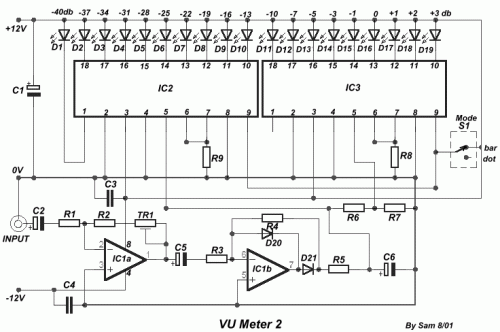
VU Meter 2
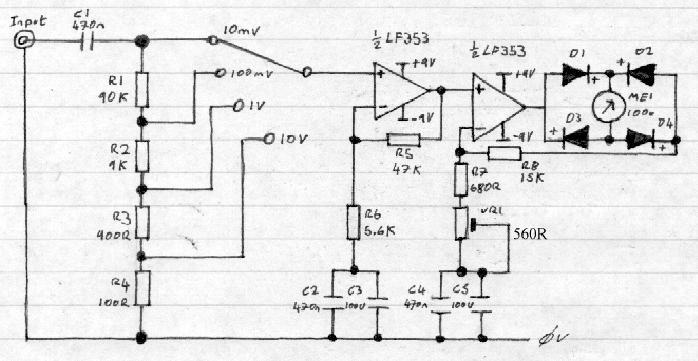
A circuit for measuring levels based on a typical application of National.
A measurement circuit designed for level detection typically employs a combination of sensors and signal processing components to provide accurate readings. In this context, the circuit can utilize a variety of technologies, such as resistive, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors, depending on the specific application requirements.
For instance, a resistive level sensor might consist of two electrodes placed at different heights within a tank. As the liquid level rises, the resistance between the electrodes changes, which can be measured and converted into a level indication. This method is straightforward but may be affected by the properties of the liquid, such as conductivity.
Alternatively, a capacitive level sensor operates by measuring the change in capacitance caused by the dielectric properties of the liquid. This type of sensor can be more versatile and less affected by the liquid's conductivity, making it suitable for a wider range of applications.
Ultrasonic level sensors utilize sound waves to measure the distance to the liquid surface. An ultrasonic transducer emits a pulse that reflects off the surface of the liquid and returns to the sensor. The time taken for the echo to return is proportional to the distance, allowing for precise level measurement. This method is non-contact and can be effective for various liquids and conditions.
The output from these sensors is typically fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to process and interpret the signal. Microcontrollers or dedicated level monitoring ICs can be employed to analyze the digital data and provide a visual or digital output indicating the liquid level. Additionally, these circuits may include alarm systems or control outputs to manage pumps or valves based on the measured levels.
Overall, the design of a level measurement circuit must consider factors such as sensor type, environmental conditions, required accuracy, and response time to ensure reliable operation in its intended application.A circuit of measurement of level based on a typical application of National 🔗 External reference
A measurement circuit designed for level detection typically employs a combination of sensors and signal processing components to provide accurate readings. In this context, the circuit can utilize a variety of technologies, such as resistive, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensors, depending on the specific application requirements.
For instance, a resistive level sensor might consist of two electrodes placed at different heights within a tank. As the liquid level rises, the resistance between the electrodes changes, which can be measured and converted into a level indication. This method is straightforward but may be affected by the properties of the liquid, such as conductivity.
Alternatively, a capacitive level sensor operates by measuring the change in capacitance caused by the dielectric properties of the liquid. This type of sensor can be more versatile and less affected by the liquid's conductivity, making it suitable for a wider range of applications.
Ultrasonic level sensors utilize sound waves to measure the distance to the liquid surface. An ultrasonic transducer emits a pulse that reflects off the surface of the liquid and returns to the sensor. The time taken for the echo to return is proportional to the distance, allowing for precise level measurement. This method is non-contact and can be effective for various liquids and conditions.
The output from these sensors is typically fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to process and interpret the signal. Microcontrollers or dedicated level monitoring ICs can be employed to analyze the digital data and provide a visual or digital output indicating the liquid level. Additionally, these circuits may include alarm systems or control outputs to manage pumps or valves based on the measured levels.
Overall, the design of a level measurement circuit must consider factors such as sensor type, environmental conditions, required accuracy, and response time to ensure reliable operation in its intended application.A circuit of measurement of level based on a typical application of National 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713