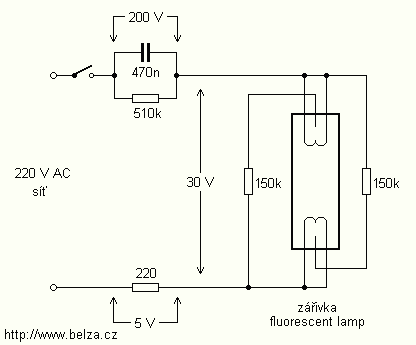
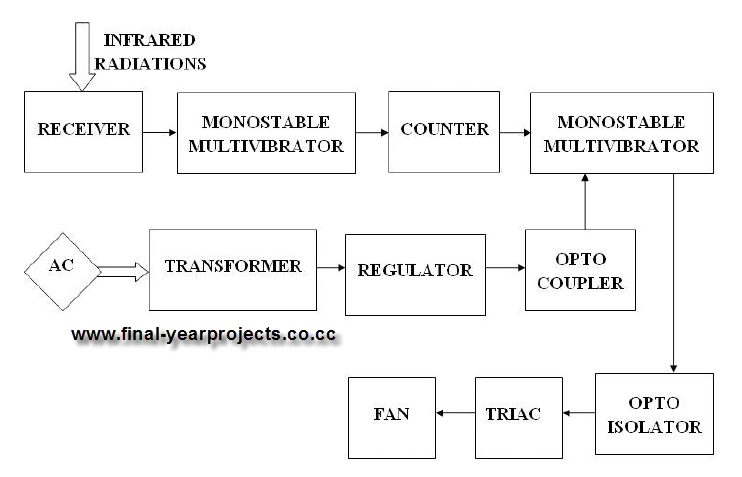
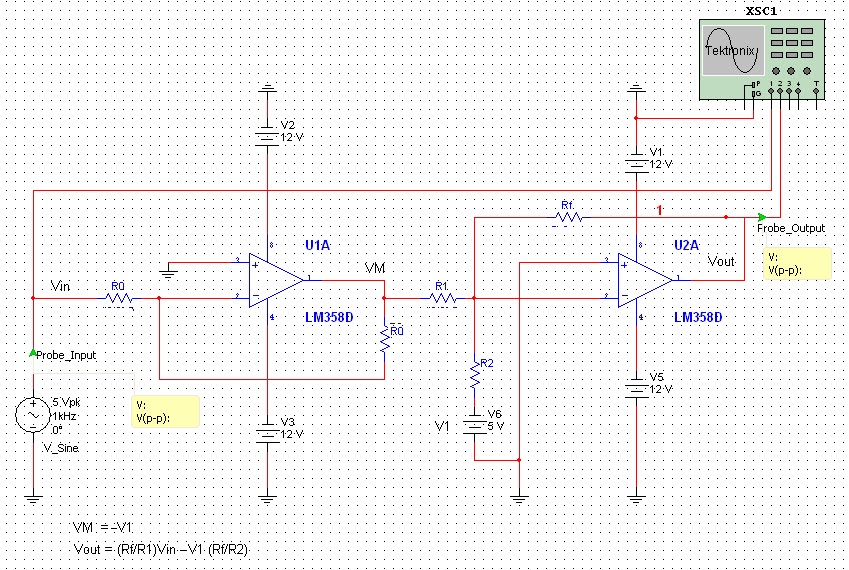
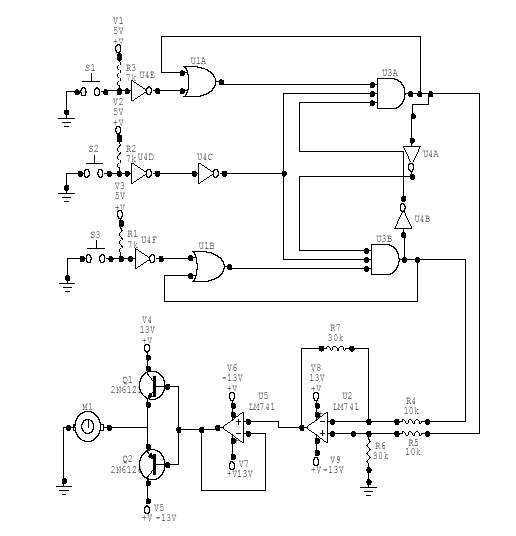
Simple Light Detector with Sensitivity Control
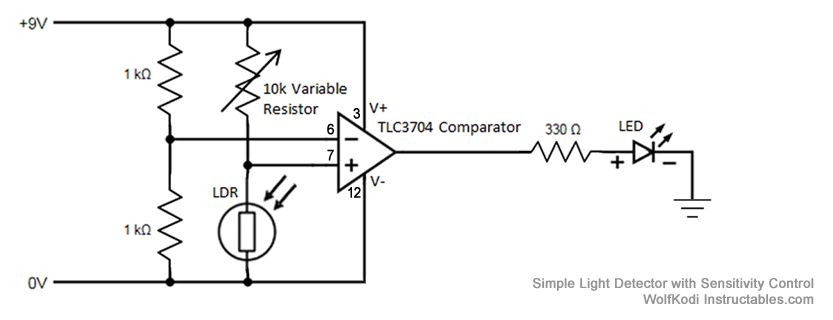
The schematic diagram for the circuit is provided in the accompanying image. As indicated by its name, a comparator is designed to compare two specified voltages. The circuit includes a pair of 1K resistors.
A comparator circuit typically utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to compare two input voltage levels. The output of the comparator indicates which of the two input voltages is higher. The circuit consists of two main inputs, referred to as the inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) inputs. The non-inverting input receives one voltage signal, while the inverting input receives the other.
In this specific schematic, the 1K resistors likely serve as part of a voltage divider or feedback network, which can help set reference levels or control the gain of the comparator. The output of the comparator is usually a digital signal that swings between the supply voltage levels, indicating the comparison result. If the voltage at the non-inverting input exceeds that of the inverting input, the output will transition to a high state, typically close to the positive supply voltage. Conversely, if the voltage at the inverting input is higher, the output will drop to a low state, usually near ground.
Additional components may include power supply connections, decoupling capacitors for stability, and possibly indicators such as LEDs to visually represent the output state. The schematic may also specify additional operational parameters such as input voltage ranges, output load capabilities, and response times, which are crucial for ensuring the comparator functions correctly within its intended application.The schematic diagram for the circuit is given in the picture above. Like its name suggests, a comparator compares two given voltages. The pair of 1K.. 🔗 External reference
A comparator circuit typically utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to compare two input voltage levels. The output of the comparator indicates which of the two input voltages is higher. The circuit consists of two main inputs, referred to as the inverting (-) and non-inverting (+) inputs. The non-inverting input receives one voltage signal, while the inverting input receives the other.
In this specific schematic, the 1K resistors likely serve as part of a voltage divider or feedback network, which can help set reference levels or control the gain of the comparator. The output of the comparator is usually a digital signal that swings between the supply voltage levels, indicating the comparison result. If the voltage at the non-inverting input exceeds that of the inverting input, the output will transition to a high state, typically close to the positive supply voltage. Conversely, if the voltage at the inverting input is higher, the output will drop to a low state, usually near ground.
Additional components may include power supply connections, decoupling capacitors for stability, and possibly indicators such as LEDs to visually represent the output state. The schematic may also specify additional operational parameters such as input voltage ranges, output load capabilities, and response times, which are crucial for ensuring the comparator functions correctly within its intended application.The schematic diagram for the circuit is given in the picture above. Like its name suggests, a comparator compares two given voltages. The pair of 1K.. 🔗 External reference