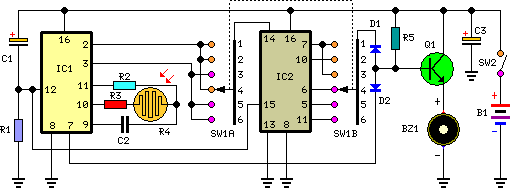
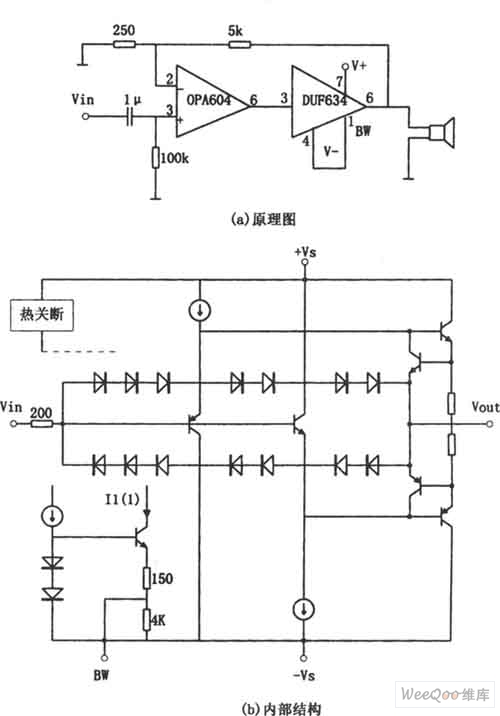
Twin-T Audio Oscillator circuit
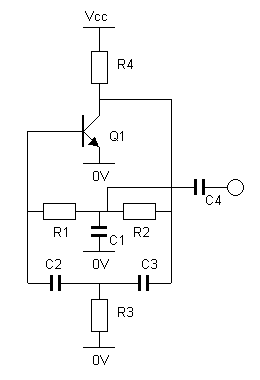
The output of this circuit should be connected to a high-impedance load, typically greater than 100K ohms, while noting that the impedance of capacitor C4 is approximately 3K ohms. A PNP transistor may also be utilized, requiring adjustments to the supply voltage. An operational amplifier (op-amp) can be employed with the following connections: Op-Amp Transistor Output Collector Inverting Input Base Non-Inverting Input Emitter. Additional specifications include: R1 = R2, R3 = 0.1 x R1, C2 = C3, C1 = 2 x C2, R4 = approximately 3K3, C4 = approximately 50nF, and Q1 can be any NPN audio amplifier, such as the BC108. The supply voltage (Vcc) is flexible, with a range of 6 to 12 volts being suitable, and higher or lower voltages may also function adequately.
This circuit is designed to drive a high-impedance load, which is essential for applications requiring minimal current draw from the signal source. The choice of components is critical for ensuring optimal performance. The PNP transistor option allows for versatility in circuit design, particularly in applications where a negative voltage supply is preferred. When using an op-amp, the configuration must ensure that the inverting and non-inverting inputs are correctly connected to maintain the desired feedback and gain characteristics.
The resistor values are defined with R1 and R2 being equal, which can help stabilize the gain of the circuit. The relationship between R3 and R1, where R3 is set to 0.1 times R1, suggests a feedback mechanism that will influence the overall gain. Capacitors C2 and C3 being equal ensures that the timing or filtering characteristics remain consistent, while C1 being twice the value of C2 indicates a deliberate design choice to modify frequency response or filter characteristics.
The approximate values for R4 and C4 suggest that they are used for biasing and frequency response shaping within the circuit. The choice of Q1 as an NPN audio amplifier like the BC108 indicates that the circuit is likely intended for audio applications, where low distortion and adequate gain are required. The flexibility in the supply voltage (Vcc) allows for adaptability in various circuit environments, making this design suitable for prototyping or integration into larger systems.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to signal amplification and processing, suitable for a range of electronic applications.The output of this circuit should be fed into a high-impedance load, say >100K, remembering that the impedance of C4 is around 3K. A PNP transistor can also be used, with the necessary changes to the supply voltage. An op-amp can also be used, connected as follows: Op-Amp Transistor Output Collector Inverting Input Base Non-Inverting Input Emitter
R1 = R2 R3 = 0.1 x R1 C2 = C3 C1 = 2 x C2 R4 = 3K3 (approx) C4 = 50nF (approx) Q1 = any NPN audio amplifier. e.g. BC108, etc Vcc is not critical, 6 to 12Vshould work fine. Higher or lower voltages may also work OK. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to drive a high-impedance load, which is essential for applications requiring minimal current draw from the signal source. The choice of components is critical for ensuring optimal performance. The PNP transistor option allows for versatility in circuit design, particularly in applications where a negative voltage supply is preferred. When using an op-amp, the configuration must ensure that the inverting and non-inverting inputs are correctly connected to maintain the desired feedback and gain characteristics.
The resistor values are defined with R1 and R2 being equal, which can help stabilize the gain of the circuit. The relationship between R3 and R1, where R3 is set to 0.1 times R1, suggests a feedback mechanism that will influence the overall gain. Capacitors C2 and C3 being equal ensures that the timing or filtering characteristics remain consistent, while C1 being twice the value of C2 indicates a deliberate design choice to modify frequency response or filter characteristics.
The approximate values for R4 and C4 suggest that they are used for biasing and frequency response shaping within the circuit. The choice of Q1 as an NPN audio amplifier like the BC108 indicates that the circuit is likely intended for audio applications, where low distortion and adequate gain are required. The flexibility in the supply voltage (Vcc) allows for adaptability in various circuit environments, making this design suitable for prototyping or integration into larger systems.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective approach to signal amplification and processing, suitable for a range of electronic applications.The output of this circuit should be fed into a high-impedance load, say >100K, remembering that the impedance of C4 is around 3K. A PNP transistor can also be used, with the necessary changes to the supply voltage. An op-amp can also be used, connected as follows: Op-Amp Transistor Output Collector Inverting Input Base Non-Inverting Input Emitter
R1 = R2 R3 = 0.1 x R1 C2 = C3 C1 = 2 x C2 R4 = 3K3 (approx) C4 = 50nF (approx) Q1 = any NPN audio amplifier. e.g. BC108, etc Vcc is not critical, 6 to 12Vshould work fine. Higher or lower voltages may also work OK. 🔗 External reference