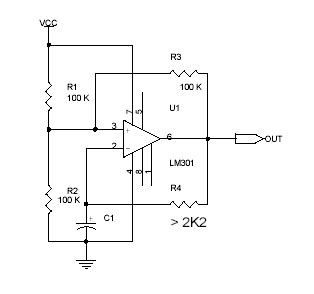
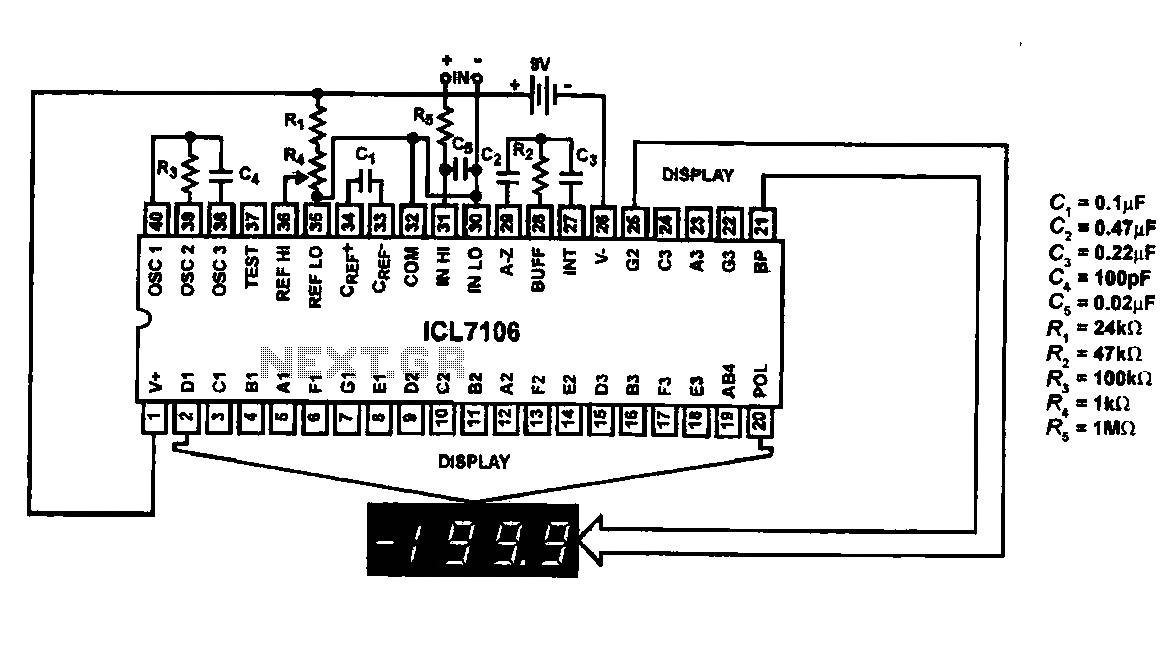
Switchable Output Crystal Oscillator
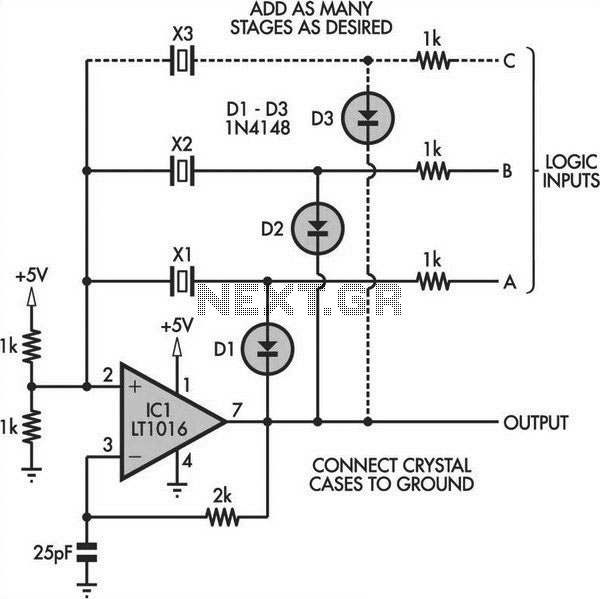
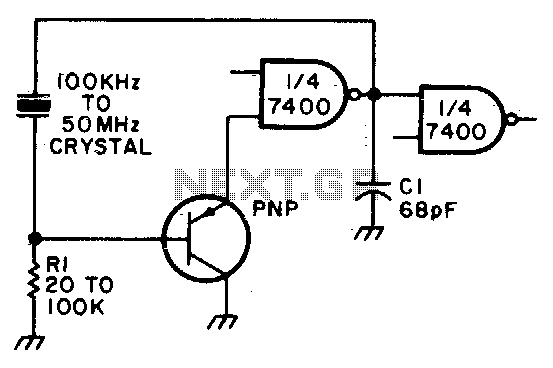
Switchable Output Crystal Oscillator Circuit. This oscillator circuit allows crystals to be electronically switched using logic commands. The circuit is best understood by initially ignoring all crystals. Furthermore, assume that a...
