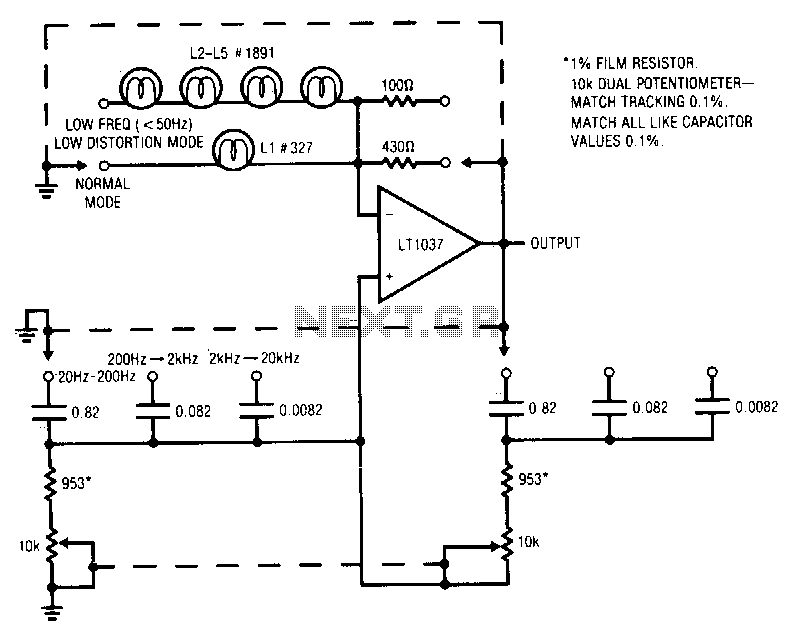
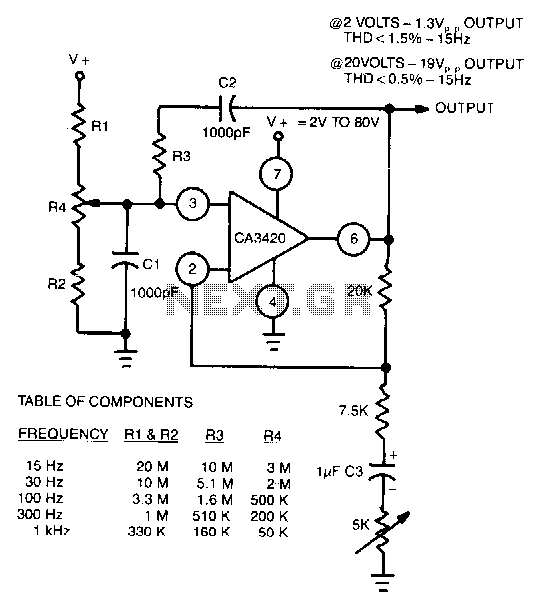
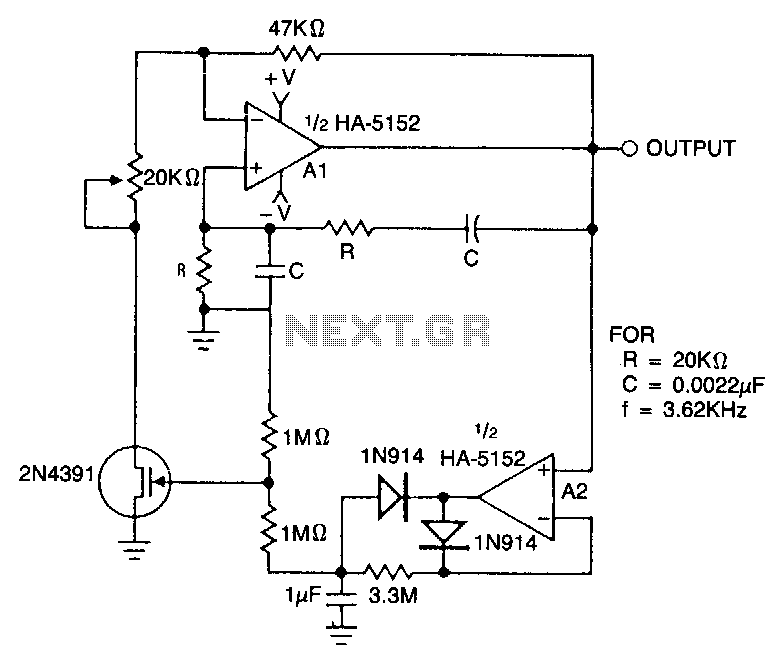
Wien-bridge-oscillator
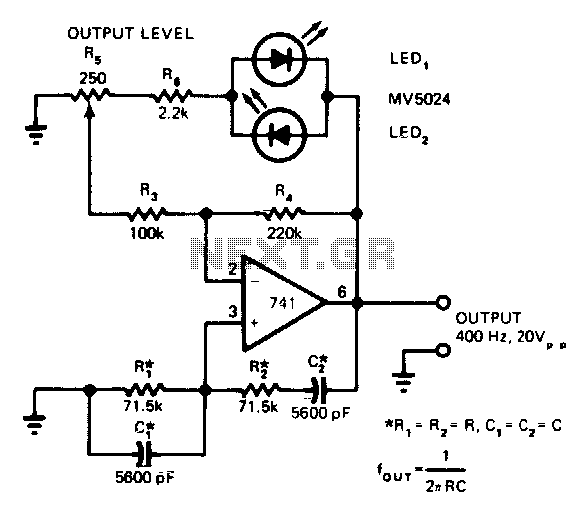
LEDs function as both pilot lamps and as an AGC (automatic gain control) in this unconventional amplitude-stabilized oscillator.
The circuit utilizes Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) for dual purposes, acting as pilot lamps to indicate operational status and as components in the automatic gain control mechanism. The amplitude-stabilized oscillator is designed to maintain consistent output levels despite variations in input conditions or load changes.
In this configuration, the LEDs are integrated into the feedback loop of the oscillator. When the output amplitude exceeds a predetermined threshold, the AGC circuit detects this condition and adjusts the gain accordingly. This adjustment is achieved through modulation of the oscillator's input signal, which may involve varying the resistance in the feedback path or altering the biasing conditions of active components such as transistors or operational amplifiers.
The choice of LEDs as pilot lamps serves a dual function; their illumination provides visual feedback to the user, indicating that the oscillator is in operation. Additionally, the forward voltage drop across the LEDs can be used as a reference voltage for the AGC circuit, allowing for precise control over the gain adjustment process.
This design is particularly advantageous in applications where stable signal amplitude is critical, such as in communication systems and audio processing equipment. The unconventional nature of the oscillator may also suggest innovative approaches to circuit stability and gain control, potentially leading to improved performance in environments with fluctuating power supply levels or varying load conditions.LEDs function as both pilot lamps and as an AGC (automatic gain control) in this unconventional amplitude-stabilized oscillator. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) for dual purposes, acting as pilot lamps to indicate operational status and as components in the automatic gain control mechanism. The amplitude-stabilized oscillator is designed to maintain consistent output levels despite variations in input conditions or load changes.
In this configuration, the LEDs are integrated into the feedback loop of the oscillator. When the output amplitude exceeds a predetermined threshold, the AGC circuit detects this condition and adjusts the gain accordingly. This adjustment is achieved through modulation of the oscillator's input signal, which may involve varying the resistance in the feedback path or altering the biasing conditions of active components such as transistors or operational amplifiers.
The choice of LEDs as pilot lamps serves a dual function; their illumination provides visual feedback to the user, indicating that the oscillator is in operation. Additionally, the forward voltage drop across the LEDs can be used as a reference voltage for the AGC circuit, allowing for precise control over the gain adjustment process.
This design is particularly advantageous in applications where stable signal amplitude is critical, such as in communication systems and audio processing equipment. The unconventional nature of the oscillator may also suggest innovative approaches to circuit stability and gain control, potentially leading to improved performance in environments with fluctuating power supply levels or varying load conditions.LEDs function as both pilot lamps and as an AGC (automatic gain control) in this unconventional amplitude-stabilized oscillator. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713