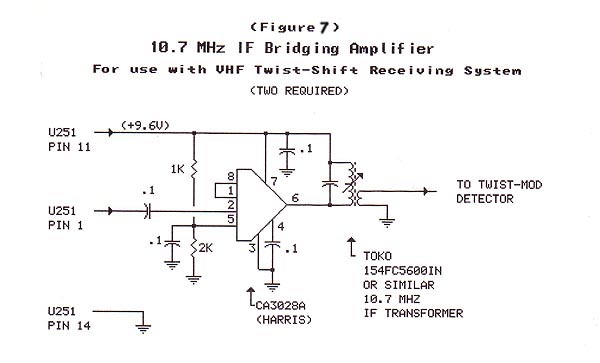
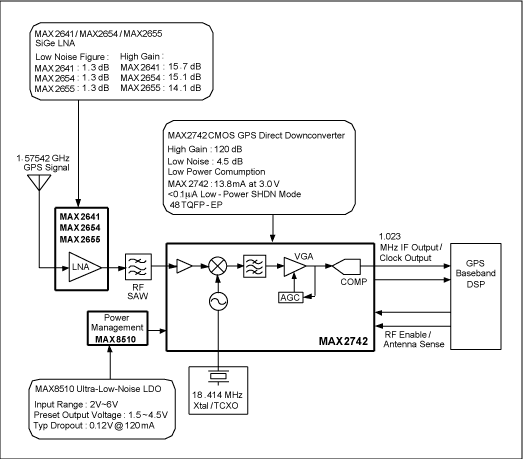
VHF radio receiver
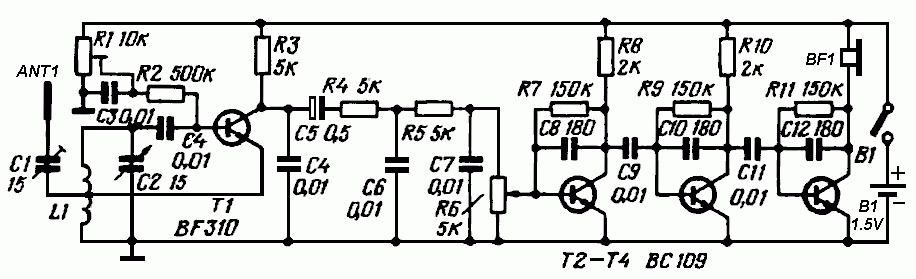
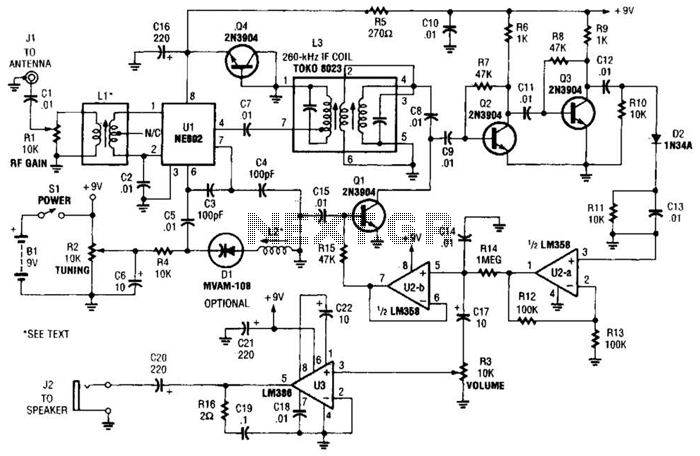
The schematic diagram presented below illustrates a simple FM receiver constructed using four transistors. The signal from the antenna passes through the trimmer capacitor C1 before reaching the input of the first stage, which operates as a super-regenerative detector utilizing the transistor T1 circuit. The potentiometer R1 is employed to adjust the regeneration. The trimmer capacitor C1 is also utilized to fine-tune the coupling between the antenna and the resonant tank formed by inductor L1 and capacitor C2. An audio signal is generated from the output of the super-regenerative detector and is subsequently processed through a low-pass filter to reduce noise levels before being amplified by the audio amplifier. This amplifier is comprised of transistors T2, T3, and T4, with each stage featuring a negative AC feedback loop facilitated by capacitors C8, C10, and C12. The load connected to the amplifier consists of high-impedance headphones. The coil L1 is constructed on a mandrel with a diameter of 12 mm and a length of 10 mm, consisting of three turns of silver-plated wire with a diameter of 1.5 mm (AWG 15). This coil is tapped at its midpoint, allowing for operation within a frequency range of 100 to 170 MHz.
