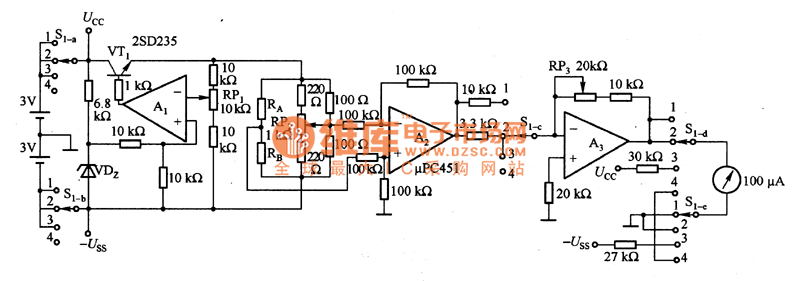
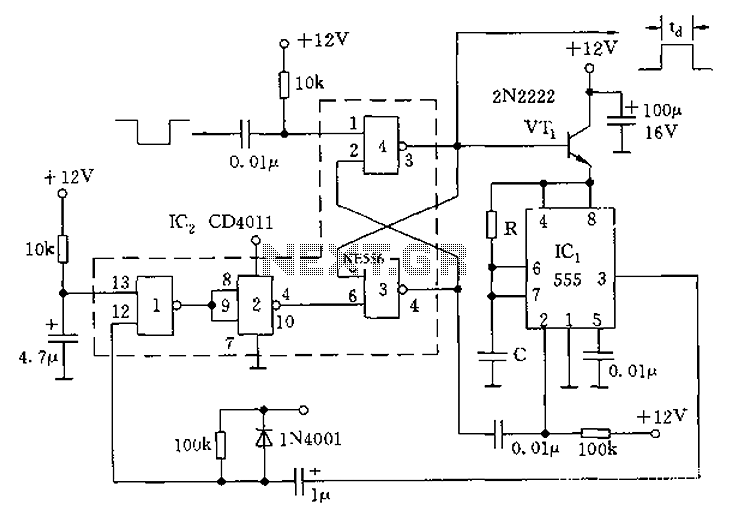
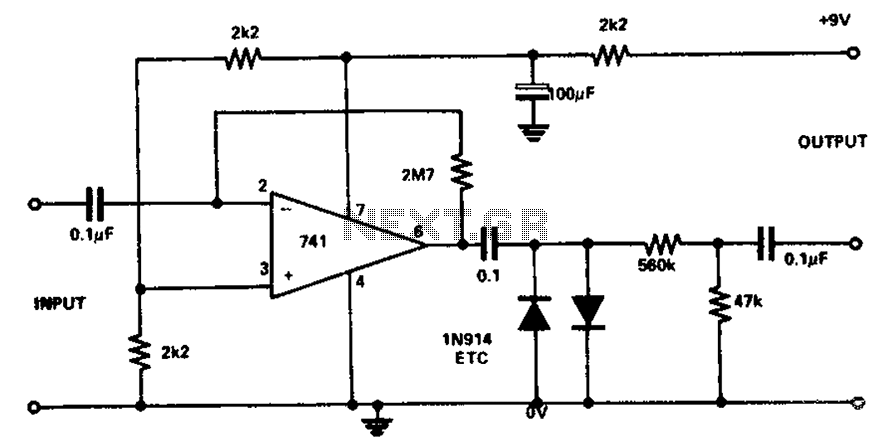
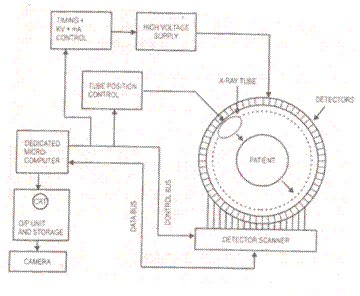
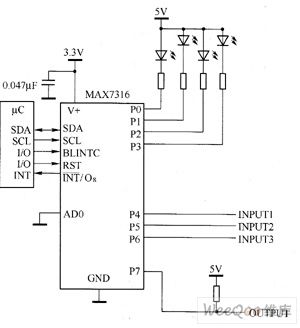
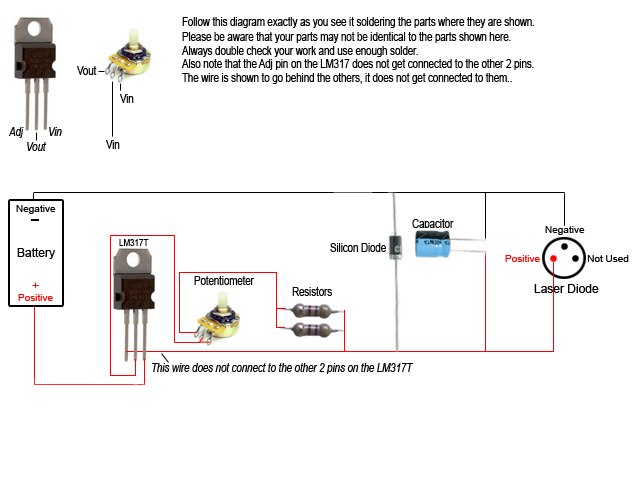
Wiring diagram for 3 way switch
This project demonstrates a visual representation of audio volume levels through the use of LEDs that illuminate in response to music. The circuit connects to the speaker output of an audio amplifier, allowing it to gauge the audio signal's intensity. Various colored LEDs can be utilized for aesthetic appeal. It is recommended to construct two identical units to display the volume levels for both the right and left audio channels. The input signal level can be adjusted using a 10k ohm variable resistor (VR).
