Tritium Solar engine
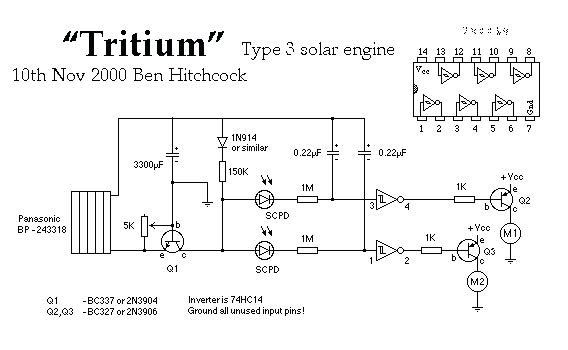
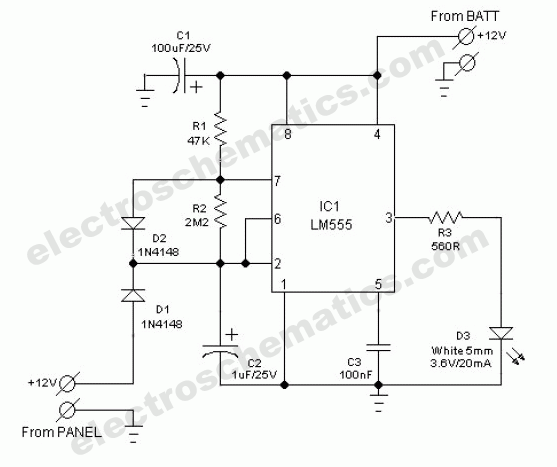
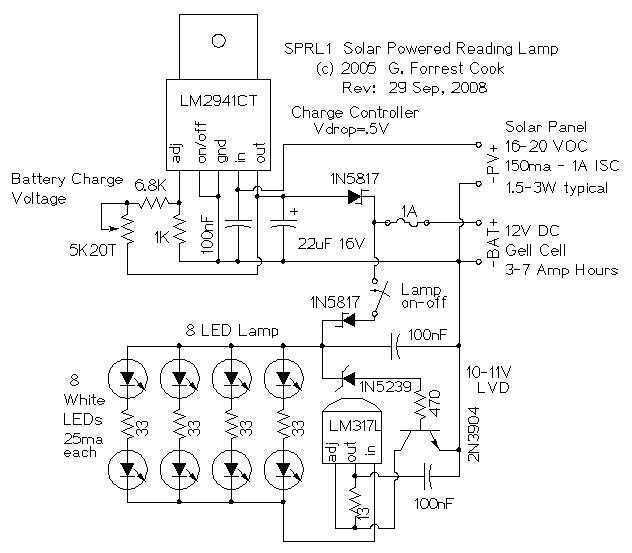
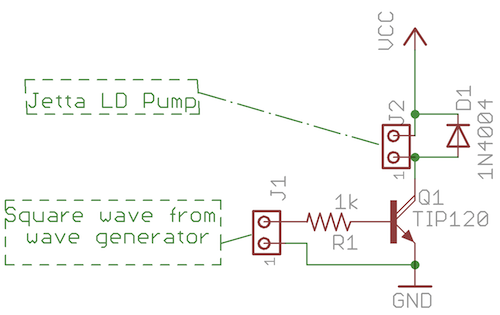
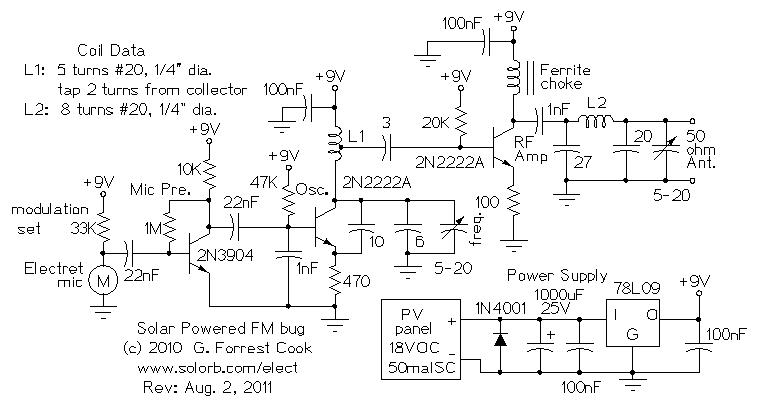
The Tritium circuit was the first type 3 SE. As such, it is quite experimental and should be regarded as a prototype rather than the state of the art. Nevertheless, it does function reasonably well, and in some circumstances outperforms other solar engines such as the Freds that I have lying around. It works by charging the capacitor through the base-emitter junction of an NPN transistor (Q1). When current is flowing through this junction, the collector is held low. When the charging current tapers off, the collector will start to drift higher pulled.
