
Three-rail-power-supply
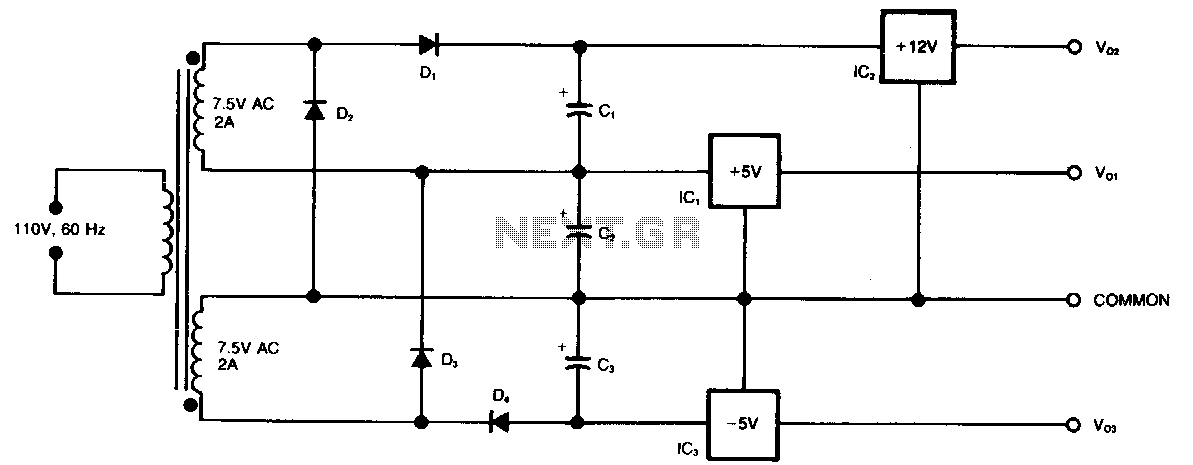
This circuit generates three supply voltages using a minimal number of components. Diodes D2 and D3 perform full-wave rectification, alternately charging capacitor C2 during both halves of the AC cycle. Meanwhile, diode D1 in conjunction with capacitor C1, and diode D4 with capacitor C3, each perform half-wave rectification. The combination of full-wave and half-wave rectification is adequate for the modest supply currents required by the -5V and +12V voltage regulators, IC3 and IC2. This circuit can serve as an auxiliary supply in an up-based instrument, thereby avoiding the less desirable options of purchasing a custom-wound transformer, constructing a more complex power supply, or utilizing a secondary winding, such as 18 Vac, which would result in wasted power in the 5V regulators.
This circuit design effectively utilizes a combination of full-wave and half-wave rectification to provide three distinct supply voltages, making it suitable for various applications where space and component count are critical. The design begins with an AC input, which is fed into diodes D2 and D3. These diodes are arranged in such a way that they allow current to flow during both the positive and negative cycles of the AC waveform, thereby achieving full-wave rectification. This process charges capacitor C2, which smooths the output voltage and provides a steady supply for the connected load.
In parallel, diodes D1 and D4 are configured to perform half-wave rectification. Diode D1, along with capacitor C1, captures only the positive half of the AC cycle, while diode D4 and capacitor C3 do the same for the negative half. This arrangement allows the circuit to generate a -5V supply from the negative half-cycle and a +12V supply from the positive half-cycle, ensuring that the output voltages are available for the connected regulators.
The regulators, IC2 for +12V and IC3 for -5V, are designed to handle the modest supply currents typically required in low-power applications. By employing this circuit, designers can significantly reduce the complexity and cost associated with traditional power supply designs. The use of a minimal number of components not only simplifies the layout but also enhances reliability and ease of maintenance.
Furthermore, the circuit can be integrated into various instruments, particularly those that rely on an up-based architecture. It provides an efficient solution for power supply needs without the drawbacks of custom transformers or secondary windings, which can introduce additional losses and complexity. This makes the circuit an optimal choice for applications requiring efficient voltage regulation with a compact and straightforward design.This circuit generates three supply voltages using a minimum of components. Diodes D2 and D3 perform full-wave rectification, alternately charging capacitor C2 on both halves of the ac cycle. On the other hand, diode D1 with capacitor C1, and diode D4 with capacitor C3 each perform half-wave rectification.
The full-and half-wave rectification arrangement is satisfactory for modest supply currents drawn from -5 and +12-V regulators IC3 and IC2. You can use this circuit as an auxiliary supply in an up-based instrument, for example, and avoid the less attractive alternatives of buying a custom-wound transformer, building a more complex supply, or using a secondary winding, say 18 Vac, and wasting power in the 5-V regulators. 🔗 External reference
This circuit design effectively utilizes a combination of full-wave and half-wave rectification to provide three distinct supply voltages, making it suitable for various applications where space and component count are critical. The design begins with an AC input, which is fed into diodes D2 and D3. These diodes are arranged in such a way that they allow current to flow during both the positive and negative cycles of the AC waveform, thereby achieving full-wave rectification. This process charges capacitor C2, which smooths the output voltage and provides a steady supply for the connected load.
In parallel, diodes D1 and D4 are configured to perform half-wave rectification. Diode D1, along with capacitor C1, captures only the positive half of the AC cycle, while diode D4 and capacitor C3 do the same for the negative half. This arrangement allows the circuit to generate a -5V supply from the negative half-cycle and a +12V supply from the positive half-cycle, ensuring that the output voltages are available for the connected regulators.
The regulators, IC2 for +12V and IC3 for -5V, are designed to handle the modest supply currents typically required in low-power applications. By employing this circuit, designers can significantly reduce the complexity and cost associated with traditional power supply designs. The use of a minimal number of components not only simplifies the layout but also enhances reliability and ease of maintenance.
Furthermore, the circuit can be integrated into various instruments, particularly those that rely on an up-based architecture. It provides an efficient solution for power supply needs without the drawbacks of custom transformers or secondary windings, which can introduce additional losses and complexity. This makes the circuit an optimal choice for applications requiring efficient voltage regulation with a compact and straightforward design.This circuit generates three supply voltages using a minimum of components. Diodes D2 and D3 perform full-wave rectification, alternately charging capacitor C2 on both halves of the ac cycle. On the other hand, diode D1 with capacitor C1, and diode D4 with capacitor C3 each perform half-wave rectification.
The full-and half-wave rectification arrangement is satisfactory for modest supply currents drawn from -5 and +12-V regulators IC3 and IC2. You can use this circuit as an auxiliary supply in an up-based instrument, for example, and avoid the less attractive alternatives of buying a custom-wound transformer, building a more complex supply, or using a secondary winding, say 18 Vac, and wasting power in the 5-V regulators. 🔗 External reference