This circuit operates by sampling the audio signal from the speaker outputs of an audio amplifier. The audio signal is fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the AC signal into a corresponding DC voltage that represents the audio volume level. This DC voltage is then used to control the brightness of the LEDs.
To implement this, a bridge rectifier can be used to ensure that the signal is always positive, regardless of the audio waveform's polarity. Following the rectification, a low-pass filter may be employed to smooth out the fluctuations in the audio signal, providing a stable voltage that corresponds to the average volume level.
The variable resistor (10k ohm VR) serves as an adjustable gain control, allowing the user to calibrate the sensitivity of the circuit to the audio input. This adjustment is crucial to ensure that the LEDs respond appropriately to the volume levels, preventing them from being overly dim or excessively bright.
For the LED configuration, a series of LEDs can be arranged in parallel, each connected to the output of the rectifier and filter circuit. The number of LEDs illuminated can correspond to the volume level, with more LEDs lighting up as the audio signal increases. Different colors can be used to create a visually appealing display, enhancing the overall experience.
To ensure proper functionality, it is important to consider the current-limiting resistors for each LED to prevent damage due to excessive current. The selection of these resistors will depend on the forward voltage of the LEDs and the supply voltage used in the circuit.
In summary, this project combines audio signal processing with visual display technology, allowing for an engaging interaction between sound and light. The design is straightforward, making it accessible for hobbyists and electronic enthusiasts looking to enhance their audio experiences visually.I like to see lights move to music. This project will indicate the volume level of the audio going to your speakers by lighting up LEDS. The LEDS can be any color so mix them up and really make it look good. The input of the circuit is connected to the speaker output of your audio amplifier. You want to build two identical units to indicate both right and left channels. The input signal level is adjusted by the 10k ohm VR. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates by sampling the audio signal from the speaker outputs of an audio amplifier. The audio signal is fed into a rectifier circuit, which converts the AC signal into a corresponding DC voltage that represents the audio volume level. This DC voltage is then used to control the brightness of the LEDs.
To implement this, a bridge rectifier can be used to ensure that the signal is always positive, regardless of the audio waveform's polarity. Following the rectification, a low-pass filter may be employed to smooth out the fluctuations in the audio signal, providing a stable voltage that corresponds to the average volume level.
The variable resistor (10k ohm VR) serves as an adjustable gain control, allowing the user to calibrate the sensitivity of the circuit to the audio input. This adjustment is crucial to ensure that the LEDs respond appropriately to the volume levels, preventing them from being overly dim or excessively bright.
For the LED configuration, a series of LEDs can be arranged in parallel, each connected to the output of the rectifier and filter circuit. The number of LEDs illuminated can correspond to the volume level, with more LEDs lighting up as the audio signal increases. Different colors can be used to create a visually appealing display, enhancing the overall experience.
To ensure proper functionality, it is important to consider the current-limiting resistors for each LED to prevent damage due to excessive current. The selection of these resistors will depend on the forward voltage of the LEDs and the supply voltage used in the circuit.
In summary, this project combines audio signal processing with visual display technology, allowing for an engaging interaction between sound and light. The design is straightforward, making it accessible for hobbyists and electronic enthusiasts looking to enhance their audio experiences visually.I like to see lights move to music. This project will indicate the volume level of the audio going to your speakers by lighting up LEDS. The LEDS can be any color so mix them up and really make it look good. The input of the circuit is connected to the speaker output of your audio amplifier. You want to build two identical units to indicate both right and left channels. The input signal level is adjusted by the 10k ohm VR. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713