
Voltage-controlled-attenuator
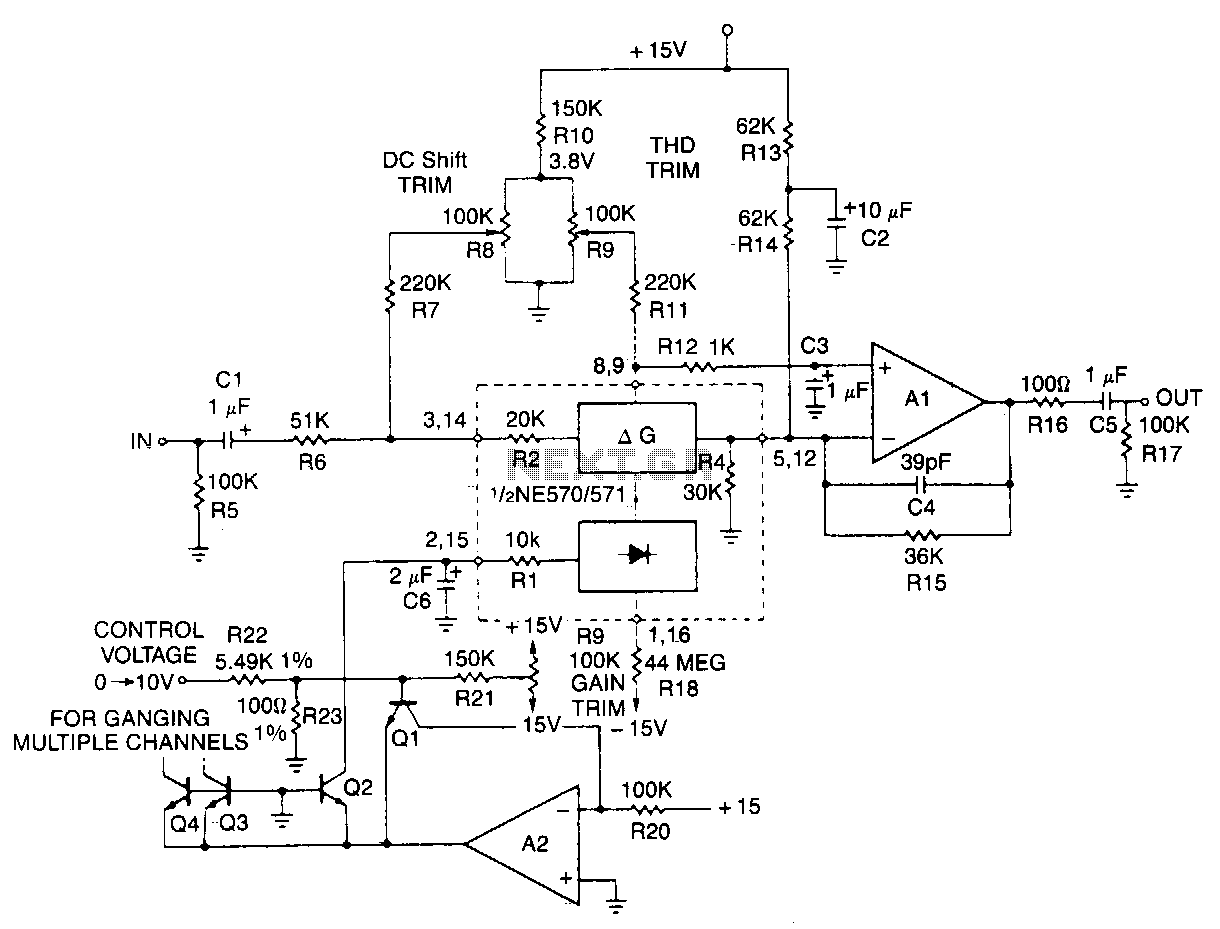
This typical circuit utilizes an external operational amplifier for improved performance, along with an exponential converter to achieve a control characteristic of -6 dB per volt. Trim networks are incorporated to eliminate distortion and offset, as well as to finely adjust the gain to 0 dB with a control voltage of 0 V.
The circuit design features an external operational amplifier (op-amp) to enhance performance characteristics compared to internal solutions. The op-amp is configured in a feedback arrangement to provide high gain stability and low distortion. The exponential converter is essential for translating the linear control voltage into a logarithmic output, achieving the desired -6 dB per volt control characteristic. This allows for precise control over the gain of the circuit, which is particularly beneficial in applications requiring fine adjustments.
Trim networks are strategically included in the design to compensate for any distortion and offset that may arise during operation. These networks typically consist of variable resistors or potentiometers that can be adjusted to null out unwanted artifacts in the signal path. The ability to finely tune the gain to 0 dB at a control voltage of 0 V ensures that the circuit can operate effectively across its specified range without introducing additional noise or distortion.
Overall, this circuit configuration is ideal for applications where high performance, precision control, and low distortion are critical, such as in audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems. The careful integration of the op-amp, exponential converter, and trim networks contributes to the circuit's robustness and reliability in various electronic applications.This typical circuit uses an external op amp for better perlormance and an exponential converter to get a control characteristic of -6 dB IV. Trim networks are shown to null out distortion and de shift, and to fine trim the gain to 0 dB with 0 V of control voltage. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design features an external operational amplifier (op-amp) to enhance performance characteristics compared to internal solutions. The op-amp is configured in a feedback arrangement to provide high gain stability and low distortion. The exponential converter is essential for translating the linear control voltage into a logarithmic output, achieving the desired -6 dB per volt control characteristic. This allows for precise control over the gain of the circuit, which is particularly beneficial in applications requiring fine adjustments.
Trim networks are strategically included in the design to compensate for any distortion and offset that may arise during operation. These networks typically consist of variable resistors or potentiometers that can be adjusted to null out unwanted artifacts in the signal path. The ability to finely tune the gain to 0 dB at a control voltage of 0 V ensures that the circuit can operate effectively across its specified range without introducing additional noise or distortion.
Overall, this circuit configuration is ideal for applications where high performance, precision control, and low distortion are critical, such as in audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems. The careful integration of the op-amp, exponential converter, and trim networks contributes to the circuit's robustness and reliability in various electronic applications.This typical circuit uses an external op amp for better perlormance and an exponential converter to get a control characteristic of -6 dB IV. Trim networks are shown to null out distortion and de shift, and to fine trim the gain to 0 dB with 0 V of control voltage. 🔗 External reference