
Totem-pole-driver-with-bootstrapping
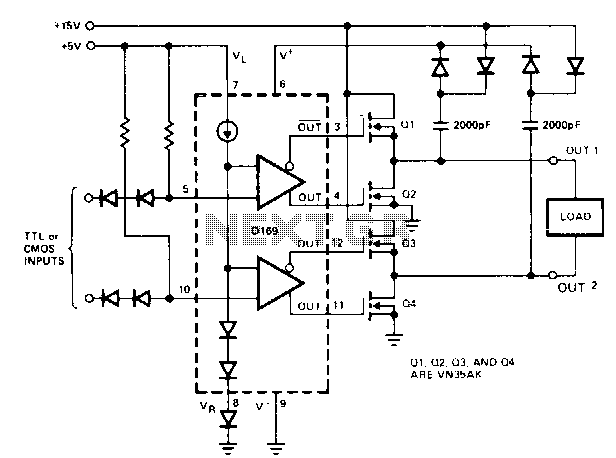
When driving MOSPOWER in a totem-pole output configuration, it is essential to maintain a gate voltage of 10 to 15 V positive relative to the source to manage load currents close to the maximum ratings of the MOSPOWER device. The D169 component is suitable for bootstrapping due to its high-voltage ratings. In the illustrated circuit, the voltage across the 2000-pF bootstrap capacitors is applied to the V+ terminal through diode OR gates. Consequently, irrespective of which output is in a high state, 30 V is present at V+. The maximum switching frequency is influenced by the input capacitance of the MOSPOWER transistors utilized.
The described circuit involves a totem-pole output configuration, which is commonly used in applications requiring efficient driving of MOSPOWER devices. In this arrangement, the gate of the MOSFET must receive a sufficiently high voltage to ensure that it remains in the enhancement mode and can effectively handle the load currents without entering the triode region, which could lead to excessive power dissipation.
The D169 component, noted for its high-voltage capabilities, allows for an effective bootstrapping technique. Bootstrapping is a method that enhances the gate drive voltage above the supply voltage, enabling better switching performance and minimizing losses. In this circuit, the bootstrap capacitors, rated at 2000 pF, are charged to a voltage level that can be utilized to ensure that the gate voltage remains sufficiently high, even under varying load conditions.
Diode OR gates are employed to facilitate the connection of the bootstrap capacitors to the V+ terminal. This configuration ensures that regardless of which output is active, the circuit maintains a constant voltage level of 30 V at the V+ terminal. This voltage is crucial for the reliable operation of the MOSPOWER devices, particularly when switching at high frequencies.
The maximum switching frequency of the circuit is primarily governed by the input capacitance of the MOSPOWER transistors. Higher input capacitance can lead to slower switching speeds due to the increased time required to charge and discharge the gate capacitance. Therefore, selecting MOSPOWER transistors with optimal input capacitance is critical for achieving the desired switching frequency while maintaining efficient operation.
In summary, the circuit design effectively utilizes bootstrapping techniques alongside diode OR gates to maintain a high gate voltage for MOSPOWER devices in totem-pole output configurations, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in high-frequency applications.When driving MOSPOWER in a totem-pole output configuration, it is necessary to have the gate voltage 10 to 15 V positive with respect to the source in order to handle load currents near the MOSPOWER maximum ratings. The D169 lends itself to bootstrapping because of its high-voltage ratings. In the circuit shown, the voltage on the 2000-pF bootstrap capacitors is applied via diode OR gates to the V + terminal.
Therefore, regardless of which output is high, 30 Vis present at V + . Maximum switching frequency is determined by the input capacitance of the MOSPOWER transistors used.
The described circuit involves a totem-pole output configuration, which is commonly used in applications requiring efficient driving of MOSPOWER devices. In this arrangement, the gate of the MOSFET must receive a sufficiently high voltage to ensure that it remains in the enhancement mode and can effectively handle the load currents without entering the triode region, which could lead to excessive power dissipation.
The D169 component, noted for its high-voltage capabilities, allows for an effective bootstrapping technique. Bootstrapping is a method that enhances the gate drive voltage above the supply voltage, enabling better switching performance and minimizing losses. In this circuit, the bootstrap capacitors, rated at 2000 pF, are charged to a voltage level that can be utilized to ensure that the gate voltage remains sufficiently high, even under varying load conditions.
Diode OR gates are employed to facilitate the connection of the bootstrap capacitors to the V+ terminal. This configuration ensures that regardless of which output is active, the circuit maintains a constant voltage level of 30 V at the V+ terminal. This voltage is crucial for the reliable operation of the MOSPOWER devices, particularly when switching at high frequencies.
The maximum switching frequency of the circuit is primarily governed by the input capacitance of the MOSPOWER transistors. Higher input capacitance can lead to slower switching speeds due to the increased time required to charge and discharge the gate capacitance. Therefore, selecting MOSPOWER transistors with optimal input capacitance is critical for achieving the desired switching frequency while maintaining efficient operation.
In summary, the circuit design effectively utilizes bootstrapping techniques alongside diode OR gates to maintain a high gate voltage for MOSPOWER devices in totem-pole output configurations, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in high-frequency applications.When driving MOSPOWER in a totem-pole output configuration, it is necessary to have the gate voltage 10 to 15 V positive with respect to the source in order to handle load currents near the MOSPOWER maximum ratings. The D169 lends itself to bootstrapping because of its high-voltage ratings. In the circuit shown, the voltage on the 2000-pF bootstrap capacitors is applied via diode OR gates to the V + terminal.
Therefore, regardless of which output is high, 30 Vis present at V + . Maximum switching frequency is determined by the input capacitance of the MOSPOWER transistors used.