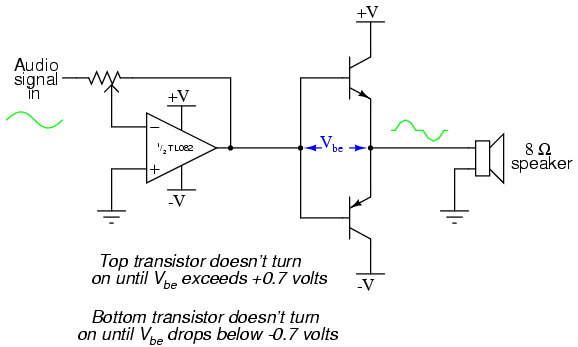
simple audio amplifier
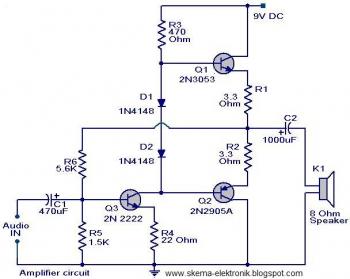
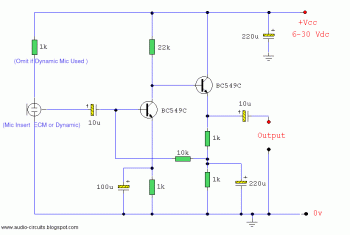
The initial section of the circuit is a preamplifier that utilizes transistor Q1 (2N2222). The collector of transistor Q3 is connected to the base of transistor Q2 (2N2905A), which creates a complementary symmetry pair with Q3 (2N3053). The amplified signal can be accessed at the junction of the emitters of the two transistors.
The described circuit begins with a preamplifier stage that employs the 2N2222 transistor (Q1). This transistor serves as the input stage, amplifying weak signals before they are processed further. The configuration of Q1 allows for significant gain, which is crucial for improving the signal strength.
Transistor Q3 (2N3053) plays a critical role in this circuit as it is connected to the base of Q2 (2N2905A). This arrangement forms a complementary symmetry output stage, which is essential for driving the load effectively. The complementary pair configuration enhances the efficiency of the circuit by allowing for push-pull operation, where one transistor conducts during one half of the signal cycle while the other conducts during the opposite half. This results in improved linearity and reduced distortion in the output signal.
The output of the preamplifier can be obtained from the junction of the emitters of Q2 and Q3. This point serves as the amplified output, providing a stronger signal that can be fed into subsequent stages of the circuit, such as additional amplification or processing stages. The careful selection of transistors and their arrangement ensures optimal performance of the preamplifier, making it suitable for a variety of applications in audio and signal processing systems.The first part of the circuit here is a preamplifier consisting of transistor Q1(2N2222). The collector of the Q3 is coupled to the base of Q2 (2N2905A), which forms a complementary symmetry pair with Q3 (2N3053). The amplified signal is available at the junction of emitter of two transistors. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit begins with a preamplifier stage that employs the 2N2222 transistor (Q1). This transistor serves as the input stage, amplifying weak signals before they are processed further. The configuration of Q1 allows for significant gain, which is crucial for improving the signal strength.
Transistor Q3 (2N3053) plays a critical role in this circuit as it is connected to the base of Q2 (2N2905A). This arrangement forms a complementary symmetry output stage, which is essential for driving the load effectively. The complementary pair configuration enhances the efficiency of the circuit by allowing for push-pull operation, where one transistor conducts during one half of the signal cycle while the other conducts during the opposite half. This results in improved linearity and reduced distortion in the output signal.
The output of the preamplifier can be obtained from the junction of the emitters of Q2 and Q3. This point serves as the amplified output, providing a stronger signal that can be fed into subsequent stages of the circuit, such as additional amplification or processing stages. The careful selection of transistors and their arrangement ensures optimal performance of the preamplifier, making it suitable for a variety of applications in audio and signal processing systems.The first part of the circuit here is a preamplifier consisting of transistor Q1(2N2222). The collector of the Q3 is coupled to the base of Q2 (2N2905A), which forms a complementary symmetry pair with Q3 (2N3053). The amplified signal is available at the junction of emitter of two transistors. 🔗 External reference