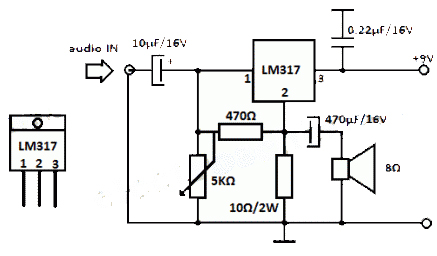
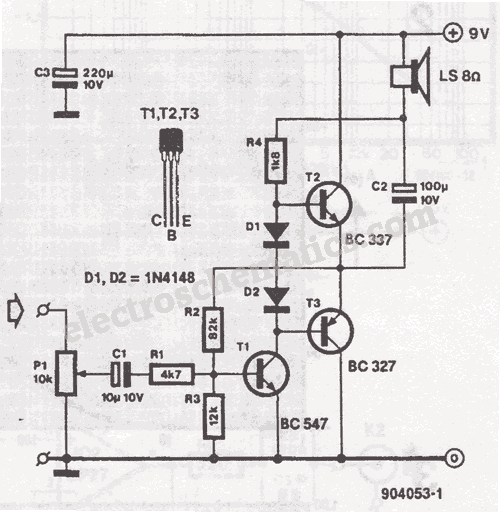
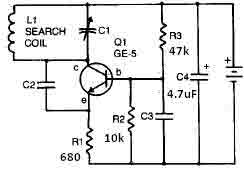
Symmetrical power supply circuit electronic project
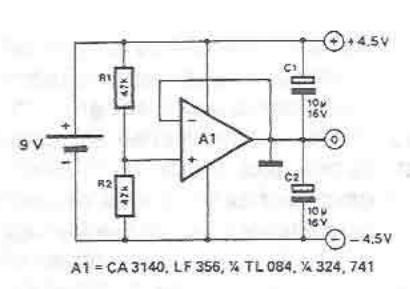
A symmetrical power supply can be designed using this circuit diagram. This symmetrical power supply is constructed with a simple operational amplifier and some classic electronic components. Resistors R1 and R2 form a high impedance voltage divider. The operational amplifier ensures that the artificial potential mass is the same as the voltage at the common point between R1 and R2. The ratio of R1 and R2 determines the relationship between the two output voltages; if R1 and R2 are identical, the two output voltages are symmetrical.
The circuit for a symmetrical power supply typically consists of an operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting mode, with resistors R1 and R2 forming a voltage divider network. The primary function of the operational amplifier in this configuration is to maintain a stable reference voltage at its non-inverting input, which is derived from the voltage divider formed by R1 and R2.
In this setup, R1 is connected from the positive supply voltage to the inverting input of the operational amplifier, while R2 is connected from the inverting input to ground. The output of the operational amplifier is fed back to the inverting input, creating a closed-loop feedback system. This feedback mechanism is essential for ensuring that the voltage at the inverting input matches the voltage at the non-inverting input, thus stabilizing the output voltage.
The output voltages of the symmetrical power supply are determined by the values of R1 and R2. When R1 and R2 are equal, the output voltages will be equal in magnitude but opposite in polarity, achieving a symmetrical output. This symmetry is critical for applications requiring balanced power supply rails, such as in audio amplifiers, operational amplifier circuits, and analog signal processing.
To further enhance the performance of the symmetrical power supply, it may be beneficial to add bypass capacitors at the power supply pins of the operational amplifier. This addition helps to filter out high-frequency noise and provides a more stable voltage reference. Additionally, incorporating a precision voltage reference can improve the accuracy of the output voltages.
Overall, this symmetrical power supply circuit is a fundamental design that leverages the properties of operational amplifiers and resistive voltage dividers to achieve balanced output voltages suitable for various electronic applications.A symmetrical power supply, can be designed using this circuit diagram. This symmetrical power supply is designed using a simple operational amplifier and some classic electronic components Resistances R1 and R2 form a high impedance voltage divider. Operational amplifier makes sure that artificial potential mass is the same as the voltage at the common point between R1 and R2. The ratio of R1 and R2 determine the relationship between the two output voltages, if R1 and R2 are identical, the two output voltages are symmetrical. 🔗 External reference
The circuit for a symmetrical power supply typically consists of an operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting mode, with resistors R1 and R2 forming a voltage divider network. The primary function of the operational amplifier in this configuration is to maintain a stable reference voltage at its non-inverting input, which is derived from the voltage divider formed by R1 and R2.
In this setup, R1 is connected from the positive supply voltage to the inverting input of the operational amplifier, while R2 is connected from the inverting input to ground. The output of the operational amplifier is fed back to the inverting input, creating a closed-loop feedback system. This feedback mechanism is essential for ensuring that the voltage at the inverting input matches the voltage at the non-inverting input, thus stabilizing the output voltage.
The output voltages of the symmetrical power supply are determined by the values of R1 and R2. When R1 and R2 are equal, the output voltages will be equal in magnitude but opposite in polarity, achieving a symmetrical output. This symmetry is critical for applications requiring balanced power supply rails, such as in audio amplifiers, operational amplifier circuits, and analog signal processing.
To further enhance the performance of the symmetrical power supply, it may be beneficial to add bypass capacitors at the power supply pins of the operational amplifier. This addition helps to filter out high-frequency noise and provides a more stable voltage reference. Additionally, incorporating a precision voltage reference can improve the accuracy of the output voltages.
Overall, this symmetrical power supply circuit is a fundamental design that leverages the properties of operational amplifiers and resistive voltage dividers to achieve balanced output voltages suitable for various electronic applications.A symmetrical power supply, can be designed using this circuit diagram. This symmetrical power supply is designed using a simple operational amplifier and some classic electronic components Resistances R1 and R2 form a high impedance voltage divider. Operational amplifier makes sure that artificial potential mass is the same as the voltage at the common point between R1 and R2. The ratio of R1 and R2 determine the relationship between the two output voltages, if R1 and R2 are identical, the two output voltages are symmetrical. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713