
Warning-light-and-marker-light
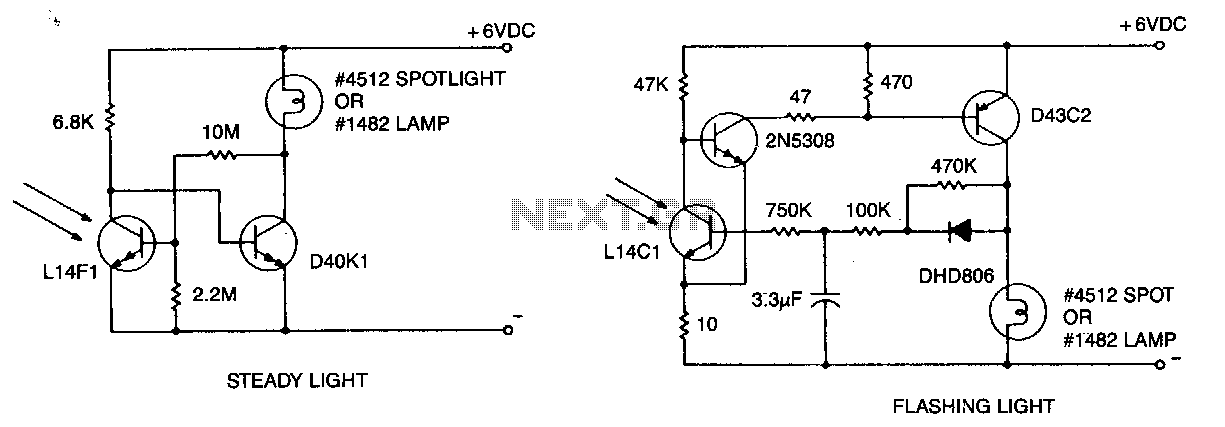
A flashing light with high brightness and a short duty cycle is often required to ensure maximum visibility and battery life. This requires the use of an output transistor capable of supplying the cold filament surge current of the lamp while keeping a low saturation voltage. The oscillation period and flash duration are determined within the feedback loop, and the implementation of a phototransistor sensor reduces sensitivity variations.
In designing a circuit for a high-brightness flashing light, several key components and considerations must be accounted for. The output transistor serves as a critical element, as it must handle the initial surge current when the lamp is turned on. This current is significantly higher than the steady-state current, especially for incandescent bulbs, which have cold filaments that present a lower resistance when unlit. A suitable transistor, such as an N-channel MOSFET or a power BJT, should be selected based on its current rating and low saturation voltage to ensure efficient operation and minimal power loss.
The feedback loop is essential for controlling the flashing behavior of the light. It typically involves a timing circuit, which can be implemented using a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller. The timing component determines the oscillation period and the duration of each flash. The duty cycle can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values in the timing circuit, allowing for flexibility in the flash rate and duration to suit specific applications.
Incorporating a phototransistor sensor into the circuit enhances performance by providing feedback on the light output. This sensor can detect the intensity of the light and adjust the duty cycle accordingly to maintain a consistent brightness level, compensating for variations in ambient light conditions or battery voltage. The phototransistor's output can be fed back into the control circuitry to dynamically adjust the flash duration and ensure optimal visibility while conserving battery life.
Overall, the design of a high-brightness flashing light circuit involves careful selection of components, precise timing control, and feedback mechanisms to achieve the desired performance characteristics while maximizing efficiency and longevity.A flashing light of high brightness and short duty cycle is often desired to provide maximum visibility and battery life. This necessitates using an output transistor, which can supply the cold filament surge current of the lamp while maintaining a low saturation voltage.
The oscillation period and flash duration are determined in the feedback loop, while the use of a phototransistor sensor minimizes sensitivity variations. 🔗 External reference
In designing a circuit for a high-brightness flashing light, several key components and considerations must be accounted for. The output transistor serves as a critical element, as it must handle the initial surge current when the lamp is turned on. This current is significantly higher than the steady-state current, especially for incandescent bulbs, which have cold filaments that present a lower resistance when unlit. A suitable transistor, such as an N-channel MOSFET or a power BJT, should be selected based on its current rating and low saturation voltage to ensure efficient operation and minimal power loss.
The feedback loop is essential for controlling the flashing behavior of the light. It typically involves a timing circuit, which can be implemented using a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller. The timing component determines the oscillation period and the duration of each flash. The duty cycle can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values in the timing circuit, allowing for flexibility in the flash rate and duration to suit specific applications.
Incorporating a phototransistor sensor into the circuit enhances performance by providing feedback on the light output. This sensor can detect the intensity of the light and adjust the duty cycle accordingly to maintain a consistent brightness level, compensating for variations in ambient light conditions or battery voltage. The phototransistor's output can be fed back into the control circuitry to dynamically adjust the flash duration and ensure optimal visibility while conserving battery life.
Overall, the design of a high-brightness flashing light circuit involves careful selection of components, precise timing control, and feedback mechanisms to achieve the desired performance characteristics while maximizing efficiency and longevity.A flashing light of high brightness and short duty cycle is often desired to provide maximum visibility and battery life. This necessitates using an output transistor, which can supply the cold filament surge current of the lamp while maintaining a low saturation voltage.
The oscillation period and flash duration are determined in the feedback loop, while the use of a phototransistor sensor minimizes sensitivity variations. 🔗 External reference