Signal Conditioning Amplifier for Piezofilm Sensor
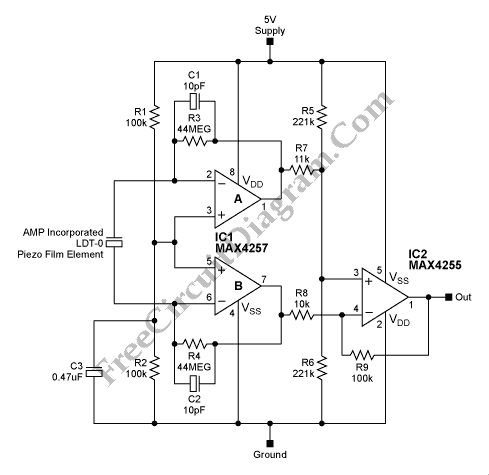
The signal can be converted by piezoelectric films in various ways, including thermal to electrical (temperature sensor) and mechanical to electrical (microphone).
Piezoelectric films are materials that generate an electrical charge in response to applied mechanical stress or temperature changes. These films are commonly used in various applications due to their ability to convert different types of energy into electrical signals.
In the context of temperature sensing, piezoelectric films can be utilized as thermal sensors. When the temperature changes, the film expands or contracts, causing mechanical stress that induces an electrical charge. This charge can be measured and calibrated to provide accurate temperature readings, making piezoelectric films suitable for applications in HVAC systems, automotive temperature monitoring, and industrial processes.
Similarly, piezoelectric films can function as microphones by converting sound waves (mechanical energy) into electrical signals. When sound waves hit the film, they create vibrations that induce a voltage across the material. This property is exploited in various audio devices, including microphones and sensors used in voice recognition systems, where the accurate conversion of sound to electrical signals is crucial for performance.
Overall, piezoelectric films serve as versatile components in electronic circuits, enabling the transformation of thermal and mechanical energy into usable electrical signals for various applications across multiple industries.The signal can be converted by piezoelectric films in many ways such as thermal to electrical (temperature sensor), mechanical to electrical (microphone), and. 🔗 External reference
Piezoelectric films are materials that generate an electrical charge in response to applied mechanical stress or temperature changes. These films are commonly used in various applications due to their ability to convert different types of energy into electrical signals.
In the context of temperature sensing, piezoelectric films can be utilized as thermal sensors. When the temperature changes, the film expands or contracts, causing mechanical stress that induces an electrical charge. This charge can be measured and calibrated to provide accurate temperature readings, making piezoelectric films suitable for applications in HVAC systems, automotive temperature monitoring, and industrial processes.
Similarly, piezoelectric films can function as microphones by converting sound waves (mechanical energy) into electrical signals. When sound waves hit the film, they create vibrations that induce a voltage across the material. This property is exploited in various audio devices, including microphones and sensors used in voice recognition systems, where the accurate conversion of sound to electrical signals is crucial for performance.
Overall, piezoelectric films serve as versatile components in electronic circuits, enabling the transformation of thermal and mechanical energy into usable electrical signals for various applications across multiple industries.The signal can be converted by piezoelectric films in many ways such as thermal to electrical (temperature sensor), mechanical to electrical (microphone), and. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713