
Sound-activated-decoder
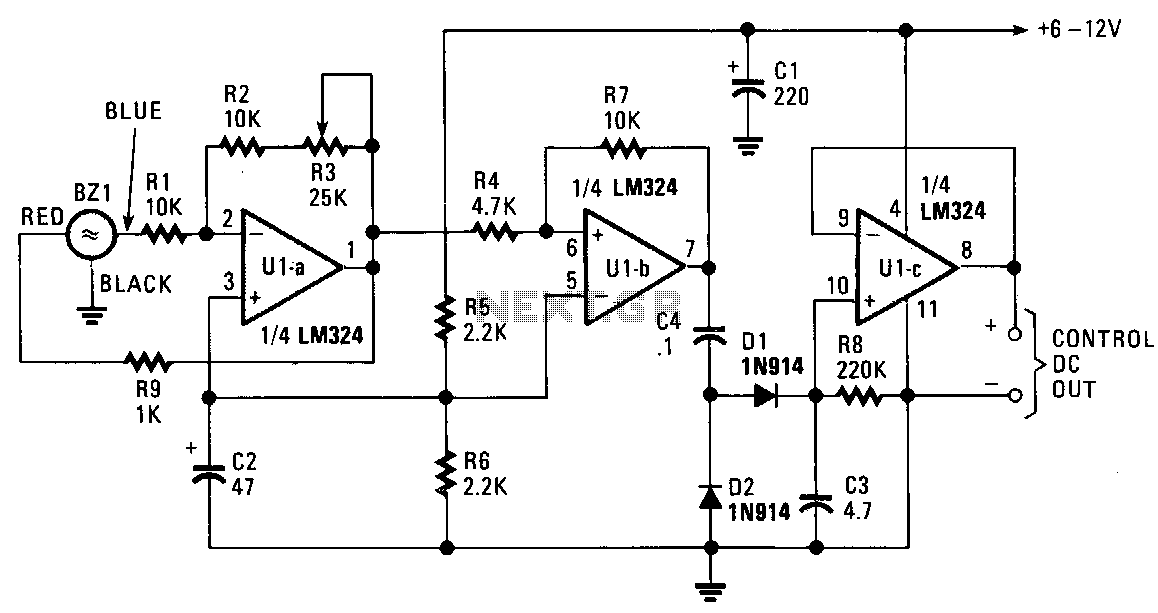
The piezo transducer functions as both a sound pickup device and a frequency-selective filter. By adjusting the gain of the operational amplifiers (op-amps), the oscillator can be configured as a sensitive and frequency-selective tone decoder circuit. When the gain of U1a is set just below the self-oscillation threshold, the transducer becomes responsive to acoustically coupled audio tones that occur at or near its resonant frequency. The output of the circuit can be utilized to activate optocouplers, drive relay circuits, or control nearly any DC-operated circuit. The DC signal at the output of U1c varies from 0 to over 6 V, depending on the input signal level. An unusual application for the sound-activated decoder is in extremely high-noise environments, where conventional broadband microphone pickup would be ineffective. Since piezo transducers respond only to frequencies within a very narrow bandwidth, minimal noise is transmitted through the transducer.
The circuit design incorporates a piezo transducer, which serves as the primary sensor for sound detection. The transducer is connected to an operational amplifier (U1a), configured to amplify the signal while maintaining sensitivity to specific frequencies. The gain setting of U1a is critical; it must be adjusted to a level just below self-oscillation to ensure that the circuit remains responsive to desired audio tones without producing unwanted oscillations.
Following the first stage of amplification, the signal is processed by additional operational amplifiers (U1b and U1c) to further refine the output. U1b may serve as a band-pass filter, allowing only frequencies around the resonant frequency of the piezo transducer to pass through, effectively filtering out extraneous noise. The final output from U1c provides a DC voltage that varies based on the amplitude of the incoming audio signal, which can be interfaced with various control systems.
The versatility of this circuit is exemplified in its ability to activate optocouplers or drive relay circuits, making it suitable for a range of applications, including automation and control systems. The ability to operate effectively in high-noise environments is a significant advantage, as the narrow frequency response of the piezo transducer minimizes the impact of background noise, allowing for accurate sound detection in challenging conditions. This feature makes the circuit particularly valuable in industrial settings or areas with significant acoustic interference, where traditional sound detection methods may fail.The piezo transducer operates as a sound-pickup device as well as a frequency-selective filter. By controlling the gain of the op amps, the oscillator can be transformed into a sensitive and frequency-selective tone-decoder circuit. With the gain of U1a set just below the point of self oscillation, the transducer becomes sensitive to acoustically coupled audio tones that occur at or near its resonant frequency.
The circuit"s output can be used to activate optocouplers, drive relay circuits, or to control almost any de-operated circuit. The de signal at the output of U1c varies with 0 to over 6 V, depending on the inputsignal level. One unusual application for the sound-activated decoder would be in extremely high-noise environments, where normal broadband microphone pickup would be useless. Because piezo transducers respond only to frequencies within a very narrow bandwidth, little if any of the noise would get through the transducer.
The circuit design incorporates a piezo transducer, which serves as the primary sensor for sound detection. The transducer is connected to an operational amplifier (U1a), configured to amplify the signal while maintaining sensitivity to specific frequencies. The gain setting of U1a is critical; it must be adjusted to a level just below self-oscillation to ensure that the circuit remains responsive to desired audio tones without producing unwanted oscillations.
Following the first stage of amplification, the signal is processed by additional operational amplifiers (U1b and U1c) to further refine the output. U1b may serve as a band-pass filter, allowing only frequencies around the resonant frequency of the piezo transducer to pass through, effectively filtering out extraneous noise. The final output from U1c provides a DC voltage that varies based on the amplitude of the incoming audio signal, which can be interfaced with various control systems.
The versatility of this circuit is exemplified in its ability to activate optocouplers or drive relay circuits, making it suitable for a range of applications, including automation and control systems. The ability to operate effectively in high-noise environments is a significant advantage, as the narrow frequency response of the piezo transducer minimizes the impact of background noise, allowing for accurate sound detection in challenging conditions. This feature makes the circuit particularly valuable in industrial settings or areas with significant acoustic interference, where traditional sound detection methods may fail.The piezo transducer operates as a sound-pickup device as well as a frequency-selective filter. By controlling the gain of the op amps, the oscillator can be transformed into a sensitive and frequency-selective tone-decoder circuit. With the gain of U1a set just below the point of self oscillation, the transducer becomes sensitive to acoustically coupled audio tones that occur at or near its resonant frequency.
The circuit"s output can be used to activate optocouplers, drive relay circuits, or to control almost any de-operated circuit. The de signal at the output of U1c varies with 0 to over 6 V, depending on the inputsignal level. One unusual application for the sound-activated decoder would be in extremely high-noise environments, where normal broadband microphone pickup would be useless. Because piezo transducers respond only to frequencies within a very narrow bandwidth, little if any of the noise would get through the transducer.