Tone detector
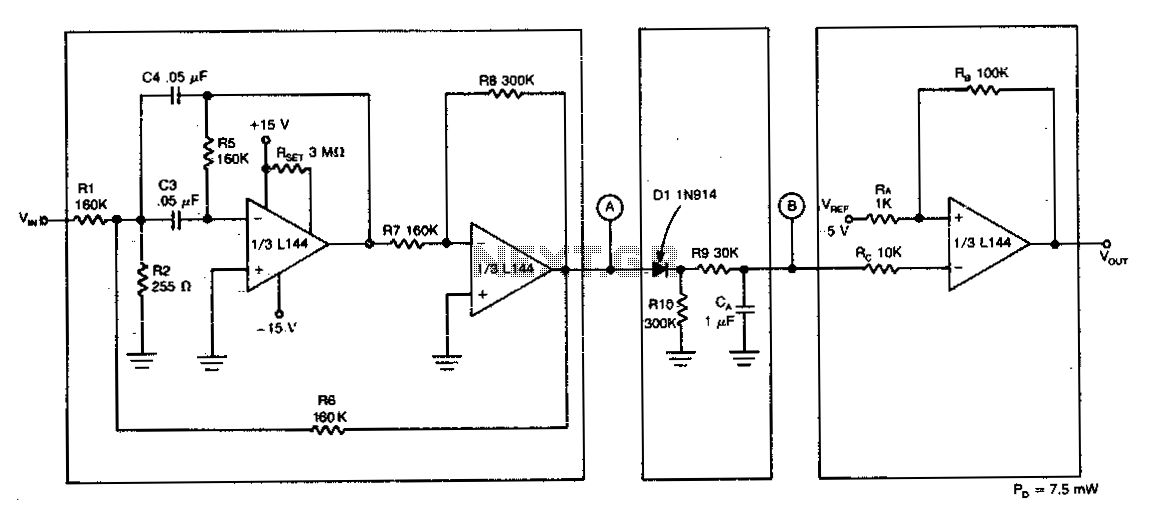
The detector circuit consists of a two-amplifier multiple feedback bandpass filter followed by an AC-to-DC detector section and a Schmitt Trigger. The bandpass filter, with a quality factor (Q) greater than 100, allows only 500 Hz inputs, which are subsequently rectified by diode D1 and filtered by resistor R9 and capacitor C1. This filtering action, combined with a trigger level of 5 V for the Schmitt Trigger, ensures that a minimum of 55 cycles of a 500 Hz input must be present before the output responds to a tone input.
The detector circuit is designed to selectively filter and process signals of a specific frequency while rejecting unwanted noise. The two-amplifier multiple feedback bandpass filter is critical in achieving a high Q factor, which enhances the circuit's selectivity and sensitivity to the desired frequency of 500 Hz. This filter configuration typically employs operational amplifiers configured in a feedback loop, allowing for precise tuning of both the center frequency and bandwidth.
The rectification stage, implemented using diode D1, converts the AC signal output from the bandpass filter into a DC voltage. The subsequent filtering by resistor R9 and capacitor C1 smoothens the rectified signal, providing a stable DC level that can be further processed. The choice of R9 and C1 values is crucial, as they determine the time constant of the filter, affecting how quickly the circuit responds to changes in the input signal.
The Schmitt Trigger serves as a level detector, ensuring that only signals that exceed a specific threshold (5 V in this case) will trigger a response. This hysteresis characteristic of the Schmitt Trigger prevents false triggering from noise or small fluctuations in the input signal, enhancing the reliability of the circuit. The requirement for at least 55 cycles of the 500 Hz input ensures that the circuit only activates in the presence of a stable and consistent tone, further improving the accuracy of detection.
Overall, this detector circuit is well-suited for applications requiring precise frequency detection and reliable output response, making it ideal for various electronic systems where tone recognition is essential.The detector circuit is made up a two-amplifier multiple feedback bandpass filter followed by an ac-to-dc detector section and a Schmitt Trigger. The bandpass filter (with a Q of greater than 100) passes only 5Q0 Hz inputs whch are in turn rectified by Dl and filtered by R9 and Ca
This filtering action in combination with the trigger level of 5 V for the Schmitt device insures that at least 55 cycles of 500 Hz input must be present before the output will react to a tone input.
The detector circuit is designed to selectively filter and process signals of a specific frequency while rejecting unwanted noise. The two-amplifier multiple feedback bandpass filter is critical in achieving a high Q factor, which enhances the circuit's selectivity and sensitivity to the desired frequency of 500 Hz. This filter configuration typically employs operational amplifiers configured in a feedback loop, allowing for precise tuning of both the center frequency and bandwidth.
The rectification stage, implemented using diode D1, converts the AC signal output from the bandpass filter into a DC voltage. The subsequent filtering by resistor R9 and capacitor C1 smoothens the rectified signal, providing a stable DC level that can be further processed. The choice of R9 and C1 values is crucial, as they determine the time constant of the filter, affecting how quickly the circuit responds to changes in the input signal.
The Schmitt Trigger serves as a level detector, ensuring that only signals that exceed a specific threshold (5 V in this case) will trigger a response. This hysteresis characteristic of the Schmitt Trigger prevents false triggering from noise or small fluctuations in the input signal, enhancing the reliability of the circuit. The requirement for at least 55 cycles of the 500 Hz input ensures that the circuit only activates in the presence of a stable and consistent tone, further improving the accuracy of detection.
Overall, this detector circuit is well-suited for applications requiring precise frequency detection and reliable output response, making it ideal for various electronic systems where tone recognition is essential.The detector circuit is made up a two-amplifier multiple feedback bandpass filter followed by an ac-to-dc detector section and a Schmitt Trigger. The bandpass filter (with a Q of greater than 100) passes only 5Q0 Hz inputs whch are in turn rectified by Dl and filtered by R9 and Ca
This filtering action in combination with the trigger level of 5 V for the Schmitt device insures that at least 55 cycles of 500 Hz input must be present before the output will react to a tone input.