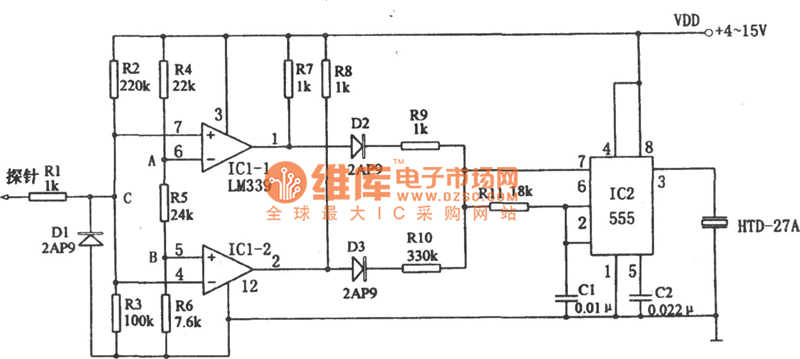
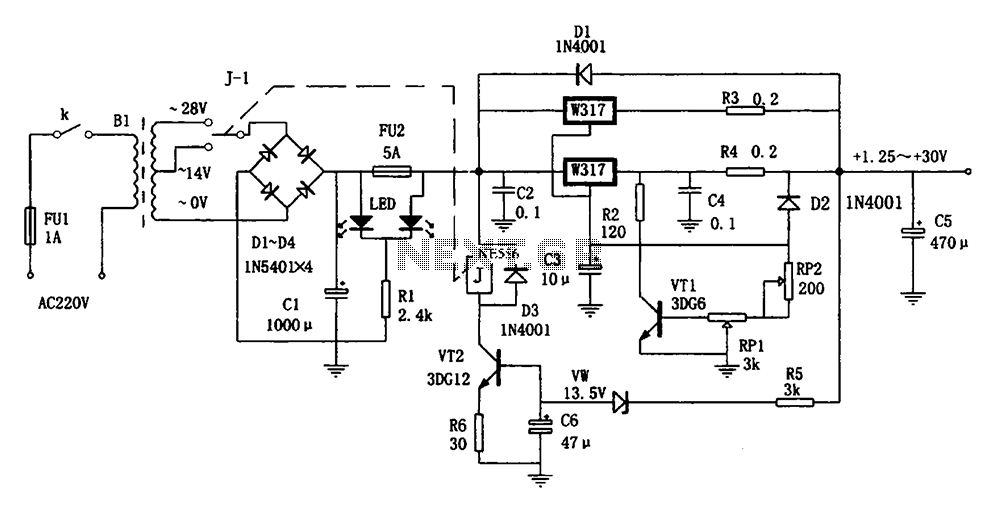
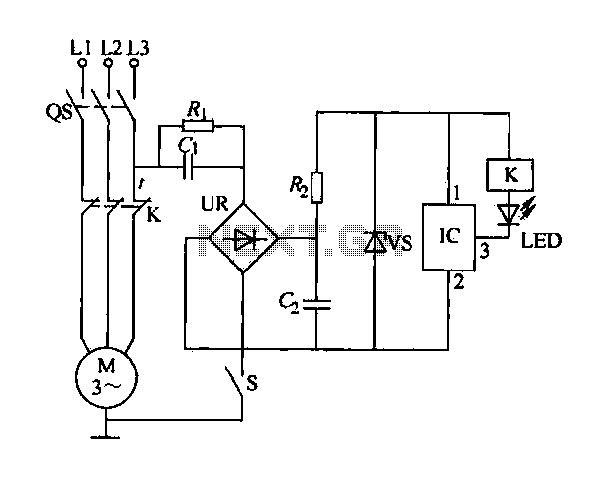
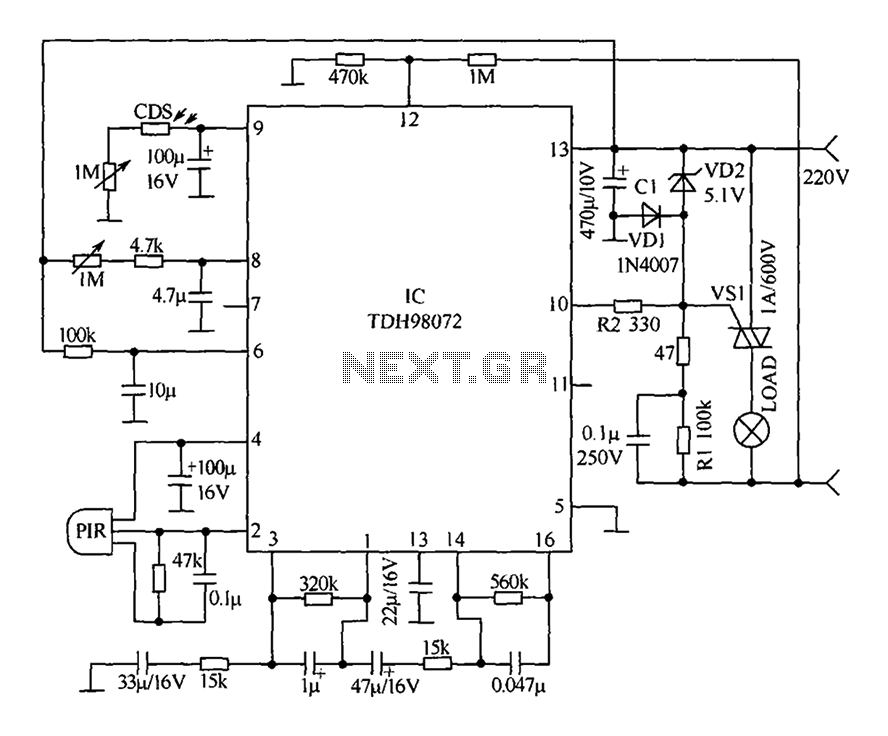
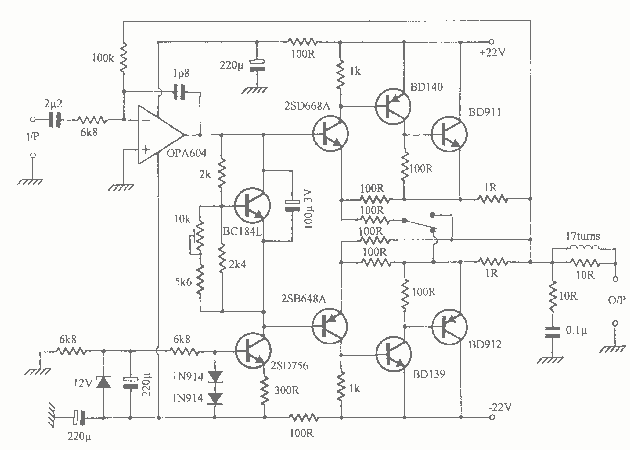
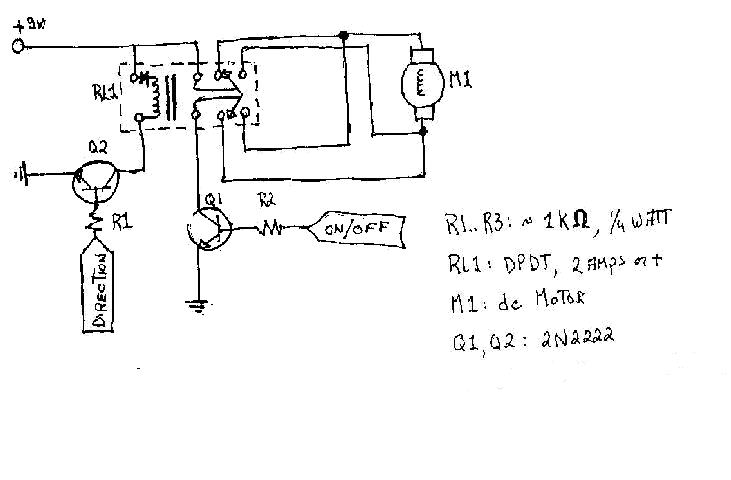
SCR AC arc welding machine load path from one power outage circuit
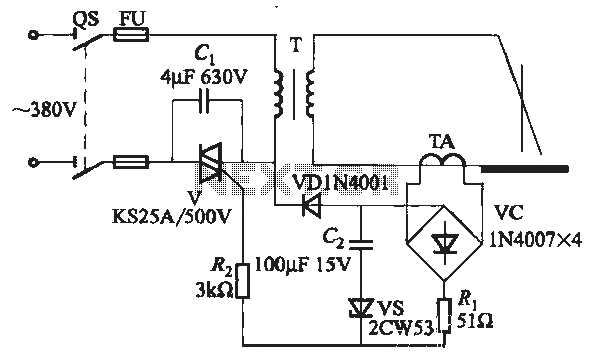
The Triac V trigger voltage is less than 1V, and the trigger current is less than 30mA.
The Triac is a semiconductor device commonly used for controlling AC power. It operates by allowing current to flow in both directions when triggered, making it ideal for applications such as light dimmers, motor speed controls, and heating elements. The specified trigger voltage of less than 1V indicates that the Triac can be activated with a low voltage signal, which minimizes the power requirements for the triggering circuit.
Additionally, the trigger current of less than 30mA suggests that the device can be controlled with relatively low current, allowing for the use of smaller, more efficient control circuitry. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications where power efficiency is critical. The low trigger requirements also enable the integration of the Triac into various microcontroller-based systems, where the output pins typically provide limited current.
When designing a circuit involving this Triac, it is essential to ensure that the trigger circuit can consistently deliver the necessary voltage and current within these limits. This can be achieved using a simple resistor-capacitor (RC) network or a dedicated opto-isolator designed for Triac triggering. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered to prevent overheating during operation, especially in high-power applications.