The Tritium circuit, classified as a type 3 solar engine (SE), represents an early experimental design that serves as a prototype for further development. The circuit's primary component is an NPN transistor (Q1), which plays a crucial role in regulating the flow of current through its base-emitter junction. The operation begins with the solar energy being harnessed to charge a capacitor, which is integral to the circuit's function.
In this configuration, the capacitor charges through the base-emitter junction of Q1. During this phase, the transistor remains in a saturated state, allowing current to flow freely. This results in the collector voltage being held low, effectively maintaining a stable state until the capacitor reaches a certain charge threshold. As the charging current diminishes, the transistor transitions from saturation, causing the collector voltage to rise due to the lack of sufficient base current to keep it in the low state.
The design of the Tritium circuit emphasizes its experimental nature, as it has been observed to outperform other existing solar engine designs, such as the Freds. This performance can be attributed to the efficient charging mechanism facilitated by the NPN transistor, which allows for a rapid response to changes in solar input. The prototype nature of the circuit suggests that while it demonstrates promising results, further refinement and optimization are necessary to enhance its reliability and efficiency in various applications.
Overall, the Tritium circuit serves as a significant step in the evolution of solar engine technology, providing insights into the potential for improved designs and applications in renewable energy systems.The Tritium circuit was the first (to my knowledge) type 3 SE. As such, it is quite experimental, and should be regarded as a prototype rather than the `state of the art`! Nevertheless, it does function reasonably well, and in some circumstances outperforms other solar engines such as the Freds that I have lying around.
It works by charging the capacitor through the base-emitter junction of an NPN transistor (Q1). When current is flowing through this junction, the collector is held low. When the charging current tapers off, the collector will start to drift higher pulled 🔗 External reference
The Tritium circuit, classified as a type 3 solar engine (SE), represents an early experimental design that serves as a prototype for further development. The circuit's primary component is an NPN transistor (Q1), which plays a crucial role in regulating the flow of current through its base-emitter junction. The operation begins with the solar energy being harnessed to charge a capacitor, which is integral to the circuit's function.
In this configuration, the capacitor charges through the base-emitter junction of Q1. During this phase, the transistor remains in a saturated state, allowing current to flow freely. This results in the collector voltage being held low, effectively maintaining a stable state until the capacitor reaches a certain charge threshold. As the charging current diminishes, the transistor transitions from saturation, causing the collector voltage to rise due to the lack of sufficient base current to keep it in the low state.
The design of the Tritium circuit emphasizes its experimental nature, as it has been observed to outperform other existing solar engine designs, such as the Freds. This performance can be attributed to the efficient charging mechanism facilitated by the NPN transistor, which allows for a rapid response to changes in solar input. The prototype nature of the circuit suggests that while it demonstrates promising results, further refinement and optimization are necessary to enhance its reliability and efficiency in various applications.
Overall, the Tritium circuit serves as a significant step in the evolution of solar engine technology, providing insights into the potential for improved designs and applications in renewable energy systems.The Tritium circuit was the first (to my knowledge) type 3 SE. As such, it is quite experimental, and should be regarded as a prototype rather than the `state of the art`! Nevertheless, it does function reasonably well, and in some circumstances outperforms other solar engines such as the Freds that I have lying around.
It works by charging the capacitor through the base-emitter junction of an NPN transistor (Q1). When current is flowing through this junction, the collector is held low. When the charging current tapers off, the collector will start to drift higher pulled 🔗 External reference