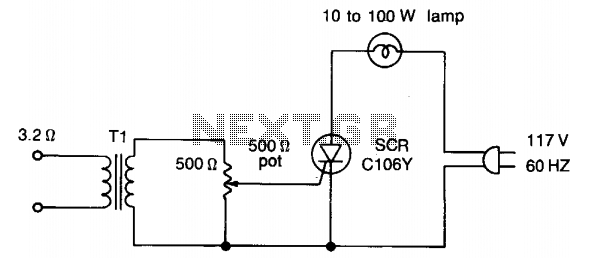
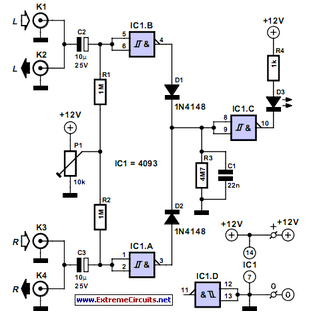
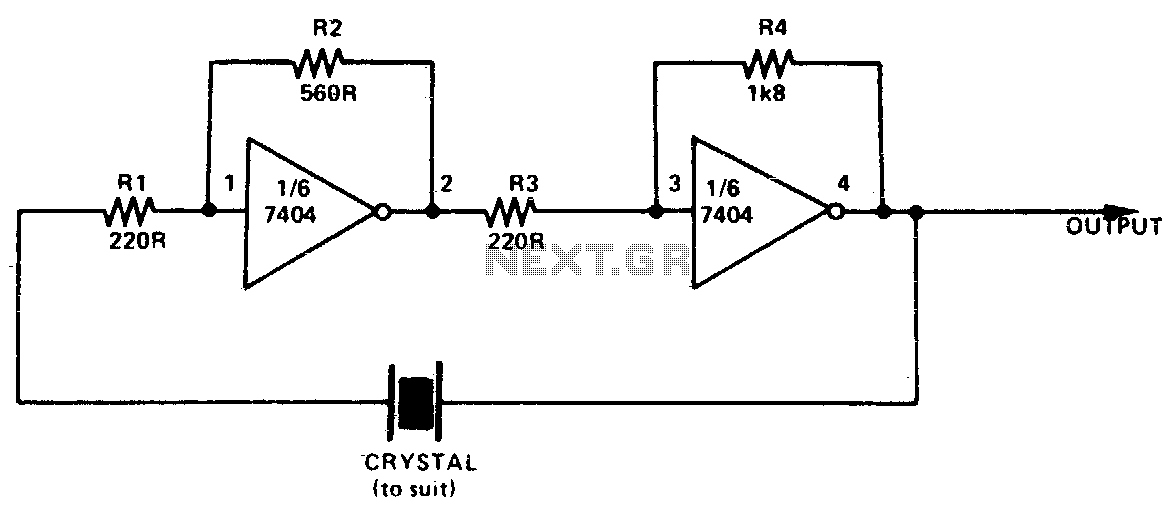
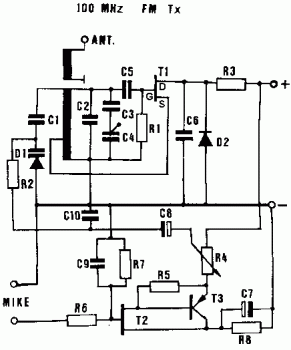
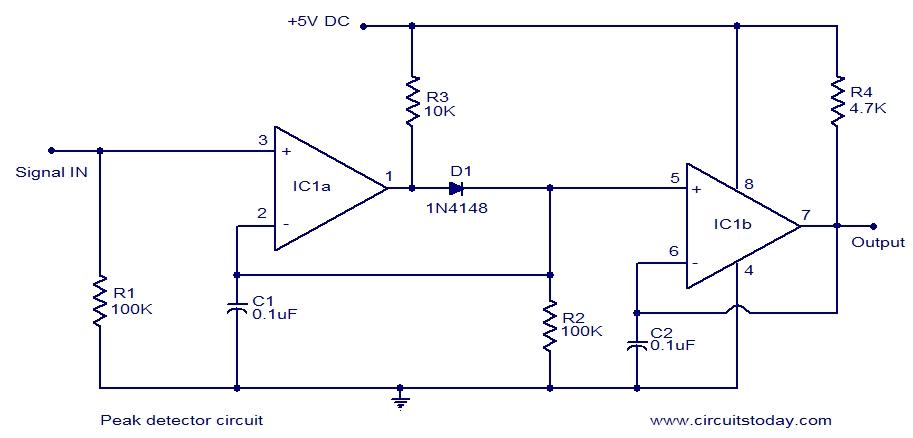
Simple Fuse Monitor Indicators
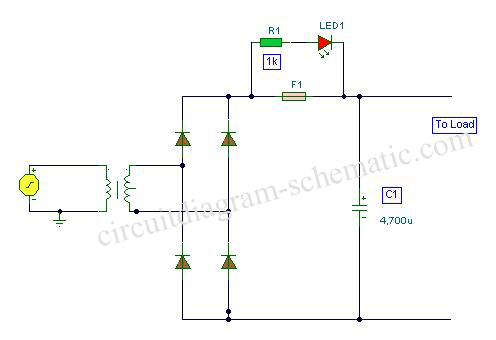
This is a circuit diagram for a fuse monitor circuit indicator. This very simple circuit utilizes only two components: a single resistor and an LED. This circuit provides a visual indication when the fuse has blown. LED1 typically remains off, indicating a short circuit across the fuse, F1. It is important to note that the LED will only illuminate in a damaged condition, such as when there is a short circuit or shunt across the load. In this scenario, the current is reduced to a safe level by R1.