The FM receiver schematic operates by first capturing radio frequency signals through the antenna, which is coupled to the resonant tank circuit formed by L1 and C2. The trimmer capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in optimizing the antenna's coupling efficiency, allowing for better signal reception. The super-regenerative detector, implemented with transistor T1, demodulates the incoming FM signals, converting them into audio frequencies. The regeneration adjustment via potentiometer R1 is essential for maximizing sensitivity and selectivity, ensuring that the receiver can effectively distinguish between different frequencies.
Following demodulation, the audio signal is filtered through a low-pass filter designed to eliminate high-frequency noise that could interfere with audio clarity. This filtering stage is critical as it enhances the overall sound quality delivered to the audio amplifier stages. The audio amplifier, composed of transistors T2, T3, and T4, amplifies the filtered audio signal. The incorporation of negative AC feedback through capacitors C8, C10, and C12 stabilizes the amplifier's gain and reduces distortion, resulting in a cleaner audio output.
The design of coil L1 is significant, as its dimensions and the number of turns directly influence the tuning characteristics of the receiver. The choice of silver-plated wire for the coil enhances conductivity, thereby improving performance. The ability to tap the coil at its midpoint allows for flexibility in tuning, enabling the receiver to operate effectively across the specified frequency range of 100 to 170 MHz. This configuration makes the FM receiver suitable for various applications, including personal listening and educational demonstrations in radio frequency technology.The figure below shows a schematic diagram of a simple FM receiver. This receiver made with four transistors. The signal from the antenna through the trimmer capacitor C1 goes to the input of the first stage. This stage is a super-regenerative detector based on the transistor T1 circuit. The potentiometer R1 is used to adjust the regeneration. The trimmer C1 is used to adjust the coupling of the antenna to the resonant tank L1C2. An audio signal from the output of the super-regenerative detector through a low-pass filter is fed to an audio amplifier. The filter reduces the noise level at the input of the audio amplifier. The audio amplifier is based on transistors T2-T4. Each stage of the amplifier has a negative AC feedback loop (capacitors C8, C10 and C12). A load of the amplifier is the high-impedance headphones. The coil L1 is wound on a mandrel of diameter 12 mm and length of 10 mm. It contains 3 turns of silver-plated wire with a diameter of 1. 5 mm (AWG 15). The coil L1 is tapped in the middle. With this coil the frequency range is 100. 170MHz. 🔗 External reference
The FM receiver schematic operates by first capturing radio frequency signals through the antenna, which is coupled to the resonant tank circuit formed by L1 and C2. The trimmer capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in optimizing the antenna's coupling efficiency, allowing for better signal reception. The super-regenerative detector, implemented with transistor T1, demodulates the incoming FM signals, converting them into audio frequencies. The regeneration adjustment via potentiometer R1 is essential for maximizing sensitivity and selectivity, ensuring that the receiver can effectively distinguish between different frequencies.
Following demodulation, the audio signal is filtered through a low-pass filter designed to eliminate high-frequency noise that could interfere with audio clarity. This filtering stage is critical as it enhances the overall sound quality delivered to the audio amplifier stages. The audio amplifier, composed of transistors T2, T3, and T4, amplifies the filtered audio signal. The incorporation of negative AC feedback through capacitors C8, C10, and C12 stabilizes the amplifier's gain and reduces distortion, resulting in a cleaner audio output.
The design of coil L1 is significant, as its dimensions and the number of turns directly influence the tuning characteristics of the receiver. The choice of silver-plated wire for the coil enhances conductivity, thereby improving performance. The ability to tap the coil at its midpoint allows for flexibility in tuning, enabling the receiver to operate effectively across the specified frequency range of 100 to 170 MHz. This configuration makes the FM receiver suitable for various applications, including personal listening and educational demonstrations in radio frequency technology.The figure below shows a schematic diagram of a simple FM receiver. This receiver made with four transistors. The signal from the antenna through the trimmer capacitor C1 goes to the input of the first stage. This stage is a super-regenerative detector based on the transistor T1 circuit. The potentiometer R1 is used to adjust the regeneration. The trimmer C1 is used to adjust the coupling of the antenna to the resonant tank L1C2. An audio signal from the output of the super-regenerative detector through a low-pass filter is fed to an audio amplifier. The filter reduces the noise level at the input of the audio amplifier. The audio amplifier is based on transistors T2-T4. Each stage of the amplifier has a negative AC feedback loop (capacitors C8, C10 and C12). A load of the amplifier is the high-impedance headphones. The coil L1 is wound on a mandrel of diameter 12 mm and length of 10 mm. It contains 3 turns of silver-plated wire with a diameter of 1. 5 mm (AWG 15). The coil L1 is tapped in the middle. With this coil the frequency range is 100. 170MHz. 🔗 External reference