
Write-amplifier
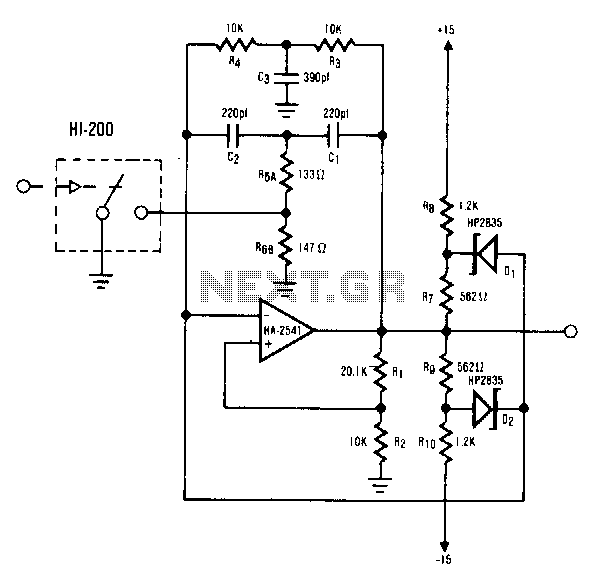
The increase in industrial and computerized equipment that utilizes programmable memory has heightened the demand for reliable recording media. Currently, magnetic tape is one of the most prevalent methods. The essential element of any magnetic recording system is the write mechanism. The principle of the write generator is straightforward, where the digital input leads to changes in both output amplitude and frequency. This operation is achieved by modifying the value of a resistor within the standard twin-tee oscillator. An HI-201 analog switch is employed to enable the switching action. The influence of external components on the feedback network necessitates that resistors R6A and R6B be significantly smaller than typically anticipated when utilizing the twin-tee feedback configuration.
The magnetic recording mechanism primarily relies on a write generator that transforms digital signals into magnetic variations on the tape medium. The write generator operates by generating a signal whose amplitude and frequency correspond to the input data, effectively encoding it onto the tape. The twin-tee oscillator configuration is a critical aspect of this process, as it allows for precise control over the frequency and amplitude of the generated signal.
In the design of the twin-tee oscillator, two resistors, R6A and R6B, are utilized to set the feedback levels. Their values are crucial, as they determine the stability and response of the oscillator. By ensuring these resistors are smaller than typically required, the circuit can achieve a higher frequency response, which is essential for accurately recording high-speed digital signals.
The HI-201 analog switch plays a pivotal role in this configuration, allowing for rapid switching between different states of the oscillator, thereby enabling dynamic adjustments to the output signal. This capability is vital in applications where real-time data recording is necessary, as it ensures that the system can adapt to varying input conditions without introducing significant latency.
Overall, the integration of these components within the magnetic recording system illustrates the sophisticated engineering required to meet the demands of modern industrial and computerized environments, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.The proliferation of industrial and computerized equipment containing programmable memory has increased the need for reliable recording media. The magnetic tape medium is presently one of the most widely used methods. The primary component of any magnetic recording mechanism is the write mechanism. The concept of the write generator is very basic. The digital input causes both a change in the output amplitude, as well as a change in frequency. This type of operation is accomplished by altering the value of a resistor in the standard twin-tee oscillator. A HI-201 analog switch was used to facilitate the switching action. The effect of the external components on the feedback network requires R6A and R6B to be much smaller than would normally have been expected when using the twin-tee feedback scheme.
🔗 External reference
The magnetic recording mechanism primarily relies on a write generator that transforms digital signals into magnetic variations on the tape medium. The write generator operates by generating a signal whose amplitude and frequency correspond to the input data, effectively encoding it onto the tape. The twin-tee oscillator configuration is a critical aspect of this process, as it allows for precise control over the frequency and amplitude of the generated signal.
In the design of the twin-tee oscillator, two resistors, R6A and R6B, are utilized to set the feedback levels. Their values are crucial, as they determine the stability and response of the oscillator. By ensuring these resistors are smaller than typically required, the circuit can achieve a higher frequency response, which is essential for accurately recording high-speed digital signals.
The HI-201 analog switch plays a pivotal role in this configuration, allowing for rapid switching between different states of the oscillator, thereby enabling dynamic adjustments to the output signal. This capability is vital in applications where real-time data recording is necessary, as it ensures that the system can adapt to varying input conditions without introducing significant latency.
Overall, the integration of these components within the magnetic recording system illustrates the sophisticated engineering required to meet the demands of modern industrial and computerized environments, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.The proliferation of industrial and computerized equipment containing programmable memory has increased the need for reliable recording media. The magnetic tape medium is presently one of the most widely used methods. The primary component of any magnetic recording mechanism is the write mechanism. The concept of the write generator is very basic. The digital input causes both a change in the output amplitude, as well as a change in frequency. This type of operation is accomplished by altering the value of a resistor in the standard twin-tee oscillator. A HI-201 analog switch was used to facilitate the switching action. The effect of the external components on the feedback network requires R6A and R6B to be much smaller than would normally have been expected when using the twin-tee feedback scheme.
🔗 External reference