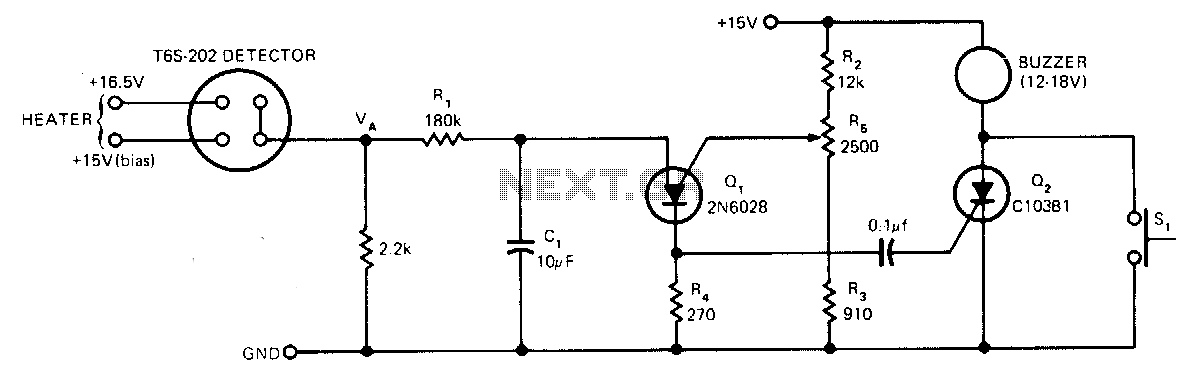
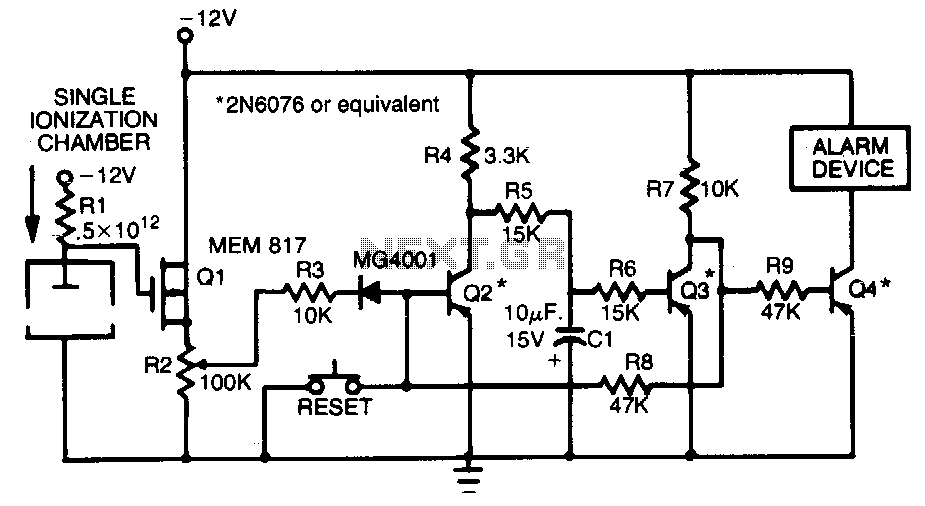
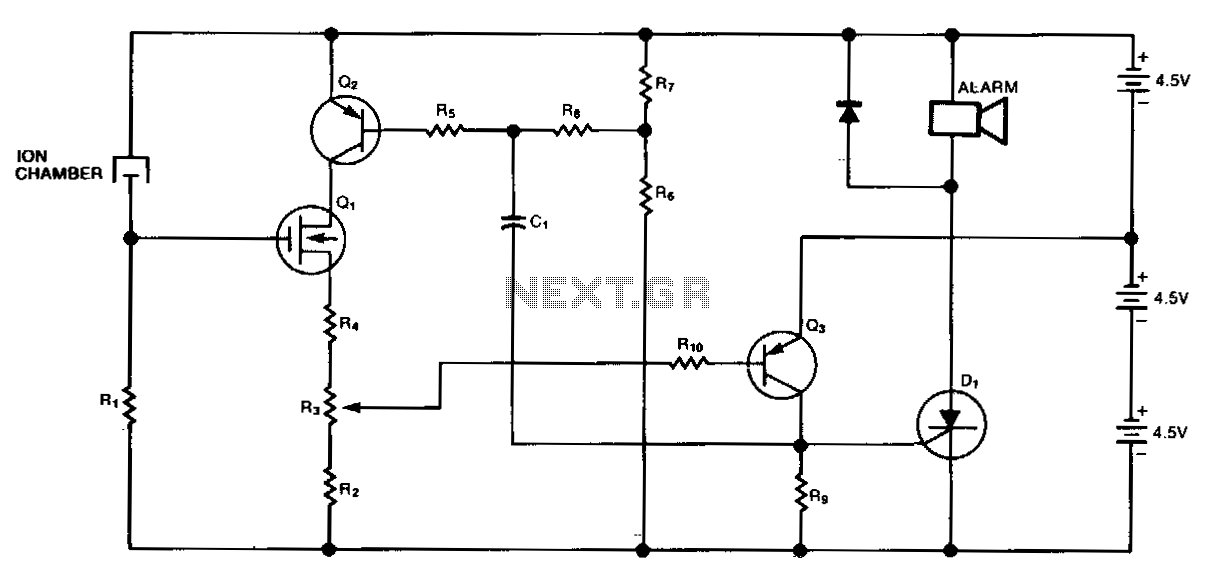
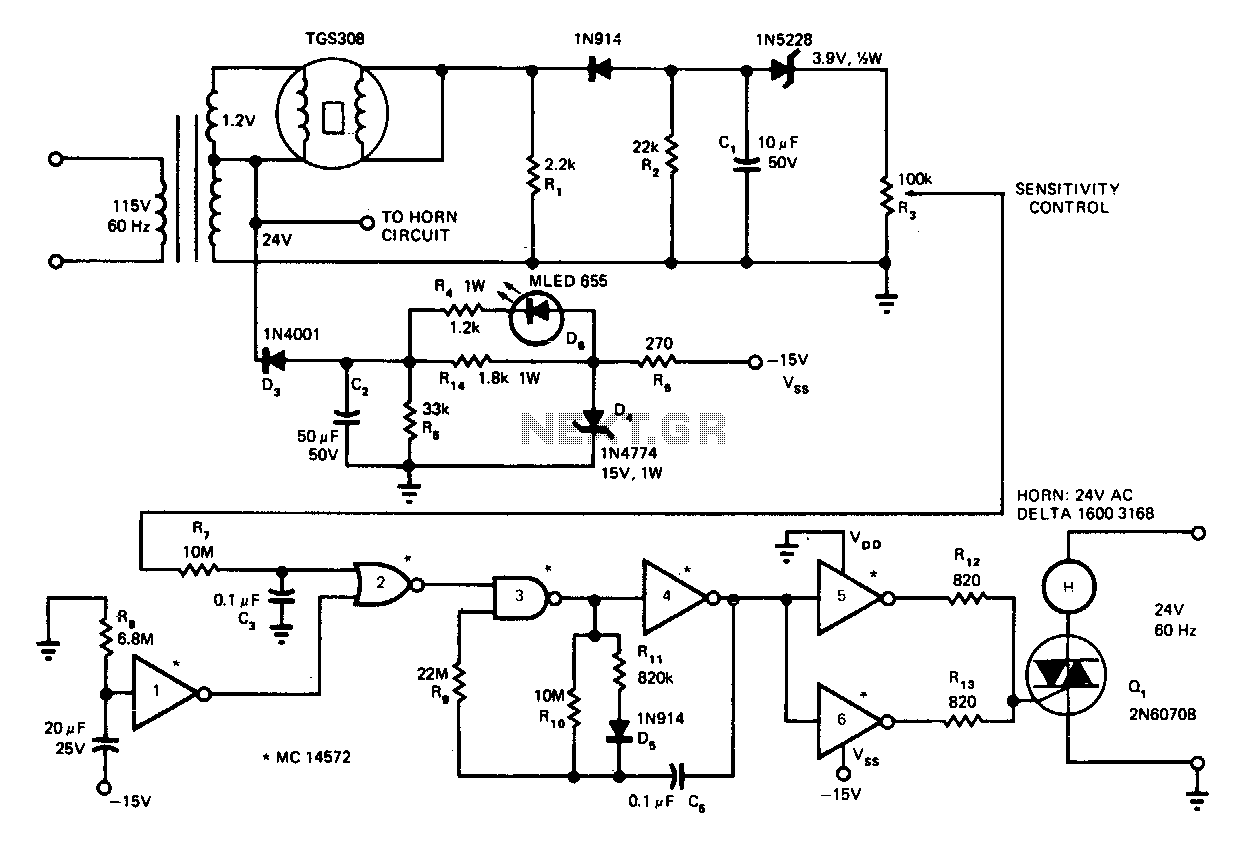
Smoke-detector
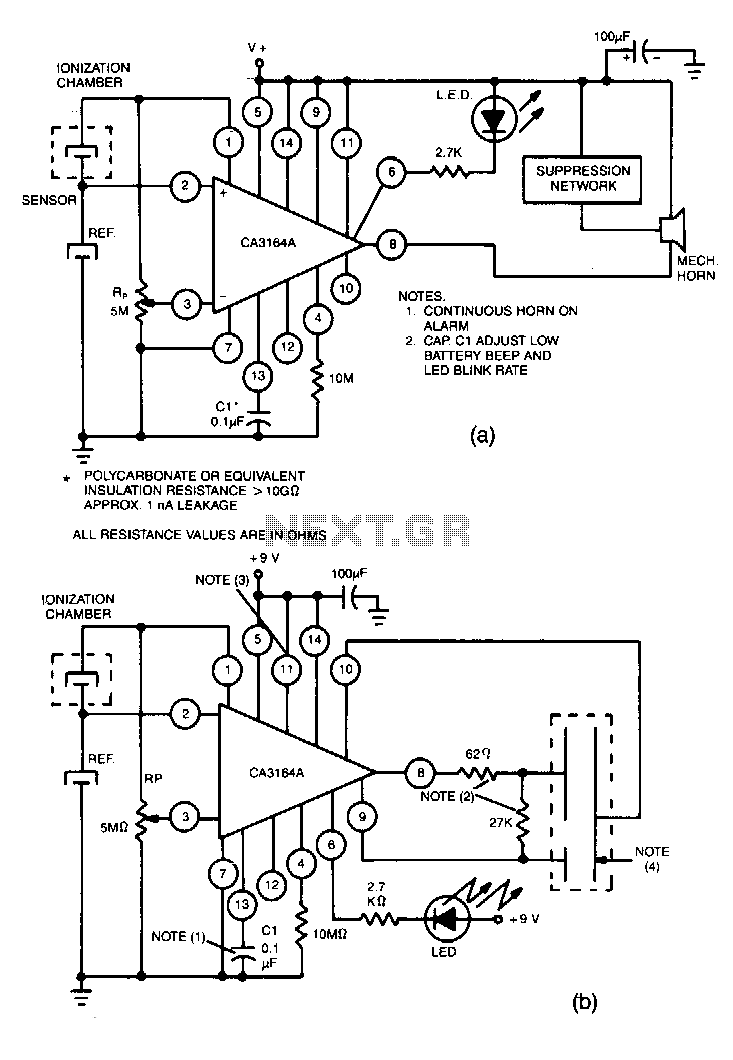
Utilize the CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system for operation as a smoke detector with an electromechanical horn (refer to Fig. 40-la). The output driver at terminal 8 is employed, utilizing a large npn transistor Q3 with an active pull-up, while transistor Q2 provides over 300 mA of drive current. Additionally, for operation as a smoke detector with a piezoelectric horn (refer to Fig. 40-lb), the circuit requires output from a second inverting amplifier at terminal 10, along with the output from terminal 8.
The CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system serves as a versatile platform for smoke detection applications, integrating both electromechanical and piezoelectric horn functionalities. When configured for use with an electromechanical horn, the circuit design leverages the capabilities of the CA3164A, particularly focusing on its output driver located at terminal 8. This driver is paired with a robust npn transistor, Q3, which is designed to handle substantial load currents. The active pull-up configuration enhances the output signal, ensuring that the horn receives sufficient drive current, exceeding 300 mA, facilitated by the additional transistor Q2.
