Transistor Tester Identifies Terminals Power

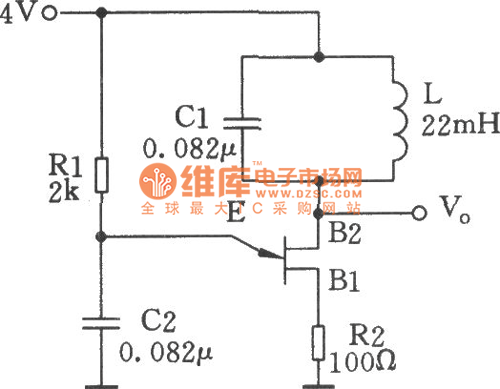
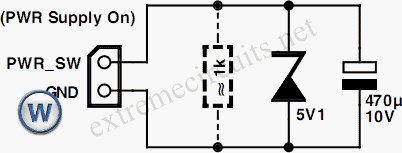
The simple transistor tester in Figure 1 allows for the identification of the type of transistor and aids in detecting the emitter, collector, and base of the transistor.
The simple transistor tester circuit is designed to facilitate the identification of transistor types (NPN or PNP) and to verify the functionality of the transistor's terminals: emitter, collector, and base. The circuit typically consists of a few key components, including resistors, a power supply, and a transistor socket for easy insertion of the device under test.
When the transistor is inserted into the socket, the circuit applies a small voltage to the base terminal, which allows for the determination of the transistor type based on its response. For an NPN transistor, a current will flow from the collector to the emitter when a positive voltage is applied to the base. Conversely, for a PNP transistor, the current will flow from the emitter to the collector when a negative voltage is applied to the base.
The circuit may also include an LED indicator that lights up when the transistor is functioning correctly, providing a visual confirmation of the transistor's operational status. Additionally, the use of multimeter probes can enhance testing capabilities, allowing for the measurement of voltage and current levels across the transistor terminals.
This simple tester is an invaluable tool for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike, as it provides a quick and effective means to assess transistor functionality without the need for complex equipment. Proper understanding and usage of this circuit can lead to more efficient troubleshooting and repair of electronic devices.The simple transistor tester in Figure 1 lets you identify the type of transistor, and it helps in detecting a transistor`s emitter, collector, and base.. 🔗 External reference
The simple transistor tester circuit is designed to facilitate the identification of transistor types (NPN or PNP) and to verify the functionality of the transistor's terminals: emitter, collector, and base. The circuit typically consists of a few key components, including resistors, a power supply, and a transistor socket for easy insertion of the device under test.
When the transistor is inserted into the socket, the circuit applies a small voltage to the base terminal, which allows for the determination of the transistor type based on its response. For an NPN transistor, a current will flow from the collector to the emitter when a positive voltage is applied to the base. Conversely, for a PNP transistor, the current will flow from the emitter to the collector when a negative voltage is applied to the base.
The circuit may also include an LED indicator that lights up when the transistor is functioning correctly, providing a visual confirmation of the transistor's operational status. Additionally, the use of multimeter probes can enhance testing capabilities, allowing for the measurement of voltage and current levels across the transistor terminals.
This simple tester is an invaluable tool for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike, as it provides a quick and effective means to assess transistor functionality without the need for complex equipment. Proper understanding and usage of this circuit can lead to more efficient troubleshooting and repair of electronic devices.The simple transistor tester in Figure 1 lets you identify the type of transistor, and it helps in detecting a transistor`s emitter, collector, and base.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713