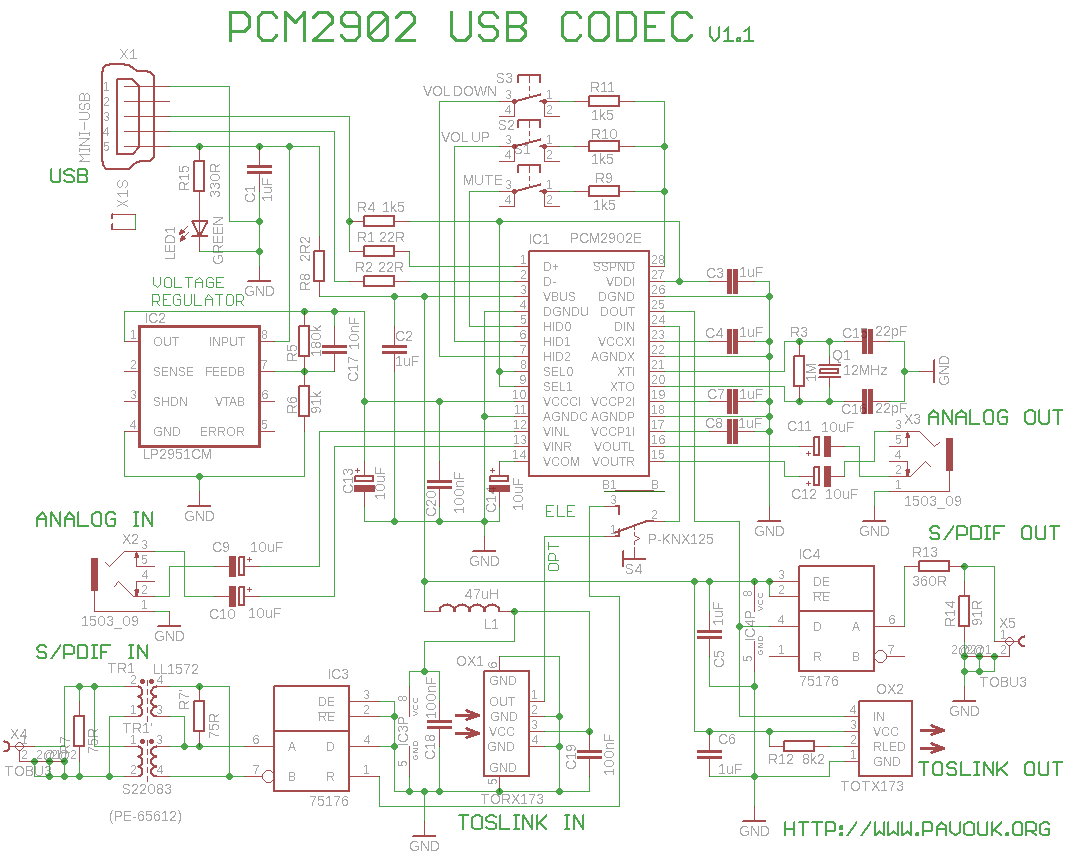
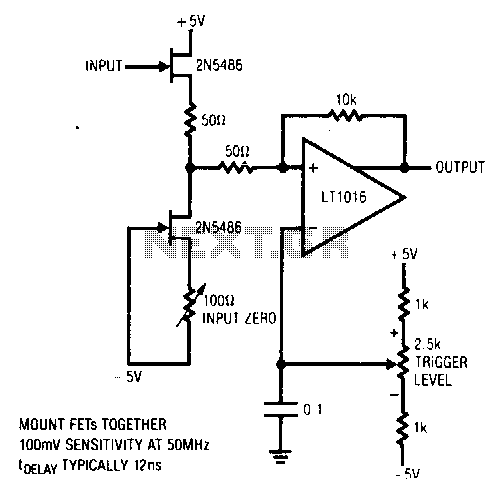
Simple sound trigger for cameras and flashes
This article describes how to build a simple yet effective sound trigger for cameras or flashes. The circuit allows for experimentation with high-speed photography.
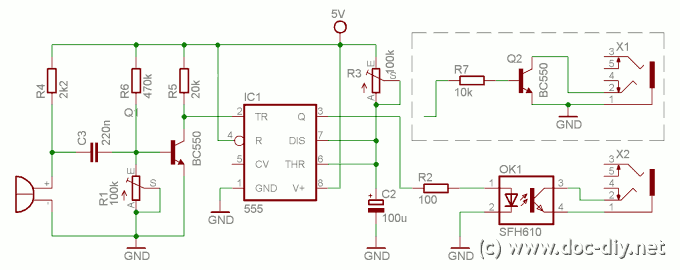
The sound trigger circuit is designed to activate a camera or flash unit in response to sound, making it particularly useful for capturing high-speed events such as balloon pops or other quick occurrences. The fundamental components of this circuit typically include a microphone, an amplifier, a comparator, and a relay or transistor to control the camera or flash.
The microphone serves as the initial sensor, detecting sound waves and converting them into an electrical signal. This signal is then amplified by an operational amplifier (op-amp) to ensure it is strong enough for further processing. The amplified signal is fed into a comparator, which is set to trigger when the sound level exceeds a predefined threshold. This threshold can be adjusted to suit various environments and sound levels.
Upon activation, the comparator output switches from low to high, which can be used to drive a transistor or relay. This component acts as a switch that closes the circuit to the camera or flash, initiating the capture of an image. The relay is particularly useful for isolating the camera's circuitry from the sound trigger circuit, protecting sensitive components from potential damage.
Additional features may include adjustable sensitivity controls, delay timers, or LED indicators to provide visual feedback when the trigger is activated. Power supply options for the circuit can vary, with battery-operated designs being common for portability, while wall adapters may be used for stationary setups.
This sound trigger circuit not only enhances the photography experience but also opens up opportunities for creative experimentation in capturing fleeting moments that would otherwise be difficult to document.This acticle describes how to build a simple yet effective sound trigger for cameras or flashes. The circuit allows to experiment with high-speed photography.. 🔗 External reference
The sound trigger circuit is designed to activate a camera or flash unit in response to sound, making it particularly useful for capturing high-speed events such as balloon pops or other quick occurrences. The fundamental components of this circuit typically include a microphone, an amplifier, a comparator, and a relay or transistor to control the camera or flash.
The microphone serves as the initial sensor, detecting sound waves and converting them into an electrical signal. This signal is then amplified by an operational amplifier (op-amp) to ensure it is strong enough for further processing. The amplified signal is fed into a comparator, which is set to trigger when the sound level exceeds a predefined threshold. This threshold can be adjusted to suit various environments and sound levels.
Upon activation, the comparator output switches from low to high, which can be used to drive a transistor or relay. This component acts as a switch that closes the circuit to the camera or flash, initiating the capture of an image. The relay is particularly useful for isolating the camera's circuitry from the sound trigger circuit, protecting sensitive components from potential damage.
Additional features may include adjustable sensitivity controls, delay timers, or LED indicators to provide visual feedback when the trigger is activated. Power supply options for the circuit can vary, with battery-operated designs being common for portability, while wall adapters may be used for stationary setups.
This sound trigger circuit not only enhances the photography experience but also opens up opportunities for creative experimentation in capturing fleeting moments that would otherwise be difficult to document.This acticle describes how to build a simple yet effective sound trigger for cameras or flashes. The circuit allows to experiment with high-speed photography.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713