In the alternative configuration for a piezoelectric horn, the circuit necessitates the integration of a second inverting amplifier output from terminal 10. This design adjustment allows for the generation of a distinct signal tailored for the piezoelectric component, while still utilizing the primary output from terminal 8. The combination of these two outputs ensures that the smoke detection system can effectively trigger either type of alarm, depending on the specific application requirements.
Overall, the CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system exemplifies a highly adaptable solution for smoke detection, providing clear pathways for interfacing with different alarm types through its well-defined terminal outputs and transistor configurations. The careful consideration of drive current and signal integrity is paramount in ensuring reliable operation in smoke detection scenarios.Use CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system. For operation as smoke detector with electromechanical hom (Fig. 40-la), the output of driver at terminal 8 is used. Large npn transistor Q3,-with an active pull-up and transistor Q2 provide over 300 mA of drive current. For operation as a smoke detector with a piezoelectric hom (Fig. 40-lb), the circuit requires output from a second inverting amplifier at terminallO, as well as the output from terminal 8.
The CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system serves as a versatile platform for smoke detection applications, integrating both electromechanical and piezoelectric horn functionalities. When configured for use with an electromechanical horn, the circuit design leverages the capabilities of the CA3164A, particularly focusing on its output driver located at terminal 8. This driver is paired with a robust npn transistor, Q3, which is designed to handle substantial load currents. The active pull-up configuration enhances the output signal, ensuring that the horn receives sufficient drive current, exceeding 300 mA, facilitated by the additional transistor Q2.
In the alternative configuration for a piezoelectric horn, the circuit necessitates the integration of a second inverting amplifier output from terminal 10. This design adjustment allows for the generation of a distinct signal tailored for the piezoelectric component, while still utilizing the primary output from terminal 8. The combination of these two outputs ensures that the smoke detection system can effectively trigger either type of alarm, depending on the specific application requirements.
Overall, the CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system exemplifies a highly adaptable solution for smoke detection, providing clear pathways for interfacing with different alarm types through its well-defined terminal outputs and transistor configurations. The careful consideration of drive current and signal integrity is paramount in ensuring reliable operation in smoke detection scenarios.Use CA3164A BiMOS detector/alarm system. For operation as smoke detector with electromechanical hom (Fig. 40-la), the output of driver at terminal 8 is used. Large npn transistor Q3,-with an active pull-up and transistor Q2 provide over 300 mA of drive current. For operation as a smoke detector with a piezoelectric hom (Fig. 40-lb), the circuit requires output from a second inverting amplifier at terminallO, as well as the output from terminal 8.