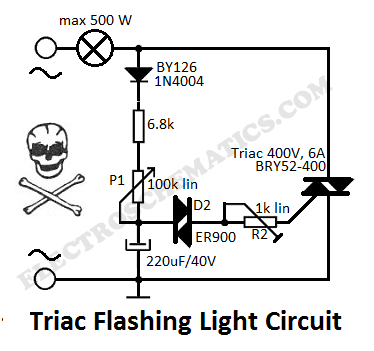
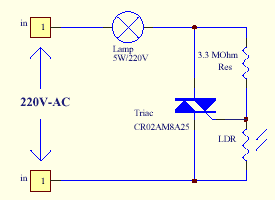
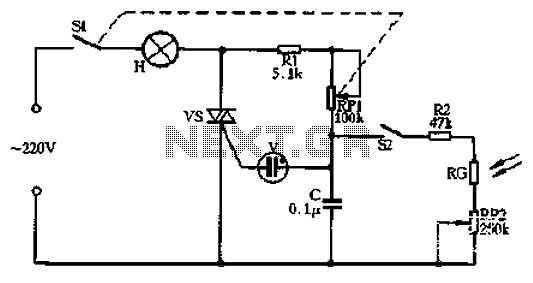
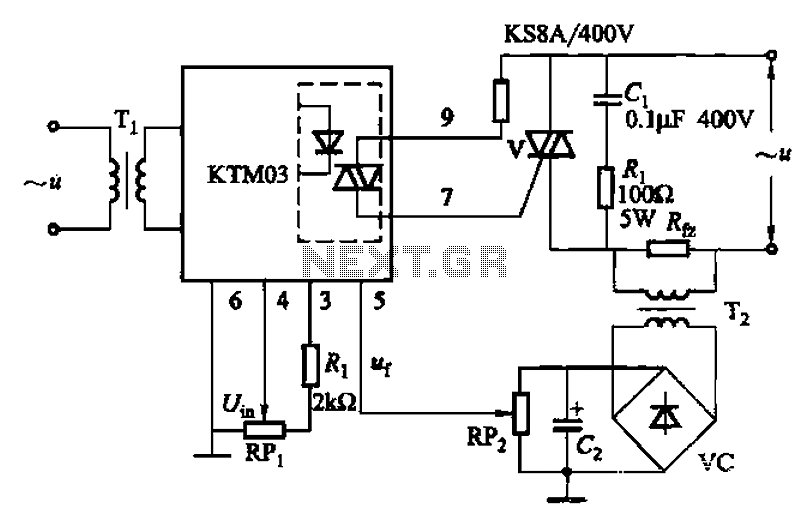
TRIAC Basic Operation
A TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) is an electronic component that can control power in both directions within an AC circuit.
The TRIAC is a semiconductor device that enables the control of alternating current by allowing current to flow in both the positive and negative cycles of the AC waveform. It is essentially a bidirectional thyristor that can be triggered into conduction by a gate signal. Once triggered, the TRIAC remains in the conducting state until the current flowing through it drops below a certain threshold, known as the holding current.
In typical applications, TRIACs are used in light dimmers, motor speed controls, and heating control systems. The ability to control power in both directions makes them particularly useful for managing AC loads.
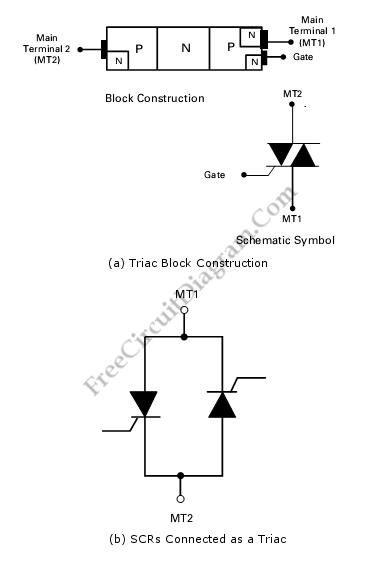
The operation of a TRIAC can be understood through its three terminals: the anode (A1), the anode (A2), and the gate (G). When a small voltage is applied to the gate, the TRIAC becomes conductive, allowing current to flow between A1 and A2. The device can handle high voltages and currents, making it suitable for various power control applications.
In terms of circuit design, the TRIAC can be integrated with additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and optoisolators to create more complex control systems. For instance, using an optoisolator in conjunction with a TRIAC allows for electrical isolation between the control signal and the AC load, enhancing safety and reliability in the circuit.
When designing circuits that utilize TRIACs, it is essential to consider parameters such as the maximum voltage rating, current rating, and the required gate trigger current to ensure proper operation and prevent damage to the component.Triode for alternating current,TRIAC, is an electronic component that can control power in two direction in an AC circuit. The figure (a) shows the block. 🔗 External reference
The TRIAC is a semiconductor device that enables the control of alternating current by allowing current to flow in both the positive and negative cycles of the AC waveform. It is essentially a bidirectional thyristor that can be triggered into conduction by a gate signal. Once triggered, the TRIAC remains in the conducting state until the current flowing through it drops below a certain threshold, known as the holding current.
In typical applications, TRIACs are used in light dimmers, motor speed controls, and heating control systems. The ability to control power in both directions makes them particularly useful for managing AC loads.
The operation of a TRIAC can be understood through its three terminals: the anode (A1), the anode (A2), and the gate (G). When a small voltage is applied to the gate, the TRIAC becomes conductive, allowing current to flow between A1 and A2. The device can handle high voltages and currents, making it suitable for various power control applications.
In terms of circuit design, the TRIAC can be integrated with additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and optoisolators to create more complex control systems. For instance, using an optoisolator in conjunction with a TRIAC allows for electrical isolation between the control signal and the AC load, enhancing safety and reliability in the circuit.
When designing circuits that utilize TRIACs, it is essential to consider parameters such as the maximum voltage rating, current rating, and the required gate trigger current to ensure proper operation and prevent damage to the component.Triode for alternating current,TRIAC, is an electronic component that can control power in two direction in an AC circuit. The figure (a) shows the block. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713