The fuse monitor circuit is designed to provide a straightforward method for detecting fuse failures within an electrical system. The circuit operates using minimal components, which enhances reliability and reduces the likelihood of component failure. The primary components involved in this circuit are an LED (LED1) and a current-limiting resistor (R1).
When the fuse (F1) is intact, the circuit remains in a normal operating state, and the LED remains off, indicating that the electrical path is complete and functioning correctly. However, if the fuse blows due to an overload or short circuit, the circuit configuration changes. The blown fuse creates a short circuit condition, allowing current to flow through the LED. As a result, LED1 illuminates, providing a clear visual indication that the fuse has failed and requires replacement.
The resistor (R1) plays a crucial role in this circuit by limiting the current flowing through the LED when it is illuminated. This current-limiting feature is essential to prevent damage to the LED due to excessive current. The value of R1 must be chosen carefully to ensure that it allows sufficient current to illuminate the LED while remaining within the safe operating limits of both the LED and the power supply.
This circuit can be implemented in various applications where fuse monitoring is critical, such as in power distribution panels, automotive systems, and consumer electronics. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it an ideal solution for providing immediate feedback on the status of fuses, enhancing safety and maintenance efficiency.This is a circuit diagram fuse monitor circuit indicators. This very simple circuit uses only two components, but only with a single resistor and LED this circuit provides visual indication when the fuse has blown. LED1 is usually dead, a short circuit by the fuse, F1. Please note that the LED will only illumininatet in damaged condition, ie with a short circuit or shunt the load.
In this case the current is reduced to a safe level by R1 🔗 External reference
The fuse monitor circuit is designed to provide a straightforward method for detecting fuse failures within an electrical system. The circuit operates using minimal components, which enhances reliability and reduces the likelihood of component failure. The primary components involved in this circuit are an LED (LED1) and a current-limiting resistor (R1).
When the fuse (F1) is intact, the circuit remains in a normal operating state, and the LED remains off, indicating that the electrical path is complete and functioning correctly. However, if the fuse blows due to an overload or short circuit, the circuit configuration changes. The blown fuse creates a short circuit condition, allowing current to flow through the LED. As a result, LED1 illuminates, providing a clear visual indication that the fuse has failed and requires replacement.
The resistor (R1) plays a crucial role in this circuit by limiting the current flowing through the LED when it is illuminated. This current-limiting feature is essential to prevent damage to the LED due to excessive current. The value of R1 must be chosen carefully to ensure that it allows sufficient current to illuminate the LED while remaining within the safe operating limits of both the LED and the power supply.
This circuit can be implemented in various applications where fuse monitoring is critical, such as in power distribution panels, automotive systems, and consumer electronics. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it an ideal solution for providing immediate feedback on the status of fuses, enhancing safety and maintenance efficiency.This is a circuit diagram fuse monitor circuit indicators. This very simple circuit uses only two components, but only with a single resistor and LED this circuit provides visual indication when the fuse has blown. LED1 is usually dead, a short circuit by the fuse, F1. Please note that the LED will only illumininatet in damaged condition, ie with a short circuit or shunt the load.
In this case the current is reduced to a safe level by R1 🔗 External reference