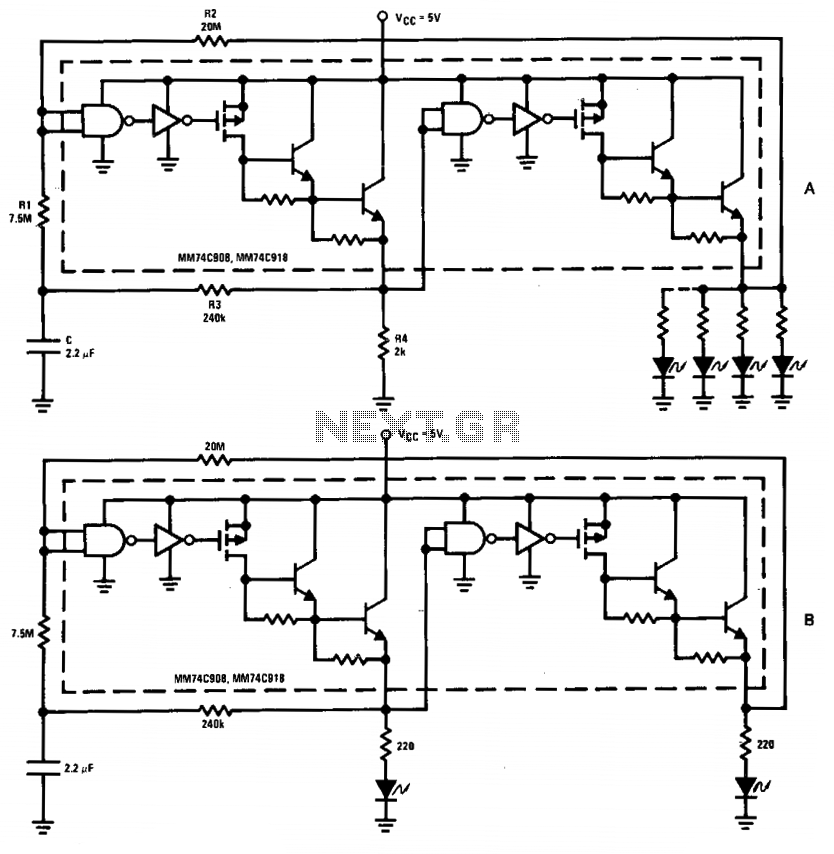
The switchable output crystal oscillator circuit is designed to provide precise frequency generation by utilizing multiple crystal resonators that can be selected via digital logic signals. The fundamental operation of this circuit involves the integration of a microcontroller or a logic gate array that interfaces with a set of crystal oscillators. Each crystal oscillator is tuned to a specific frequency, and the selection mechanism relies on electronic switching, typically achieved through analog switches or multiplexers.
In the circuit, the microcontroller sends control signals to the switching mechanism, enabling the desired crystal oscillator while disabling the others. This allows for dynamic frequency adjustment without the need for mechanical switching, which can introduce wear and reliability issues. The output of the selected crystal oscillator is then fed into a buffer stage to ensure signal integrity and drive capability, allowing the output to interface with other circuit components or systems.
The circuit design should include considerations for power supply decoupling, ensuring stable operation of the oscillators. Additionally, the layout should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect the frequency stability and performance of the oscillators. Proper grounding techniques and the use of ground planes can further enhance the circuit's performance.
Overall, this switchable output crystal oscillator circuit is highly versatile and can be employed in various applications such as communication systems, signal processing, and frequency synthesis, where precise timing and frequency control are essential.Switchable Output Crystal Oscillator Circuit This oscillator circuit permits crystals to be electronically switched by logic commands. The circuit is best understood by initially ignoring all crystals. Furthermore, assume that a.. 🔗 External reference
The switchable output crystal oscillator circuit is designed to provide precise frequency generation by utilizing multiple crystal resonators that can be selected via digital logic signals. The fundamental operation of this circuit involves the integration of a microcontroller or a logic gate array that interfaces with a set of crystal oscillators. Each crystal oscillator is tuned to a specific frequency, and the selection mechanism relies on electronic switching, typically achieved through analog switches or multiplexers.
In the circuit, the microcontroller sends control signals to the switching mechanism, enabling the desired crystal oscillator while disabling the others. This allows for dynamic frequency adjustment without the need for mechanical switching, which can introduce wear and reliability issues. The output of the selected crystal oscillator is then fed into a buffer stage to ensure signal integrity and drive capability, allowing the output to interface with other circuit components or systems.
The circuit design should include considerations for power supply decoupling, ensuring stable operation of the oscillators. Additionally, the layout should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect the frequency stability and performance of the oscillators. Proper grounding techniques and the use of ground planes can further enhance the circuit's performance.
Overall, this switchable output crystal oscillator circuit is highly versatile and can be employed in various applications such as communication systems, signal processing, and frequency synthesis, where precise timing and frequency control are essential.Switchable Output Crystal Oscillator Circuit This oscillator circuit permits crystals to be electronically switched by logic commands. The circuit is best understood by initially ignoring all crystals. Furthermore, assume that a.. 🔗 External reference