Overall, the low trigger voltage and current specifications of the Triac facilitate versatile and efficient design options in various electronic control systems.Drawing, Triac V trigger voltage is less than 1V, trigger current less than 30mA.
The Triac is a semiconductor device commonly used for controlling AC power. It operates by allowing current to flow in both directions when triggered, making it ideal for applications such as light dimmers, motor speed controls, and heating elements. The specified trigger voltage of less than 1V indicates that the Triac can be activated with a low voltage signal, which minimizes the power requirements for the triggering circuit.
Additionally, the trigger current of less than 30mA suggests that the device can be controlled with relatively low current, allowing for the use of smaller, more efficient control circuitry. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications where power efficiency is critical. The low trigger requirements also enable the integration of the Triac into various microcontroller-based systems, where the output pins typically provide limited current.
When designing a circuit involving this Triac, it is essential to ensure that the trigger circuit can consistently deliver the necessary voltage and current within these limits. This can be achieved using a simple resistor-capacitor (RC) network or a dedicated opto-isolator designed for Triac triggering. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered to prevent overheating during operation, especially in high-power applications.
Overall, the low trigger voltage and current specifications of the Triac facilitate versatile and efficient design options in various electronic control systems.Drawing, Triac V trigger voltage is less than 1V, trigger current less than 30mA.