single transistor flyback Joule Thief circuit
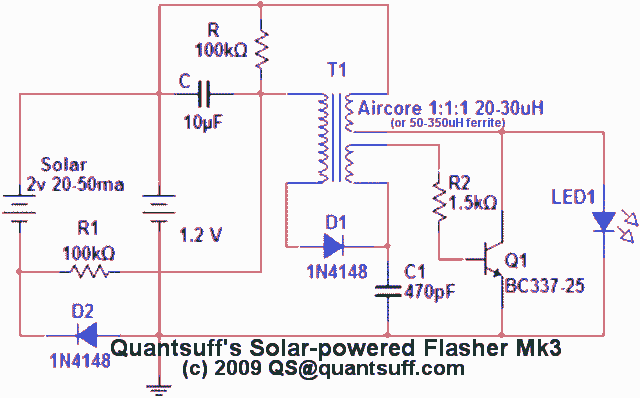
This circuit is a single transistor flyback (Joule Thief) circuit that features a third coil. With it, flash duration and brightness are significantly enhanced.
The single transistor flyback circuit, commonly known as a Joule Thief, is designed to efficiently convert low voltage energy into a higher voltage output. This circuit typically utilizes a single NPN transistor, a primary coil, and a feedback mechanism that allows for the oscillation of current. The addition of a third coil in this configuration serves to increase the energy transfer efficiency and enhance the output characteristics.
In this circuit, the primary coil is connected to the base of the transistor, while the secondary coil is linked to the collector. The third coil, often referred to as the flash coil, is strategically placed to capture the energy generated during the oscillation process. When the circuit is powered, the transistor switches on and off rapidly, inducing a magnetic field in the primary coil. As the magnetic field collapses, a high voltage is generated in the secondary and third coils.
The enhanced flash duration and brightness are attributed to the third coil's ability to store and release energy more effectively. This results in a more intense output, suitable for applications such as LED flashlights or other devices requiring brief, high-intensity light bursts. The circuit's design allows for minimal component usage while maximizing performance, making it an efficient solution for low-power applications where energy conservation is critical.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the principles of electromagnetic induction and energy conversion, showcasing how simple modifications can lead to significant improvements in performance.This circuit is a single transistor flyback (Joule Thief) circuit that features a third coil. With it, flash duration and brightness is much enhanced 🔗 External reference
The single transistor flyback circuit, commonly known as a Joule Thief, is designed to efficiently convert low voltage energy into a higher voltage output. This circuit typically utilizes a single NPN transistor, a primary coil, and a feedback mechanism that allows for the oscillation of current. The addition of a third coil in this configuration serves to increase the energy transfer efficiency and enhance the output characteristics.
In this circuit, the primary coil is connected to the base of the transistor, while the secondary coil is linked to the collector. The third coil, often referred to as the flash coil, is strategically placed to capture the energy generated during the oscillation process. When the circuit is powered, the transistor switches on and off rapidly, inducing a magnetic field in the primary coil. As the magnetic field collapses, a high voltage is generated in the secondary and third coils.
The enhanced flash duration and brightness are attributed to the third coil's ability to store and release energy more effectively. This results in a more intense output, suitable for applications such as LED flashlights or other devices requiring brief, high-intensity light bursts. The circuit's design allows for minimal component usage while maximizing performance, making it an efficient solution for low-power applications where energy conservation is critical.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the principles of electromagnetic induction and energy conversion, showcasing how simple modifications can lead to significant improvements in performance.This circuit is a single transistor flyback (Joule Thief) circuit that features a third coil. With it, flash duration and brightness is much enhanced 🔗 External reference