
Temperature-sensor
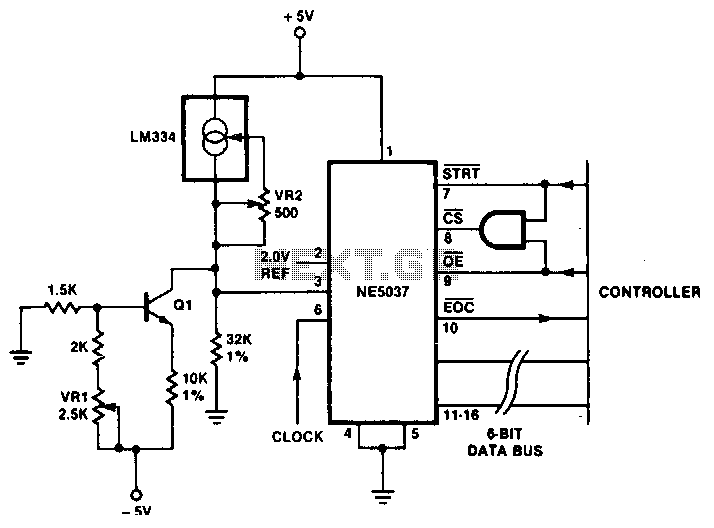
The temperature sensor provides an input to pin 3 of the NE5037 with a sensitivity of 32 mV/°C. This 32 mV represents the value of one least significant bit (LSB) for the NE5037. The LM334 is a three-terminal temperature sensor that delivers a current of 1 pA for each degree Kelvin. A 32 kΩ resistor generates the 32 mV for each microamp flowing through it, while a transistor bleeds off 273 pA of the LM334's current. This current bleeding adjusts the reading by reducing it by 273 K, effectively converting the temperature scale from Kelvin to Celsius. To initiate temperature reading, a momentary low signal is sent to pin 7 of the NE5037. When pin 10 of the NE5037 goes low, the conversion process is complete, and a low signal is applied to pin 9 of the NE5037 to read the data from pins 11 through 16. It is important to note that the temperature data is in straight binary format. The controller used can either be a microprocessor in a temperature control application or discrete circuitry in a simple temperature reporting application.
The described circuit involves a temperature sensing system utilizing the NE5037 integrated circuit, which is designed for precise temperature measurement and conversion. The input from the temperature sensor, the LM334, is calibrated to provide a current output that is directly proportional to the temperature in Kelvin. The choice of a 32 kΩ resistor is critical, as it ensures that the voltage output corresponds accurately to the temperature reading by producing 32 mV for each microamp of current flowing through it.
The NE5037 has a specific operational sequence for temperature conversion. The process begins when a low signal is applied to pin 7, which triggers the internal conversion mechanism. This action prepares the NE5037 to process the input voltage signal from the LM334. Once the conversion is complete, indicated by pin 10 going low, the data can be accessed. The low signal on pin 9 allows for the output of the temperature data, which is available in binary format on pins 11 through 16.
In practical applications, this system can be integrated into various temperature monitoring and control systems. For instance, in a microprocessor-controlled environment, the temperature data can be processed and utilized for feedback in heating or cooling systems, ensuring optimal temperature management. Alternatively, in simpler applications, discrete circuitry can be employed to display temperature readings directly, making this circuit versatile for both complex and straightforward temperature measurement tasks. The precision of temperature readings and the ease of integration with other electronic components make this circuit an effective solution for a wide range of temperature sensing applications.The temperature sensor provides an input to pin 3 of the NE5037 of 32 mV/°C. This 32 mV is the value of one LSB for the NE5037. The LM334 is a three-terminal temperature sensor and provides a current of 1 p.A for each degree Kelvin. The 32-KO resistor provides the 32 mV for each microamp through it, while the transistor bleeds off 273 p.A of the temperature sensor (LM334) current.
This bleeding lowers the reading by 273 K, thus converting from Kelvin to Celsius. To read temperature, conversion is started by sending a momentary low signal to pin 7 of the NE5037. When pin 10 of the NE5037 becomes low, conversion is complete and a low is applied to pin 9 of the NE5037 to read data on pins 11 and through 16. Note that this temperature data is in straight binary format. The controller can be a microprocessor in a temperature controLapplication, or discrete circuitry in a simple temperature reporting application.
The described circuit involves a temperature sensing system utilizing the NE5037 integrated circuit, which is designed for precise temperature measurement and conversion. The input from the temperature sensor, the LM334, is calibrated to provide a current output that is directly proportional to the temperature in Kelvin. The choice of a 32 kΩ resistor is critical, as it ensures that the voltage output corresponds accurately to the temperature reading by producing 32 mV for each microamp of current flowing through it.
The NE5037 has a specific operational sequence for temperature conversion. The process begins when a low signal is applied to pin 7, which triggers the internal conversion mechanism. This action prepares the NE5037 to process the input voltage signal from the LM334. Once the conversion is complete, indicated by pin 10 going low, the data can be accessed. The low signal on pin 9 allows for the output of the temperature data, which is available in binary format on pins 11 through 16.
In practical applications, this system can be integrated into various temperature monitoring and control systems. For instance, in a microprocessor-controlled environment, the temperature data can be processed and utilized for feedback in heating or cooling systems, ensuring optimal temperature management. Alternatively, in simpler applications, discrete circuitry can be employed to display temperature readings directly, making this circuit versatile for both complex and straightforward temperature measurement tasks. The precision of temperature readings and the ease of integration with other electronic components make this circuit an effective solution for a wide range of temperature sensing applications.The temperature sensor provides an input to pin 3 of the NE5037 of 32 mV/°C. This 32 mV is the value of one LSB for the NE5037. The LM334 is a three-terminal temperature sensor and provides a current of 1 p.A for each degree Kelvin. The 32-KO resistor provides the 32 mV for each microamp through it, while the transistor bleeds off 273 p.A of the temperature sensor (LM334) current.
This bleeding lowers the reading by 273 K, thus converting from Kelvin to Celsius. To read temperature, conversion is started by sending a momentary low signal to pin 7 of the NE5037. When pin 10 of the NE5037 becomes low, conversion is complete and a low is applied to pin 9 of the NE5037 to read data on pins 11 and through 16. Note that this temperature data is in straight binary format. The controller can be a microprocessor in a temperature controLapplication, or discrete circuitry in a simple temperature reporting application.